Jiahui Zhao
Reasoning over Precedents Alongside Statutes: Case-Augmented Deliberative Alignment for LLM Safety
Jan 12, 2026Abstract:Ensuring that Large Language Models (LLMs) adhere to safety principles without refusing benign requests remains a significant challenge. While OpenAI introduces deliberative alignment (DA) to enhance the safety of its o-series models through reasoning over detailed ``code-like'' safety rules, the effectiveness of this approach in open-source LLMs, which typically lack advanced reasoning capabilities, is understudied. In this work, we systematically evaluate the impact of explicitly specifying extensive safety codes versus demonstrating them through illustrative cases. We find that referencing explicit codes inconsistently improves harmlessness and systematically degrades helpfulness, whereas training on case-augmented simple codes yields more robust and generalized safety behaviors. By guiding LLMs with case-augmented reasoning instead of extensive code-like safety rules, we avoid rigid adherence to narrowly enumerated rules and enable broader adaptability. Building on these insights, we propose CADA, a case-augmented deliberative alignment method for LLMs utilizing reinforcement learning on self-generated safety reasoning chains. CADA effectively enhances harmlessness, improves robustness against attacks, and reduces over-refusal while preserving utility across diverse benchmarks, offering a practical alternative to rule-only DA for improving safety while maintaining helpfulness.
Commercial Vehicle Braking Optimization: A Robust SIFT-Trajectory Approach
Dec 21, 2025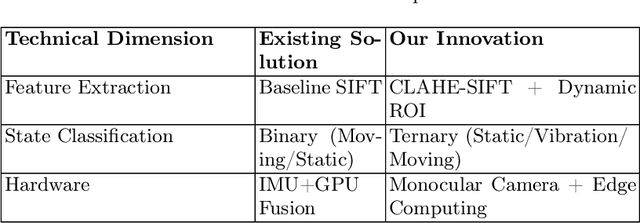
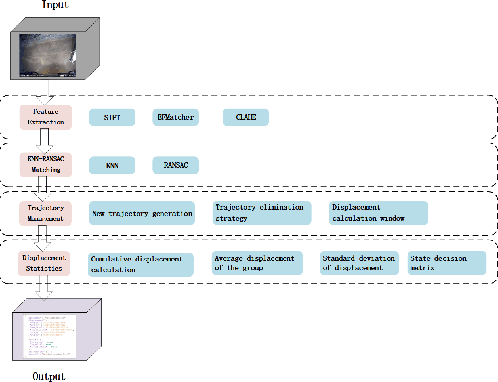

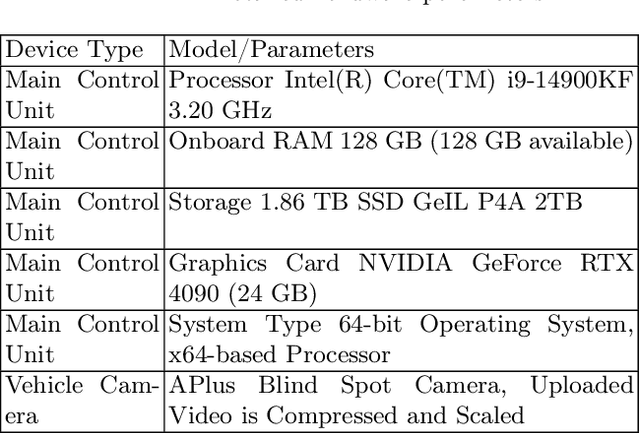
Abstract:A vision-based trajectory analysis solution is proposed to address the "zero-speed braking" issue caused by inaccurate Controller Area Network (CAN) signals in commercial vehicle Automatic Emergency Braking (AEB) systems during low-speed operation. The algorithm utilizes the NVIDIA Jetson AGX Xavier platform to process sequential video frames from a blind spot camera, employing self-adaptive Contrast Limited Adaptive Histogram Equalization (CLAHE)-enhanced Scale-Invariant Feature Transform (SIFT) feature extraction and K-Nearest Neighbors (KNN)-Random Sample Consensus (RANSAC) matching. This allows for precise classification of the vehicle's motion state (static, vibration, moving). Key innovations include 1) multiframe trajectory displacement statistics (5-frame sliding window), 2) a dual-threshold state decision matrix, and 3) OBD-II driven dynamic Region of Interest (ROI) configuration. The system effectively suppresses environmental interference and false detection of dynamic objects, directly addressing the challenge of low-speed false activation in commercial vehicle safety systems. Evaluation in a real-world dataset (32,454 video segments from 1,852 vehicles) demonstrates an F1-score of 99.96% for static detection, 97.78% for moving state recognition, and a processing delay of 14.2 milliseconds (resolution 704x576). The deployment on-site shows an 89% reduction in false braking events, a 100% success rate in emergency braking, and a fault rate below 5%.
Kling-Foley: Multimodal Diffusion Transformer for High-Quality Video-to-Audio Generation
Jun 24, 2025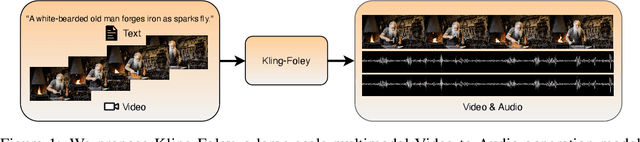
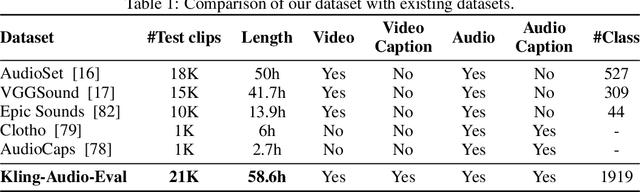
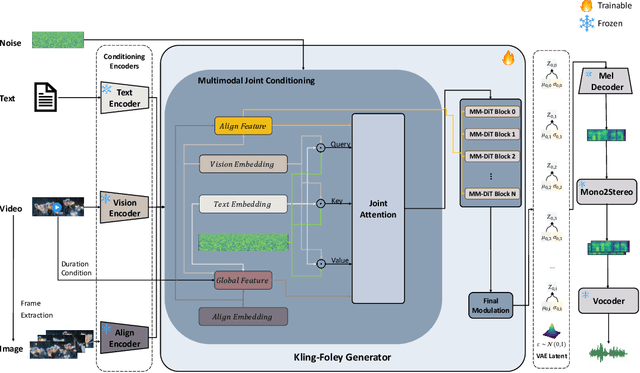
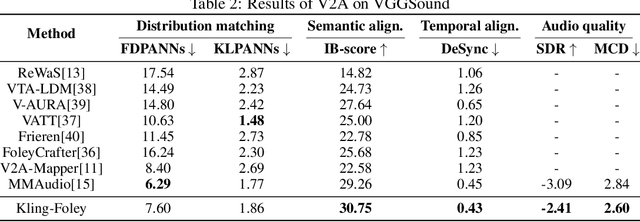
Abstract:We propose Kling-Foley, a large-scale multimodal Video-to-Audio generation model that synthesizes high-quality audio synchronized with video content. In Kling-Foley, we introduce multimodal diffusion transformers to model the interactions between video, audio, and text modalities, and combine it with a visual semantic representation module and an audio-visual synchronization module to enhance alignment capabilities. Specifically, these modules align video conditions with latent audio elements at the frame level, thereby improving semantic alignment and audio-visual synchronization. Together with text conditions, this integrated approach enables precise generation of video-matching sound effects. In addition, we propose a universal latent audio codec that can achieve high-quality modeling in various scenarios such as sound effects, speech, singing, and music. We employ a stereo rendering method that imbues synthesized audio with a spatial presence. At the same time, in order to make up for the incomplete types and annotations of the open-source benchmark, we also open-source an industrial-level benchmark Kling-Audio-Eval. Our experiments show that Kling-Foley trained with the flow matching objective achieves new audio-visual SOTA performance among public models in terms of distribution matching, semantic alignment, temporal alignment and audio quality.
RankFlow: A Multi-Role Collaborative Reranking Workflow Utilizing Large Language Models
Feb 04, 2025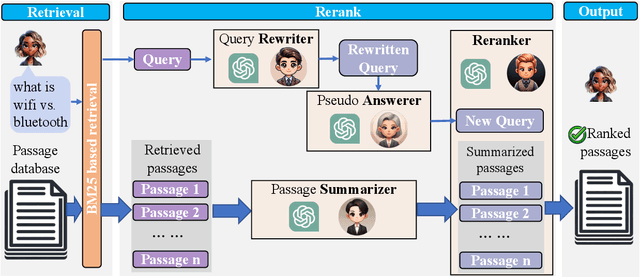
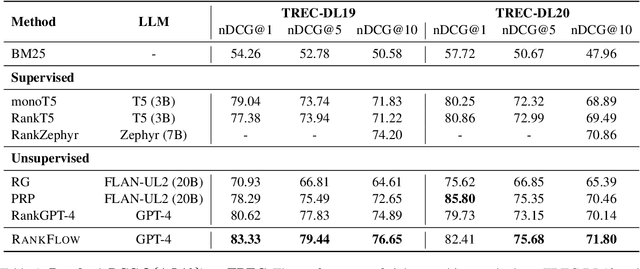
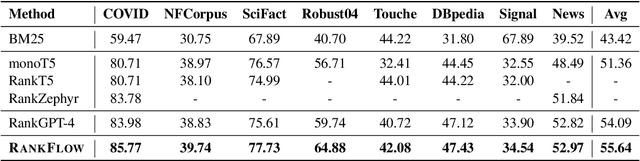
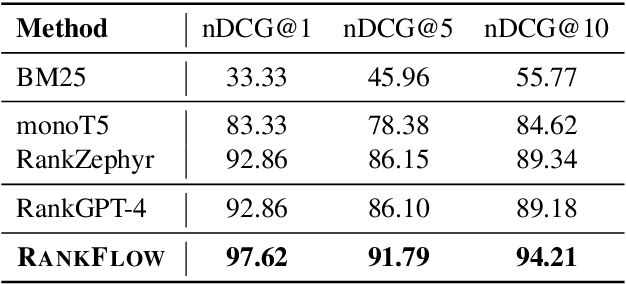
Abstract:In an Information Retrieval (IR) system, reranking plays a critical role by sorting candidate passages according to their relevance to a specific query. This process demands a nuanced understanding of the variations among passages linked to the query. In this work, we introduce RankFlow, a multi-role reranking workflow that leverages the capabilities of Large Language Models (LLMs) and role specializations to improve reranking performance. RankFlow enlists LLMs to fulfill four distinct roles: the query Rewriter, the pseudo Answerer, the passage Summarizer, and the Reranker. This orchestrated approach enables RankFlow to: (1) accurately interpret queries, (2) draw upon LLMs' extensive pre-existing knowledge, (3) distill passages into concise versions, and (4) assess passages in a comprehensive manner, resulting in notably better reranking results. Our experimental results reveal that RankFlow outperforms existing leading approaches on widely recognized IR benchmarks, such as TREC-DL, BEIR, and NovelEval. Additionally, we investigate the individual contributions of each role in RankFlow. Code is available at https://github.com/jincan333/RankFlow.
Adapting Whisper for Code-Switching through Encoding Refining and Language-Aware Decoding
Dec 24, 2024


Abstract:Code-switching (CS) automatic speech recognition (ASR) faces challenges due to the language confusion resulting from accents, auditory similarity, and seamless language switches. Adaptation on the pre-trained multi-lingual model has shown promising performance for CS-ASR. In this paper, we adapt Whisper, which is a large-scale multilingual pre-trained speech recognition model, to CS from both encoder and decoder parts. First, we propose an encoder refiner to enhance the encoder's capacity of intra-sentence swithching. Second, we propose using two sets of language-aware adapters with different language prompt embeddings to achieve language-specific decoding information in each decoder layer. Then, a fusion module is added to fuse the language-aware decoding. The experimental results using the SEAME dataset show that, compared with the baseline model, the proposed approach achieves a relative MER reduction of 4.1% and 7.2% on the dev_man and dev_sge test sets, respectively, surpassing state-of-the-art methods. Through experiments, we found that the proposed method significantly improves the performance on non-native language in CS speech, indicating that our approach enables Whisper to better distinguish between the two languages.
CMoralEval: A Moral Evaluation Benchmark for Chinese Large Language Models
Aug 19, 2024



Abstract:What a large language model (LLM) would respond in ethically relevant context? In this paper, we curate a large benchmark CMoralEval for morality evaluation of Chinese LLMs. The data sources of CMoralEval are two-fold: 1) a Chinese TV program discussing Chinese moral norms with stories from the society and 2) a collection of Chinese moral anomies from various newspapers and academic papers on morality. With these sources, we aim to create a moral evaluation dataset characterized by diversity and authenticity. We develop a morality taxonomy and a set of fundamental moral principles that are not only rooted in traditional Chinese culture but also consistent with contemporary societal norms. To facilitate efficient construction and annotation of instances in CMoralEval, we establish a platform with AI-assisted instance generation to streamline the annotation process. These help us curate CMoralEval that encompasses both explicit moral scenarios (14,964 instances) and moral dilemma scenarios (15,424 instances), each with instances from different data sources. We conduct extensive experiments with CMoralEval to examine a variety of Chinese LLMs. Experiment results demonstrate that CMoralEval is a challenging benchmark for Chinese LLMs. The dataset is publicly available at \url{https://github.com/tjunlp-lab/CMoralEval}.
Establishing Rigorous and Cost-effective Clinical Trials for Artificial Intelligence Models
Jul 11, 2024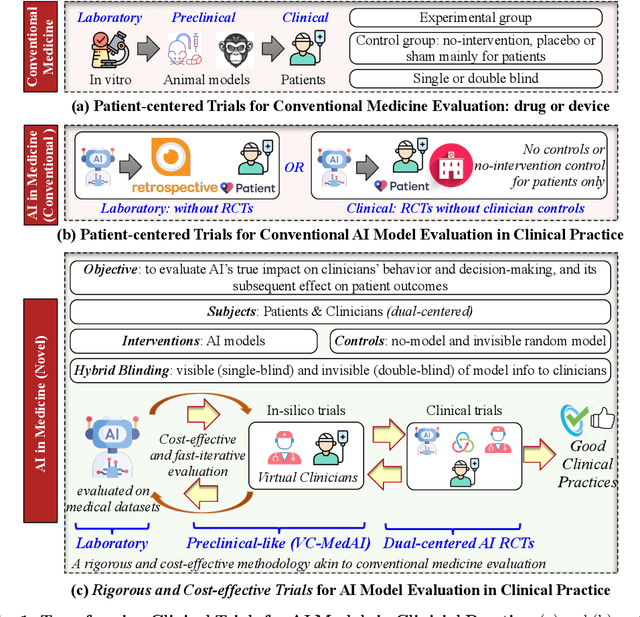
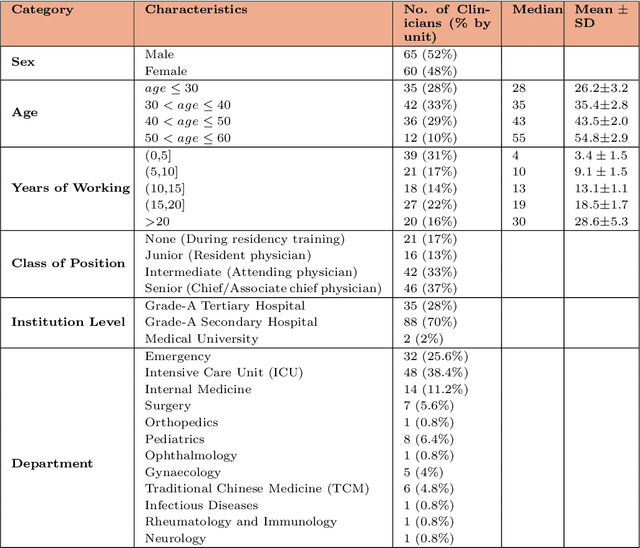
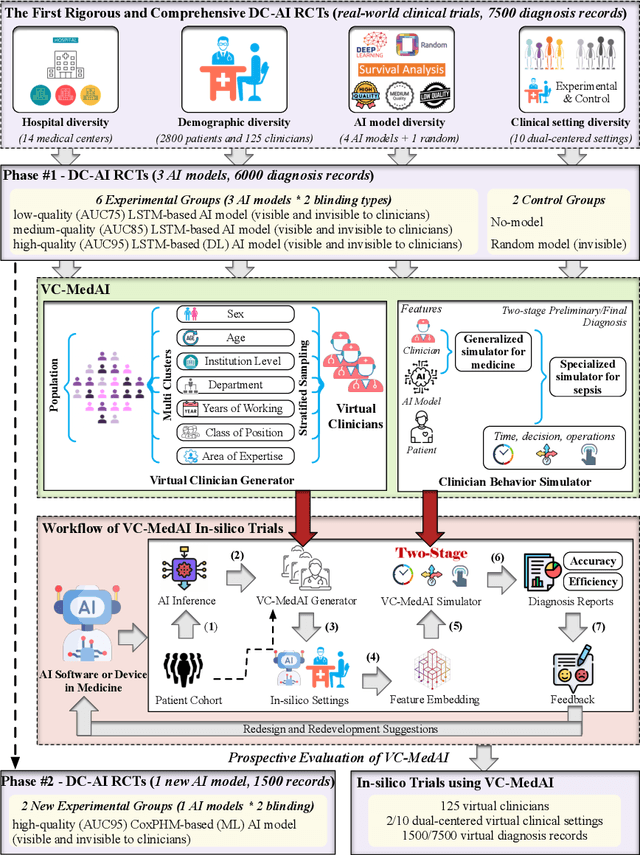
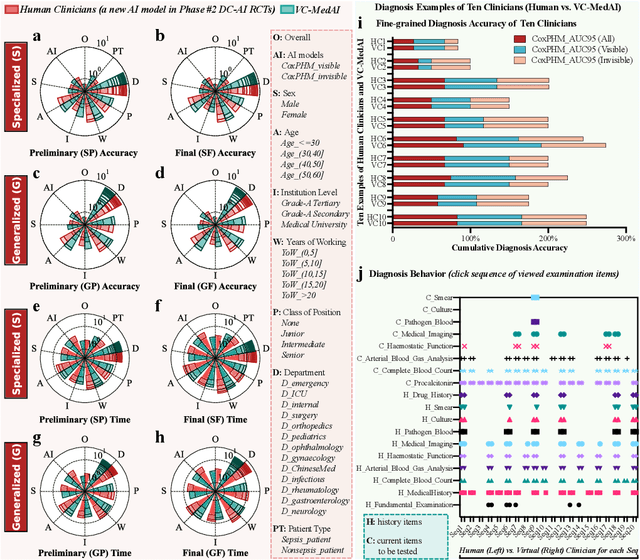
Abstract:A profound gap persists between artificial intelligence (AI) and clinical practice in medicine, primarily due to the lack of rigorous and cost-effective evaluation methodologies. State-of-the-art and state-of-the-practice AI model evaluations are limited to laboratory studies on medical datasets or direct clinical trials with no or solely patient-centered controls. Moreover, the crucial role of clinicians in collaborating with AI, pivotal for determining its impact on clinical practice, is often overlooked. For the first time, we emphasize the critical necessity for rigorous and cost-effective evaluation methodologies for AI models in clinical practice, featuring patient/clinician-centered (dual-centered) AI randomized controlled trials (DC-AI RCTs) and virtual clinician-based in-silico trials (VC-MedAI) as an effective proxy for DC-AI RCTs. Leveraging 7500 diagnosis records from two-phase inaugural DC-AI RCTs across 14 medical centers with 125 clinicians, our results demonstrate the necessity of DC-AI RCTs and the effectiveness of VC-MedAI. Notably, VC-MedAI performs comparably to human clinicians, replicating insights and conclusions from prospective DC-AI RCTs. We envision DC-AI RCTs and VC-MedAI as pivotal advancements, presenting innovative and transformative evaluation methodologies for AI models in clinical practice, offering a preclinical-like setting mirroring conventional medicine, and reshaping development paradigms in a cost-effective and fast-iterative manner. Chinese Clinical Trial Registration: ChiCTR2400086816.
AdaPI: Facilitating DNN Model Adaptivity for Efficient Private Inference in Edge Computing
Jul 08, 2024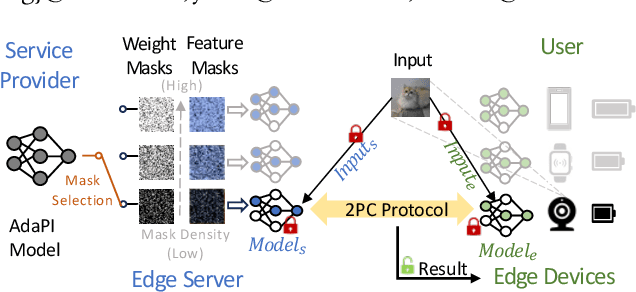
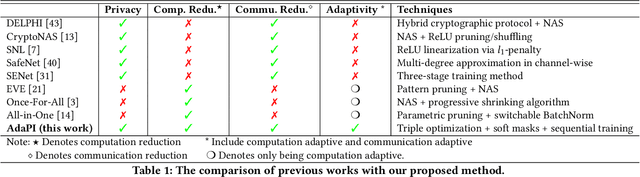
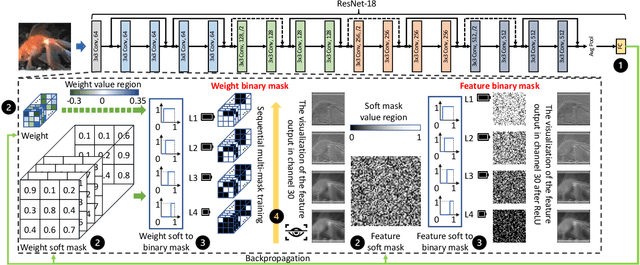
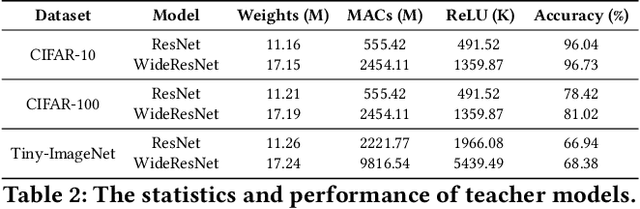
Abstract:Private inference (PI) has emerged as a promising solution to execute computations on encrypted data, safeguarding user privacy and model parameters in edge computing. However, existing PI methods are predominantly developed considering constant resource constraints, overlooking the varied and dynamic resource constraints in diverse edge devices, like energy budgets. Consequently, model providers have to design specialized models for different devices, where all of them have to be stored on the edge server, resulting in inefficient deployment. To fill this gap, this work presents AdaPI, a novel approach that achieves adaptive PI by allowing a model to perform well across edge devices with diverse energy budgets. AdaPI employs a PI-aware training strategy that optimizes the model weights alongside weight-level and feature-level soft masks. These soft masks are subsequently transformed into multiple binary masks to enable adjustments in communication and computation workloads. Through sequentially training the model with increasingly dense binary masks, AdaPI attains optimal accuracy for each energy budget, which outperforms the state-of-the-art PI methods by 7.3\% in terms of test accuracy on CIFAR-100. The code of AdaPI can be accessed via https://github.com/jiahuiiiiii/AdaPI.
APEER: Automatic Prompt Engineering Enhances Large Language Model Reranking
Jun 20, 2024Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have significantly enhanced Information Retrieval (IR) across various modules, such as reranking. Despite impressive performance, current zero-shot relevance ranking with LLMs heavily relies on human prompt engineering. Existing automatic prompt engineering algorithms primarily focus on language modeling and classification tasks, leaving the domain of IR, particularly reranking, underexplored. Directly applying current prompt engineering algorithms to relevance ranking is challenging due to the integration of query and long passage pairs in the input, where the ranking complexity surpasses classification tasks. To reduce human effort and unlock the potential of prompt optimization in reranking, we introduce a novel automatic prompt engineering algorithm named APEER. APEER iteratively generates refined prompts through feedback and preference optimization. Extensive experiments with four LLMs and ten datasets demonstrate the substantial performance improvement of APEER over existing state-of-the-art (SoTA) manual prompts. Furthermore, we find that the prompts generated by APEER exhibit better transferability across diverse tasks and LLMs. Code is available at https://github.com/jincan333/APEER.
Key Information Retrieval to Classify the Unstructured Data Content of Preferential Trade Agreements
Jan 23, 2024Abstract:With the rapid proliferation of textual data, predicting long texts has emerged as a significant challenge in the domain of natural language processing. Traditional text prediction methods encounter substantial difficulties when grappling with long texts, primarily due to the presence of redundant and irrelevant information, which impedes the model's capacity to capture pivotal insights from the text. To address this issue, we introduce a novel approach to long-text classification and prediction. Initially, we employ embedding techniques to condense the long texts, aiming to diminish the redundancy therein. Subsequently,the Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers (BERT) embedding method is utilized for text classification training. Experimental outcomes indicate that our method realizes considerable performance enhancements in classifying long texts of Preferential Trade Agreements. Furthermore, the condensation of text through embedding methods not only augments prediction accuracy but also substantially reduces computational complexity. Overall, this paper presents a strategy for long-text prediction, offering a valuable reference for researchers and engineers in the natural language processing sphere.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge