Xinyue Huo
SAM-CP: Marrying SAM with Composable Prompts for Versatile Segmentation
Jul 23, 2024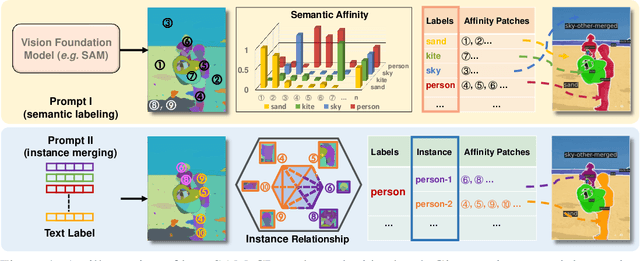
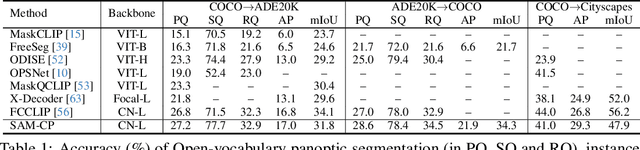

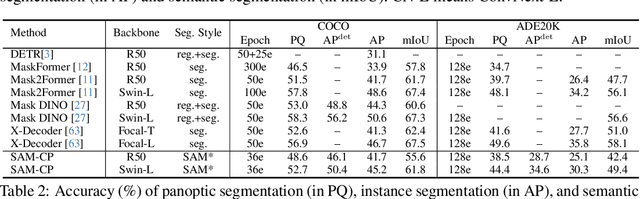
Abstract:The Segment Anything model (SAM) has shown a generalized ability to group image pixels into patches, but applying it to semantic-aware segmentation still faces major challenges. This paper presents SAM-CP, a simple approach that establishes two types of composable prompts beyond SAM and composes them for versatile segmentation. Specifically, given a set of classes (in texts) and a set of SAM patches, the Type-I prompt judges whether a SAM patch aligns with a text label, and the Type-II prompt judges whether two SAM patches with the same text label also belong to the same instance. To decrease the complexity in dealing with a large number of semantic classes and patches, we establish a unified framework that calculates the affinity between (semantic and instance) queries and SAM patches and merges patches with high affinity to the query. Experiments show that SAM-CP achieves semantic, instance, and panoptic segmentation in both open and closed domains. In particular, it achieves state-of-the-art performance in open-vocabulary segmentation. Our research offers a novel and generalized methodology for equipping vision foundation models like SAM with multi-grained semantic perception abilities.
Decoding Matters: Addressing Amplification Bias and Homogeneity Issue for LLM-based Recommendation
Jun 21, 2024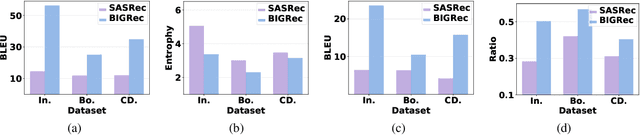
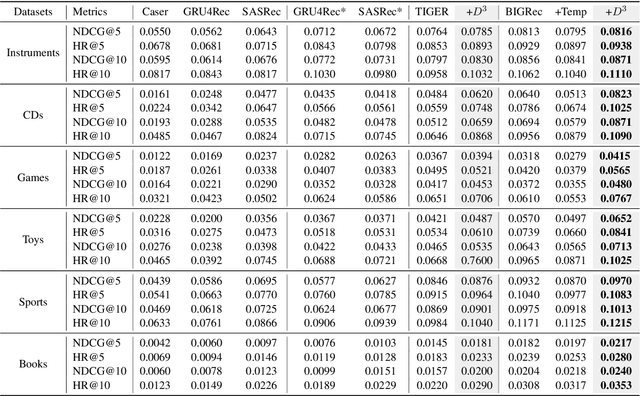
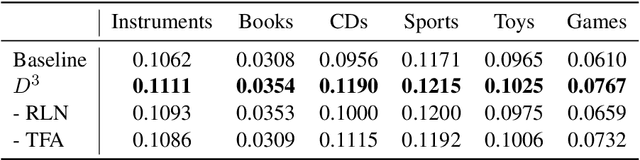
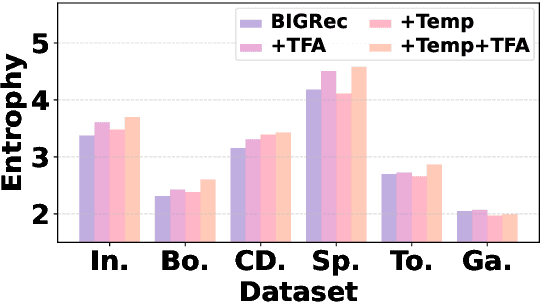
Abstract:Adapting Large Language Models (LLMs) for recommendation requires careful consideration of the decoding process, given the inherent differences between generating items and natural language. Existing approaches often directly apply LLMs' original decoding methods. However, we find these methods encounter significant challenges: 1) amplification bias -- where standard length normalization inflates scores for items containing tokens with generation probabilities close to 1 (termed ghost tokens), and 2) homogeneity issue -- generating multiple similar or repetitive items for a user. To tackle these challenges, we introduce a new decoding approach named Debiasing-Diversifying Decoding (D3). D3 disables length normalization for ghost tokens to alleviate amplification bias, and it incorporates a text-free assistant model to encourage tokens less frequently generated by LLMs for counteracting recommendation homogeneity. Extensive experiments on real-world datasets demonstrate the method's effectiveness in enhancing accuracy and diversity.
Focus on Your Target: A Dual Teacher-Student Framework for Domain-adaptive Semantic Segmentation
Mar 16, 2023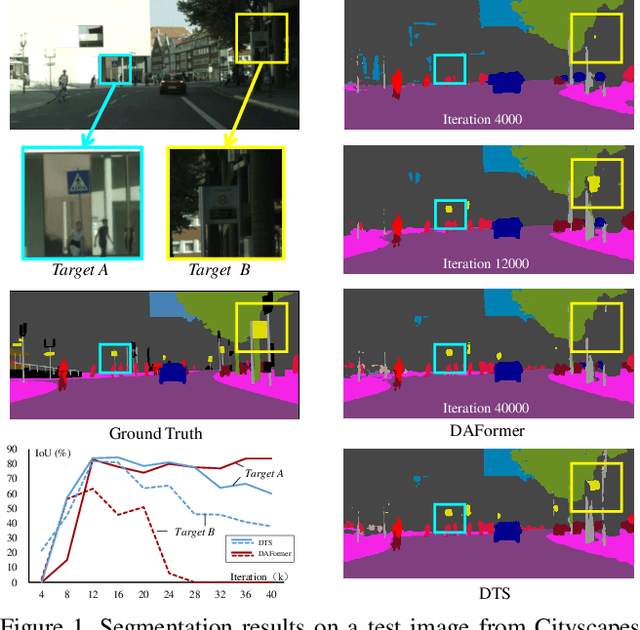
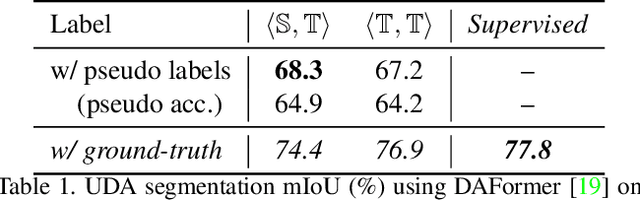
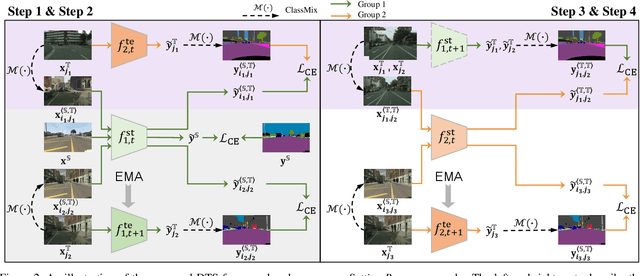
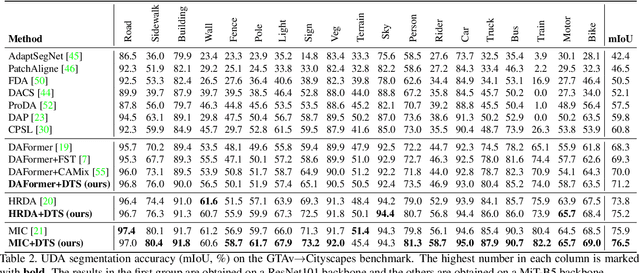
Abstract:We study unsupervised domain adaptation (UDA) for semantic segmentation. Currently, a popular UDA framework lies in self-training which endows the model with two-fold abilities: (i) learning reliable semantics from the labeled images in the source domain, and (ii) adapting to the target domain via generating pseudo labels on the unlabeled images. We find that, by decreasing/increasing the proportion of training samples from the target domain, the 'learning ability' is strengthened/weakened while the 'adapting ability' goes in the opposite direction, implying a conflict between these two abilities, especially for a single model. To alleviate the issue, we propose a novel dual teacher-student (DTS) framework and equip it with a bidirectional learning strategy. By increasing the proportion of target-domain data, the second teacher-student model learns to 'Focus on Your Target' while the first model is not affected. DTS is easily plugged into existing self-training approaches. In a standard UDA scenario (training on synthetic, labeled data and real, unlabeled data), DTS shows consistent gains over the baselines and sets new state-of-the-art results of 76.5\% and 75.1\% mIoUs on GTAv$\rightarrow$Cityscapes and SYNTHIA$\rightarrow$Cityscapes, respectively.
Domain-Agnostic Prior for Transfer Semantic Segmentation
Apr 20, 2022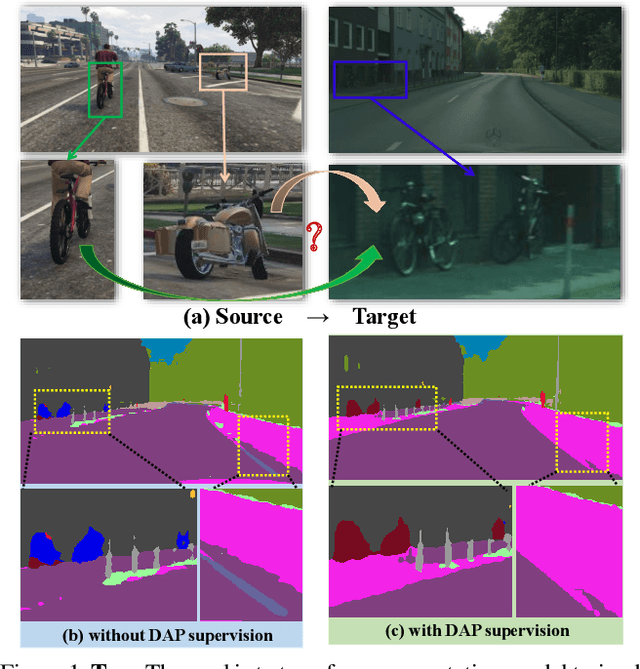
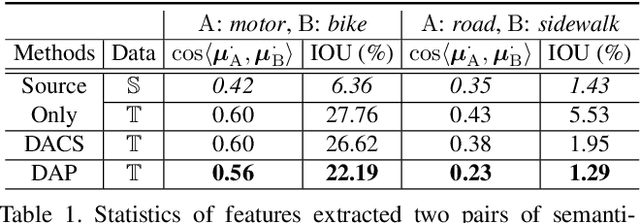
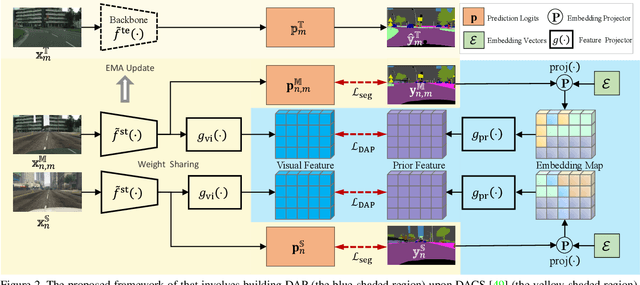
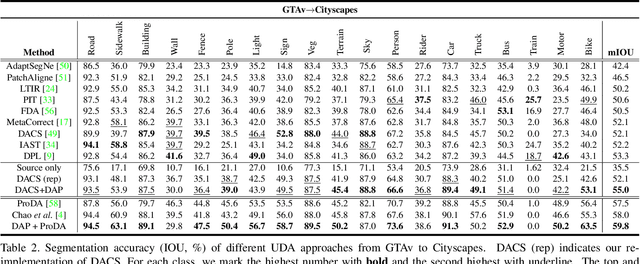
Abstract:Unsupervised domain adaptation (UDA) is an important topic in the computer vision community. The key difficulty lies in defining a common property between the source and target domains so that the source-domain features can align with the target-domain semantics. In this paper, we present a simple and effective mechanism that regularizes cross-domain representation learning with a domain-agnostic prior (DAP) that constrains the features extracted from source and target domains to align with a domain-agnostic space. In practice, this is easily implemented as an extra loss term that requires a little extra costs. In the standard evaluation protocol of transferring synthesized data to real data, we validate the effectiveness of different types of DAP, especially that borrowed from a text embedding model that shows favorable performance beyond the state-of-the-art UDA approaches in terms of segmentation accuracy. Our research reveals that UDA benefits much from better proxies, possibly from other data modalities.
Heterogeneous Contrastive Learning: Encoding Spatial Information for Compact Visual Representations
Nov 19, 2020


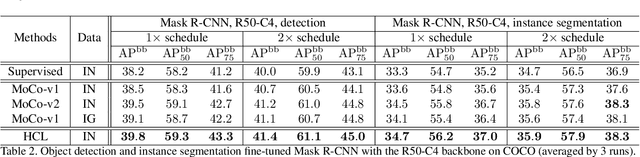
Abstract:Contrastive learning has achieved great success in self-supervised visual representation learning, but existing approaches mostly ignored spatial information which is often crucial for visual representation. This paper presents heterogeneous contrastive learning (HCL), an effective approach that adds spatial information to the encoding stage to alleviate the learning inconsistency between the contrastive objective and strong data augmentation operations. We demonstrate the effectiveness of HCL by showing that (i) it achieves higher accuracy in instance discrimination and (ii) it surpasses existing pre-training methods in a series of downstream tasks while shrinking the pre-training costs by half. More importantly, we show that our approach achieves higher efficiency in visual representations, and thus delivers a key message to inspire the future research of self-supervised visual representation learning.
ATSO: Asynchronous Teacher-Student Optimization for Semi-Supervised Medical Image Segmentation
Jul 16, 2020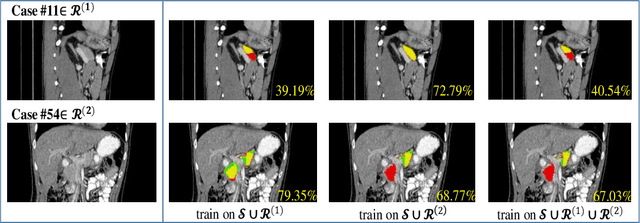
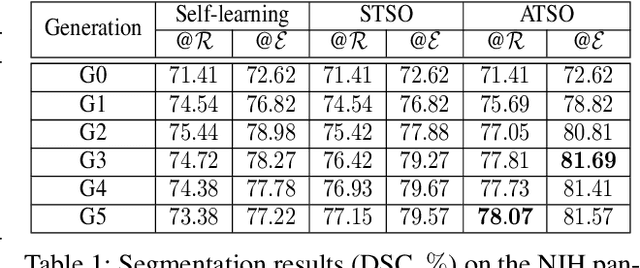
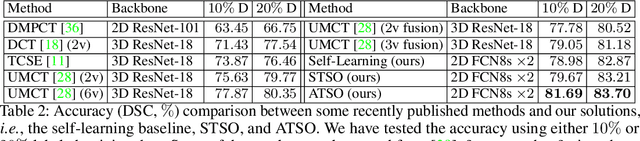
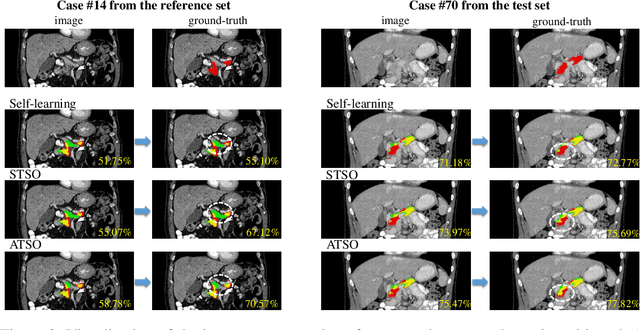
Abstract:In medical image analysis, semi-supervised learning is an effective method to extract knowledge from a small amount of labeled data and a large amount of unlabeled data. This paper focuses on a popular pipeline known as self learning, and points out a weakness named lazy learning that refers to the difficulty for a model to learn from the pseudo labels generated by itself. To alleviate this issue, we propose ATSO, an asynchronous version of teacher-student optimization. ATSO partitions the unlabeled data into two subsets and alternately uses one subset to fine-tune the model and updates the label on the other subset. We evaluate ATSO on two popular medical image segmentation datasets and show its superior performance in various semi-supervised settings. With slight modification, ATSO transfers well to natural image segmentation for autonomous driving data.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge