Ziwei Gong
May
Factuality on Demand: Controlling the Factuality-Informativeness Trade-off in Text Generation
Jan 31, 2026Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) encode knowledge with varying degrees of confidence. When responding to queries, models face an inherent trade-off: they can generate responses that are less informative but highly factual, or more informative but potentially less accurate. Different applications demand different balances between informativeness and factuality. We introduce Factuality-Controlled Generation (FCG), a framework that enables users to specify factuality constraints alongside their queries. We propose to evaluate FCG performance on two dimensions: adherence to factuality constraints and response informativeness. We propose to train models on the FCG task using synthetic data, and show that our synthetic training significantly improves models' ability to both respect factuality requirements and maintain informativeness in their outputs.
Detecting Mental Manipulation in Speech via Synthetic Multi-Speaker Dialogue
Jan 13, 2026Abstract:Mental manipulation, the strategic use of language to covertly influence or exploit others, is a newly emerging task in computational social reasoning. Prior work has focused exclusively on textual conversations, overlooking how manipulative tactics manifest in speech. We present the first study of mental manipulation detection in spoken dialogues, introducing a synthetic multi-speaker benchmark SPEECHMENTALMANIP that augments a text-based dataset with high-quality, voice-consistent Text-to-Speech rendered audio. Using few-shot large audio-language models and human annotation, we evaluate how modality affects detection accuracy and perception. Our results reveal that models exhibit high specificity but markedly lower recall on speech compared to text, suggesting sensitivity to missing acoustic or prosodic cues in training. Human raters show similar uncertainty in the audio setting, underscoring the inherent ambiguity of manipulative speech. Together, these findings highlight the need for modality-aware evaluation and safety alignment in multimodal dialogue systems.
CantoASR: Prosody-Aware ASR-LALM Collaboration for Low-Resource Cantonese
Nov 06, 2025Abstract:Automatic speech recognition (ASR) is critical for language accessibility, yet low-resource Cantonese remains challenging due to limited annotated data, six lexical tones, tone sandhi, and accent variation. Existing ASR models, such as Whisper, often suffer from high word error rates. Large audio-language models (LALMs), in contrast, can leverage broader contextual reasoning but still require explicit tonal and prosodic acoustic cues. We introduce CantoASR, a collaborative ASR-LALM error correction framework that integrates forced alignment for acoustic feature extraction, a LoRA-finetuned Whisper for improved tone discrimination, and an instruction-tuned Qwen-Audio for prosody-aware correction. Evaluations on spontaneous Cantonese data show substantial CER gains over Whisper-Large-V3. These findings suggest that integrating acoustic cues with LALM reasoning provides a scalable strategy for low-resource tonal and dialectal ASR.
Multimodal Emotion Recognition in Conversations: A Survey of Methods, Trends, Challenges and Prospects
May 26, 2025Abstract:While text-based emotion recognition methods have achieved notable success, real-world dialogue systems often demand a more nuanced emotional understanding than any single modality can offer. Multimodal Emotion Recognition in Conversations (MERC) has thus emerged as a crucial direction for enhancing the naturalness and emotional understanding of human-computer interaction. Its goal is to accurately recognize emotions by integrating information from various modalities such as text, speech, and visual signals. This survey offers a systematic overview of MERC, including its motivations, core tasks, representative methods, and evaluation strategies. We further examine recent trends, highlight key challenges, and outline future directions. As interest in emotionally intelligent systems grows, this survey provides timely guidance for advancing MERC research.
Pragmatics in the Era of Large Language Models: A Survey on Datasets, Evaluation, Opportunities and Challenges
Feb 17, 2025Abstract:Understanding pragmatics-the use of language in context-is crucial for developing NLP systems capable of interpreting nuanced language use. Despite recent advances in language technologies, including large language models, evaluating their ability to handle pragmatic phenomena such as implicatures and references remains challenging. To advance pragmatic abilities in models, it is essential to understand current evaluation trends and identify existing limitations. In this survey, we provide a comprehensive review of resources designed for evaluating pragmatic capabilities in NLP, categorizing datasets by the pragmatics phenomena they address. We analyze task designs, data collection methods, evaluation approaches, and their relevance to real-world applications. By examining these resources in the context of modern language models, we highlight emerging trends, challenges, and gaps in existing benchmarks. Our survey aims to clarify the landscape of pragmatic evaluation and guide the development of more comprehensive and targeted benchmarks, ultimately contributing to more nuanced and context-aware NLP models.
CREAM: Comparison-Based Reference-Free ELO-Ranked Automatic Evaluation for Meeting Summarization
Sep 17, 2024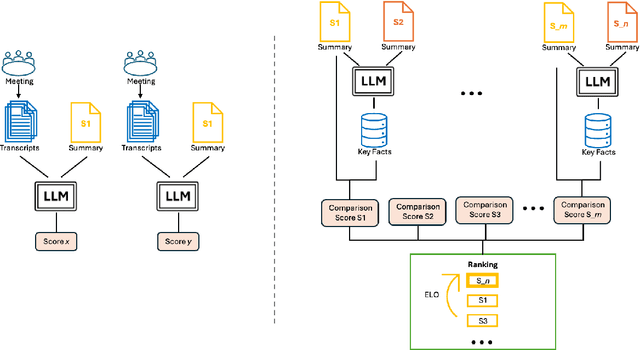


Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have spurred interest in automatic evaluation methods for summarization, offering a faster, more cost-effective alternative to human evaluation. However, existing methods often fall short when applied to complex tasks like long-context summarizations and dialogue-based meeting summarizations. In this paper, we introduce CREAM (Comparison-Based Reference-Free Elo-Ranked Automatic Evaluation for Meeting Summarization), a novel framework that addresses the unique challenges of evaluating meeting summaries. CREAM leverages a combination of chain-of-thought reasoning and key facts alignment to assess conciseness and completeness of model-generated summaries without requiring reference. By employing an ELO ranking system, our approach provides a robust mechanism for comparing the quality of different models or prompt configurations.
NovAScore: A New Automated Metric for Evaluating Document Level Novelty
Sep 14, 2024Abstract:The rapid expansion of online content has intensified the issue of information redundancy, underscoring the need for solutions that can identify genuinely new information. Despite this challenge, the research community has seen a decline in focus on novelty detection, particularly with the rise of large language models (LLMs). Additionally, previous approaches have relied heavily on human annotation, which is time-consuming, costly, and particularly challenging when annotators must compare a target document against a vast number of historical documents. In this work, we introduce NovAScore (Novelty Evaluation in Atomicity Score), an automated metric for evaluating document-level novelty. NovAScore aggregates the novelty and salience scores of atomic information, providing high interpretability and a detailed analysis of a document's novelty. With its dynamic weight adjustment scheme, NovAScore offers enhanced flexibility and an additional dimension to assess both the novelty level and the importance of information within a document. Our experiments show that NovAScore strongly correlates with human judgments of novelty, achieving a 0.626 Point-Biserial correlation on the TAP-DLND 1.0 dataset and a 0.920 Pearson correlation on an internal human-annotated dataset.
Beyond Silent Letters: Amplifying LLMs in Emotion Recognition with Vocal Nuances
Aug 01, 2024
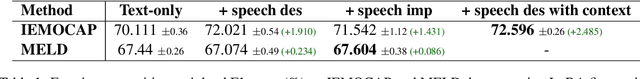

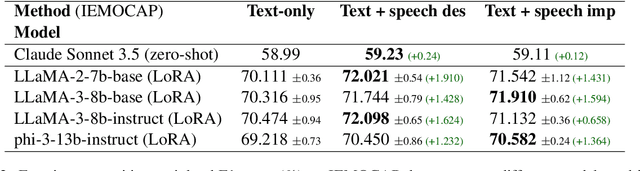
Abstract:This paper introduces a novel approach to emotion detection in speech using Large Language Models (LLMs). We address the limitation of LLMs in processing audio inputs by translating speech characteristics into natural language descriptions. Our method integrates these descriptions into text prompts, enabling LLMs to perform multimodal emotion analysis without architectural modifications. We evaluate our approach on two datasets: IEMOCAP and MELD, demonstrating significant improvements in emotion recognition accuracy, particularly for high-quality audio data. Our experiments show that incorporating speech descriptions yields a 2 percentage point increase in weighted F1 score on IEMOCAP (from 70.111\% to 72.596\%). We also compare various LLM architectures and explore the effectiveness of different feature representations. Our findings highlight the potential of this approach in enhancing emotion detection capabilities of LLMs and underscore the importance of audio quality in speech-based emotion recognition tasks. We'll release the source code on Github.
Multi-Modality Multi-Loss Fusion Network
Aug 01, 2023Abstract:In this work we investigate the optimal selection and fusion of features across multiple modalities and combine these in a neural network to improve emotion detection. We compare different fusion methods and examine the impact of multi-loss training within the multi-modality fusion network, identifying useful findings relating to subnet performance. Our best model achieves state-of-the-art performance for three datasets (CMU-MOSI, CMU-MOSEI and CH-SIMS), and outperforms the other methods in most metrics. We have found that training on multimodal features improves single modality testing and designing fusion methods based on dataset annotation schema enhances model performance. These results suggest a roadmap towards an optimized feature selection and fusion approach for enhancing emotion detection in neural networks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge