Caixia Gong
Reducing the Gap Between Pretrained Speech Enhancement and Recognition Models Using a Real Speech-Trained Bridging Module
Jan 05, 2025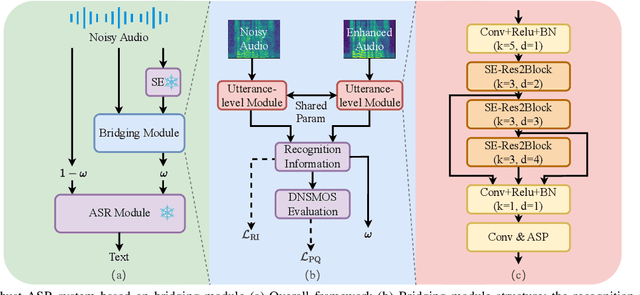
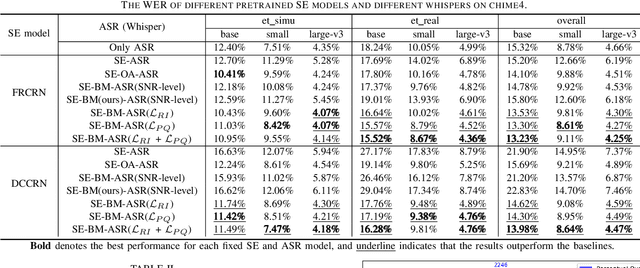
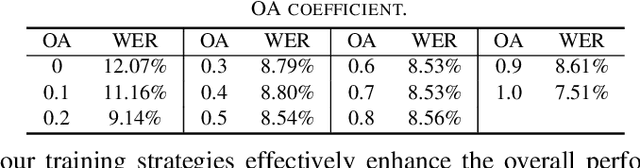
Abstract:The information loss or distortion caused by single-channel speech enhancement (SE) harms the performance of automatic speech recognition (ASR). Observation addition (OA) is an effective post-processing method to improve ASR performance by balancing noisy and enhanced speech. Determining the OA coefficient is crucial. However, the currently supervised OA coefficient module, called the bridging module, only utilizes simulated noisy speech for training, which has a severe mismatch with real noisy speech. In this paper, we propose training strategies to train the bridging module with real noisy speech. First, DNSMOS is selected to evaluate the perceptual quality of real noisy speech with no need for the corresponding clean label to train the bridging module. Additional constraints during training are introduced to enhance the robustness of the bridging module further. Each utterance is evaluated by the ASR back-end using various OA coefficients to obtain the word error rates (WERs). The WERs are used to construct a multidimensional vector. This vector is introduced into the bridging module with multi-task learning and is used to determine the optimal OA coefficients. The experimental results on the CHiME-4 dataset show that the proposed methods all had significant improvement compared with the simulated data trained bridging module, especially under real evaluation sets.
VISinger 2: High-Fidelity End-to-End Singing Voice Synthesis Enhanced by Digital Signal Processing Synthesizer
Nov 05, 2022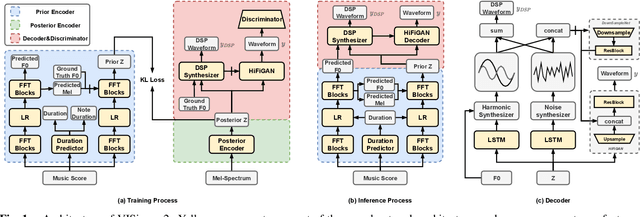
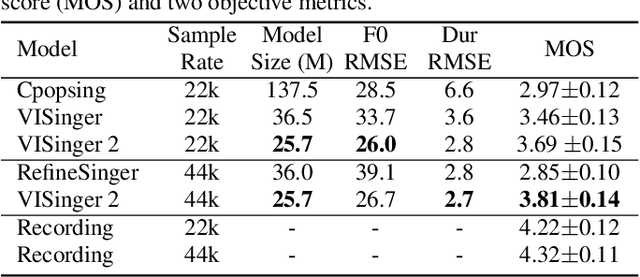
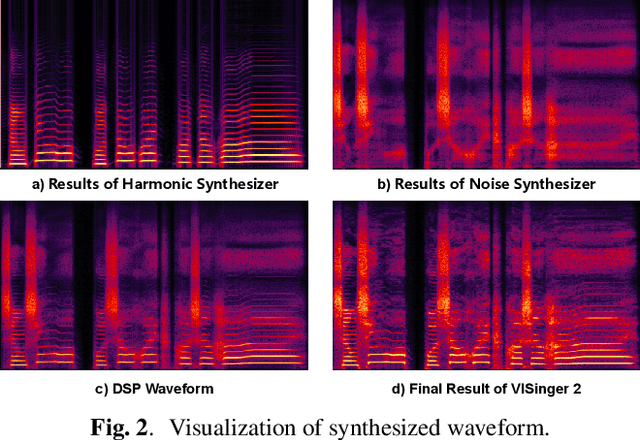
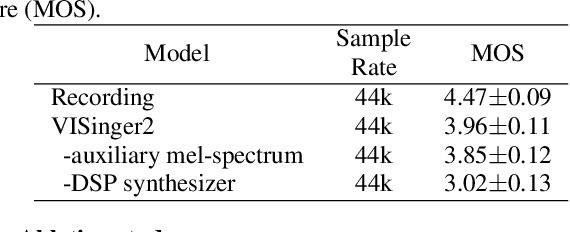
Abstract:End-to-end singing voice synthesis (SVS) model VISinger can achieve better performance than the typical two-stage model with fewer parameters. However, VISinger has several problems: text-to-phase problem, the end-to-end model learns the meaningless mapping of text-to-phase; glitches problem, the harmonic components corresponding to the periodic signal of the voiced segment occurs a sudden change with audible artefacts; low sampling rate, the sampling rate of 24KHz does not meet the application needs of high-fidelity generation with the full-band rate (44.1KHz or higher). In this paper, we propose VISinger 2 to address these issues by integrating the digital signal processing (DSP) methods with VISinger. Specifically, inspired by recent advances in differentiable digital signal processing (DDSP), we incorporate a DSP synthesizer into the decoder to solve the above issues. The DSP synthesizer consists of a harmonic synthesizer and a noise synthesizer to generate periodic and aperiodic signals, respectively, from the latent representation z in VISinger. It supervises the posterior encoder to extract the latent representation without phase information and avoid the prior encoder modelling text-to-phase mapping. To avoid glitch artefacts, the HiFi-GAN is modified to accept the waveforms generated by the DSP synthesizer as a condition to produce the singing voice. Moreover, with the improved waveform decoder, VISinger 2 manages to generate 44.1kHz singing audio with richer expression and better quality. Experiments on OpenCpop corpus show that VISinger 2 outperforms VISinger, CpopSing and RefineSinger in both subjective and objective metrics.
A Post Auto-regressive GAN Vocoder Focused on Spectrum Fracture
Apr 12, 2022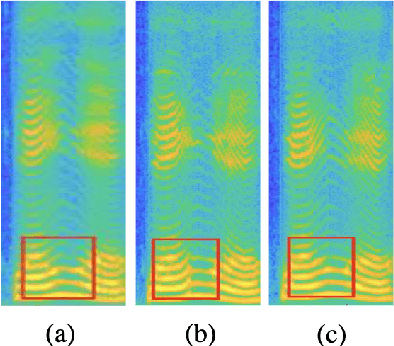
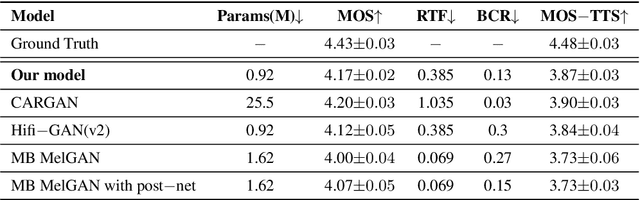
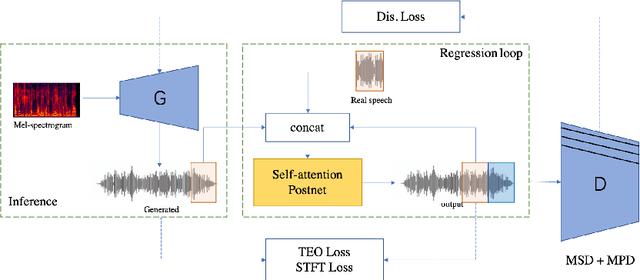
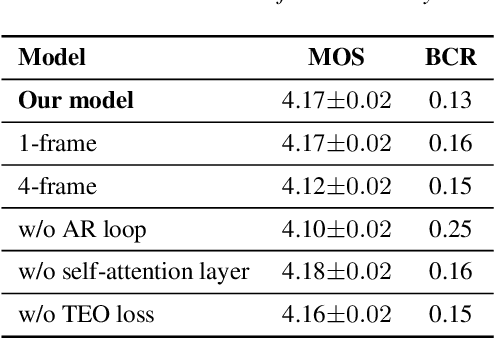
Abstract:Generative adversarial networks (GANs) have been indicated their superiority in usage of the real-time speech synthesis. Nevertheless, most of them make use of deep convolutional layers as their backbone, which may cause the absence of previous signal information. However, the generation of speech signals invariably require preceding waveform samples in its reconstruction, as the lack of this can lead to artifacts in generated speech. To address this conflict, in this paper, we propose an improved model: a post auto-regressive (AR) GAN vocoder with a self-attention layer, which merging self-attention in an AR loop. It will not participate in inference, but can assist the generator to learn temporal dependencies within frames in training. Furthermore, an ablation study was done to confirm the contribution of each part. Systematic experiments show that our model leads to a consistent improvement on both objective and subjective evaluation performance.
Improving Prosody for Unseen Texts in Speech Synthesis by Utilizing Linguistic Information and Noisy Data
Nov 15, 2021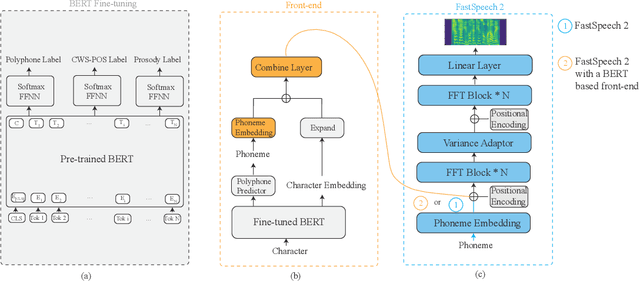
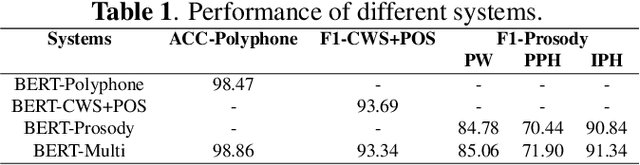
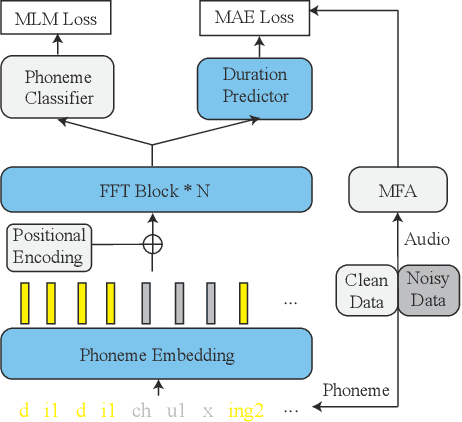
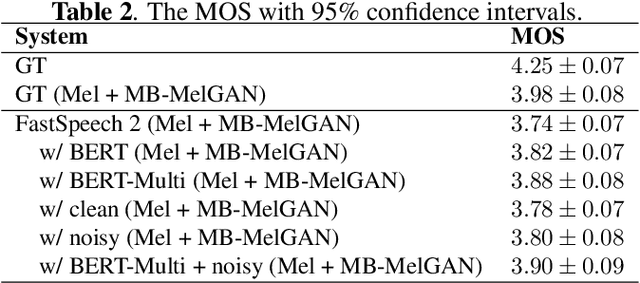
Abstract:Recent advancements in end-to-end speech synthesis have made it possible to generate highly natural speech. However, training these models typically requires a large amount of high-fidelity speech data, and for unseen texts, the prosody of synthesized speech is relatively unnatural. To address these issues, we propose to combine a fine-tuned BERT-based front-end with a pre-trained FastSpeech2-based acoustic model to improve prosody modeling. The pre-trained BERT is fine-tuned on the polyphone disambiguation task, the joint Chinese word segmentation (CWS) and part-of-speech (POS) tagging task, and the prosody structure prediction (PSP) task in a multi-task learning framework. FastSpeech 2 is pre-trained on large-scale external data that are noisy but easier to obtain. Experimental results show that both the fine-tuned BERT model and the pre-trained FastSpeech 2 can improve prosody, especially for those structurally complex sentences.
Towards End-to-End Code-Switching Speech Recognition
Nov 01, 2018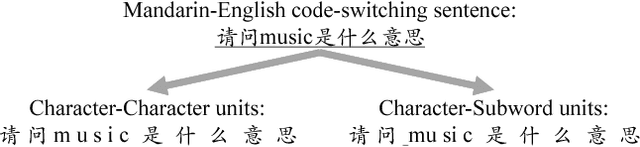
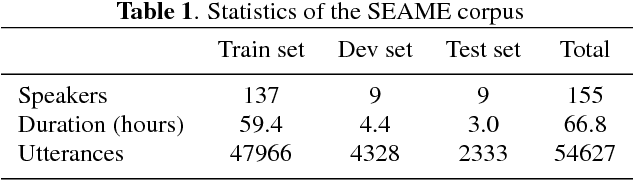
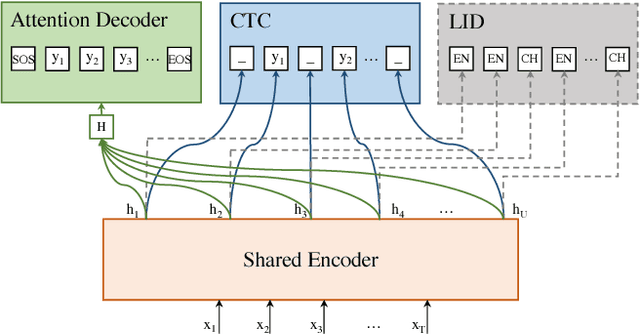
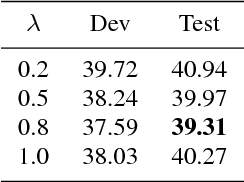
Abstract:Code-switching speech recognition has attracted an increasing interest recently, but the need for expert linguistic knowledge has always been a big issue. End-to-end automatic speech recognition (ASR) simplifies the building of ASR systems considerably by predicting graphemes or characters directly from acoustic input. In the mean time, the need of expert linguistic knowledge is also eliminated, which makes it an attractive choice for code-switching ASR. This paper presents a hybrid CTC-Attention based end-to-end Mandarin-English code-switching (CS) speech recognition system and studies the effect of hybrid CTC-Attention based models, different modeling units, the inclusion of language identification and different decoding strategies on the task of code-switching ASR. On the SEAME corpus, our system achieves a mixed error rate (MER) of 34.24%.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge