Pengyuan Shi
LAVID: An Agentic LVLM Framework for Diffusion-Generated Video Detection
Feb 20, 2025Abstract:The impressive achievements of generative models in creating high-quality videos have raised concerns about digital integrity and privacy vulnerabilities. Recent works of AI-generated content detection have been widely studied in the image field (e.g., deepfake), yet the video field has been unexplored. Large Vision Language Model (LVLM) has become an emerging tool for AI-generated content detection for its strong reasoning and multimodal capabilities. It breaks the limitations of traditional deep learning based methods faced with like lack of transparency and inability to recognize new artifacts. Motivated by this, we propose LAVID, a novel LVLMs-based ai-generated video detection with explicit knowledge enhancement. Our insight list as follows: (1) The leading LVLMs can call external tools to extract useful information to facilitate its own video detection task; (2) Structuring the prompt can affect LVLM's reasoning ability to interpret information in video content. Our proposed pipeline automatically selects a set of explicit knowledge tools for detection, and then adaptively adjusts the structure prompt by self-rewriting. Different from prior SOTA that trains additional detectors, our method is fully training-free and only requires inference of the LVLM for detection. To facilitate our research, we also create a new benchmark \vidfor with high-quality videos generated from multiple sources of video generation tools. Evaluation results show that LAVID improves F1 scores by 6.2 to 30.2% over the top baselines on our datasets across four SOTA LVLMs.
Beyond Silent Letters: Amplifying LLMs in Emotion Recognition with Vocal Nuances
Aug 01, 2024
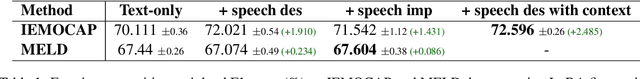

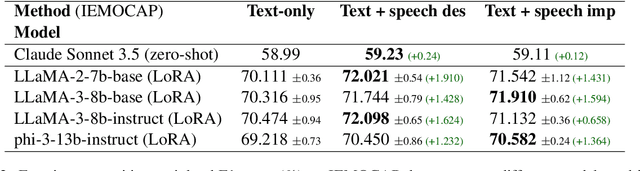
Abstract:This paper introduces a novel approach to emotion detection in speech using Large Language Models (LLMs). We address the limitation of LLMs in processing audio inputs by translating speech characteristics into natural language descriptions. Our method integrates these descriptions into text prompts, enabling LLMs to perform multimodal emotion analysis without architectural modifications. We evaluate our approach on two datasets: IEMOCAP and MELD, demonstrating significant improvements in emotion recognition accuracy, particularly for high-quality audio data. Our experiments show that incorporating speech descriptions yields a 2 percentage point increase in weighted F1 score on IEMOCAP (from 70.111\% to 72.596\%). We also compare various LLM architectures and explore the effectiveness of different feature representations. Our findings highlight the potential of this approach in enhancing emotion detection capabilities of LLMs and underscore the importance of audio quality in speech-based emotion recognition tasks. We'll release the source code on Github.
Turns Out I'm Not Real: Towards Robust Detection of AI-Generated Videos
Jun 13, 2024Abstract:The impressive achievements of generative models in creating high-quality videos have raised concerns about digital integrity and privacy vulnerabilities. Recent works to combat Deepfakes videos have developed detectors that are highly accurate at identifying GAN-generated samples. However, the robustness of these detectors on diffusion-generated videos generated from video creation tools (e.g., SORA by OpenAI, Runway Gen-2, and Pika, etc.) is still unexplored. In this paper, we propose a novel framework for detecting videos synthesized from multiple state-of-the-art (SOTA) generative models, such as Stable Video Diffusion. We find that the SOTA methods for detecting diffusion-generated images lack robustness in identifying diffusion-generated videos. Our analysis reveals that the effectiveness of these detectors diminishes when applied to out-of-domain videos, primarily because they struggle to track the temporal features and dynamic variations between frames. To address the above-mentioned challenge, we collect a new benchmark video dataset for diffusion-generated videos using SOTA video creation tools. We extract representation within explicit knowledge from the diffusion model for video frames and train our detector with a CNN + LSTM architecture. The evaluation shows that our framework can well capture the temporal features between frames, achieves 93.7% detection accuracy for in-domain videos, and improves the accuracy of out-domain videos by up to 16 points.
COVID-Net Assistant: A Deep Learning-Driven Virtual Assistant for COVID-19 Symptom Prediction and Recommendation
Nov 22, 2022



Abstract:As the COVID-19 pandemic continues to put a significant burden on healthcare systems worldwide, there has been growing interest in finding inexpensive symptom pre-screening and recommendation methods to assist in efficiently using available medical resources such as PCR tests. In this study, we introduce the design of COVID-Net Assistant, an efficient virtual assistant designed to provide symptom prediction and recommendations for COVID-19 by analyzing users' cough recordings through deep convolutional neural networks. We explore a variety of highly customized, lightweight convolutional neural network architectures generated via machine-driven design exploration (which we refer to as COVID-Net Assistant neural networks) on the Covid19-Cough benchmark dataset. The Covid19-Cough dataset comprises 682 cough recordings from a COVID-19 positive cohort and 642 from a COVID-19 negative cohort. Among the 682 cough recordings labeled positive, 382 recordings were verified by PCR test. Our experimental results show promising, with the COVID-Net Assistant neural networks demonstrating robust predictive performance, achieving AUC scores of over 0.93, with the best score over 0.95 while being fast and efficient in inference. The COVID-Net Assistant models are made available in an open source manner through the COVID-Net open initiative and, while not a production-ready solution, we hope their availability acts as a good resource for clinical scientists, machine learning researchers, as well as citizen scientists to develop innovative solutions.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge