Yufei Huang
ProAct: A Benchmark and Multimodal Framework for Structure-Aware Proactive Response
Feb 03, 2026Abstract:While passive agents merely follow instructions, proactive agents align with higher-level objectives, such as assistance and safety by continuously monitoring the environment to determine when and how to act. However, developing proactive agents is hindered by the lack of specialized resources. To address this, we introduce ProAct-75, a benchmark designed to train and evaluate proactive agents across diverse domains, including assistance, maintenance, and safety monitoring. Spanning 75 tasks, our dataset features 91,581 step-level annotations enriched with explicit task graphs. These graphs encode step dependencies and parallel execution possibilities, providing the structural grounding necessary for complex decision-making. Building on this benchmark, we propose ProAct-Helper, a reference baseline powered by a Multimodal Large Language Model (MLLM) that grounds decision-making in state detection, and leveraging task graphs to enable entropy-driven heuristic search for action selection, allowing agents to execute parallel threads independently rather than mirroring the human's next step. Extensive experiments demonstrate that ProAct-Helper outperforms strong closed-source models, improving trigger detection mF1 by 6.21%, saving 0.25 more steps in online one-step decision, and increasing the rate of parallel actions by 15.58%.
FigEx2: Visual-Conditioned Panel Detection and Captioning for Scientific Compound Figures
Jan 12, 2026Abstract:Scientific compound figures combine multiple labeled panels into a single image, but captions in real pipelines are often missing or only provide figure-level summaries, making panel-level understanding difficult. In this paper, we propose FigEx2, visual-conditioned framework that localizes panels and generates panel-wise captions directly from the compound figure. To mitigate the impact of diverse phrasing in open-ended captioning, we introduce a noise-aware gated fusion module that adaptively filters token-level features to stabilize the detection query space. Furthermore, we employ a staged optimization strategy combining supervised learning with reinforcement learning (RL), utilizing CLIP-based alignment and BERTScore-based semantic rewards to enforce strict multimodal consistency. To support high-quality supervision, we curate BioSci-Fig-Cap, a refined benchmark for panel-level grounding, alongside cross-disciplinary test suites in physics and chemistry. Experimental results demonstrate that FigEx2 achieves a superior 0.726 mAP@0.5:0.95 for detection and significantly outperforms Qwen3-VL-8B by 0.51 in METEOR and 0.24 in BERTScore. Notably, FigEx2 exhibits remarkable zero-shot transferability to out-of-distribution scientific domains without any fine-tuning.
UltraLogic: Enhancing LLM Reasoning through Large-Scale Data Synthesis and Bipolar Float Reward
Jan 06, 2026Abstract:While Large Language Models (LLMs) have demonstrated significant potential in natural language processing , complex general-purpose reasoning requiring multi-step logic, planning, and verification remains a critical bottleneck. Although Reinforcement Learning with Verifiable Rewards (RLVR) has succeeded in specific domains , the field lacks large-scale, high-quality, and difficulty-calibrated data for general reasoning. To address this, we propose UltraLogic, a framework that decouples the logical core of a problem from its natural language expression through a Code-based Solving methodology to automate high-quality data production. The framework comprises hundreds of unique task types and an automated calibration pipeline across ten difficulty levels. Furthermore, to mitigate binary reward sparsity and the Non-negative Reward Trap, we introduce the Bipolar Float Reward (BFR) mechanism, utilizing graded penalties to effectively distinguish perfect responses from those with logical flaws. Our experiments demonstrate that task diversity is the primary driver for reasoning enhancement , and that BFR, combined with a difficulty matching strategy, significantly improves training efficiency, guiding models toward global logical optima.
Departures: Distributional Transport for Single-Cell Perturbation Prediction with Neural Schrödinger Bridges
Nov 17, 2025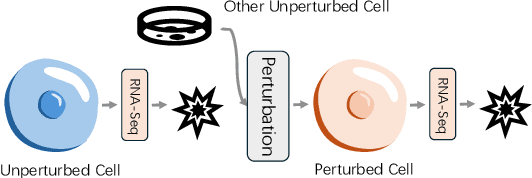
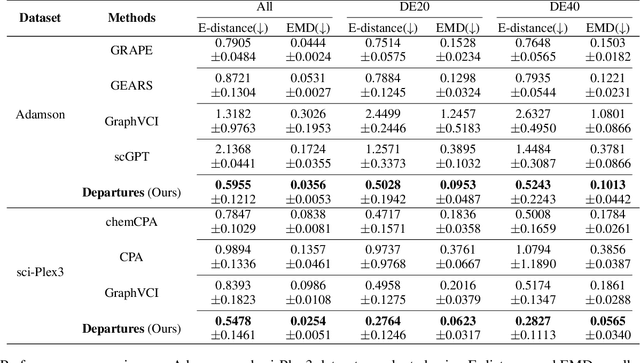
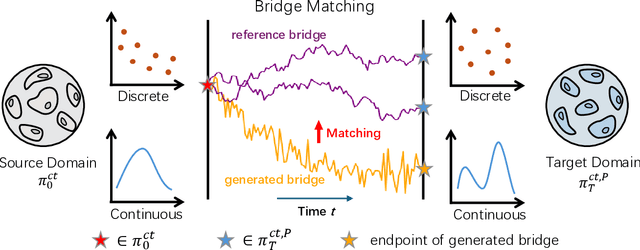

Abstract:Predicting single-cell perturbation outcomes directly advances gene function analysis and facilitates drug candidate selection, making it a key driver of both basic and translational biomedical research. However, a major bottleneck in this task is the unpaired nature of single-cell data, as the same cell cannot be observed both before and after perturbation due to the destructive nature of sequencing. Although some neural generative transport models attempt to tackle unpaired single-cell perturbation data, they either lack explicit conditioning or depend on prior spaces for indirect distribution alignment, limiting precise perturbation modeling. In this work, we approximate Schrödinger Bridge (SB), which defines stochastic dynamic mappings recovering the entropy-regularized optimal transport (OT), to directly align the distributions of control and perturbed single-cell populations across different perturbation conditions. Unlike prior SB approximations that rely on bidirectional modeling to infer optimal source-target sample coupling, we leverage Minibatch-OT based pairing to avoid such bidirectional inference and the associated ill-posedness of defining the reverse process. This pairing directly guides bridge learning, yielding a scalable approximation to the SB. We approximate two SB models, one modeling discrete gene activation states and the other continuous expression distributions. Joint training enables accurate perturbation modeling and captures single-cell heterogeneity. Experiments on public genetic and drug perturbation datasets show that our model effectively captures heterogeneous single-cell responses and achieves state-of-the-art performance.
AlphaFold Database Debiasing for Robust Inverse Folding
Jun 10, 2025Abstract:The AlphaFold Protein Structure Database (AFDB) offers unparalleled structural coverage at near-experimental accuracy, positioning it as a valuable resource for data-driven protein design. However, its direct use in training deep models that are sensitive to fine-grained atomic geometry, such as inverse folding, exposes a critical limitation. Comparative analysis of structural feature distributions reveals that AFDB structures exhibit distinct statistical regularities, reflecting a systematic geometric bias that deviates from the conformational diversity found in experimentally determined structures from the Protein Data Bank (PDB). While AFDB structures are cleaner and more idealized, PDB structures capture the intrinsic variability and physical realism essential for generalization in downstream tasks. To address this discrepancy, we introduce a Debiasing Structure AutoEncoder (DeSAE) that learns to reconstruct native-like conformations from intentionally corrupted backbone geometries. By training the model to recover plausible structural states, DeSAE implicitly captures a more robust and natural structural manifold. At inference, applying DeSAE to AFDB structures produces debiased structures that significantly improve inverse folding performance across multiple benchmarks. This work highlights the critical impact of subtle systematic biases in predicted structures and presents a principled framework for debiasing, significantly boosting the performance of structure-based learning tasks like inverse folding.
Tokenizing Electron Cloud in Protein-Ligand Interaction Learning
May 25, 2025



Abstract:The affinity and specificity of protein-molecule binding directly impact functional outcomes, uncovering the mechanisms underlying biological regulation and signal transduction. Most deep-learning-based prediction approaches focus on structures of atoms or fragments. However, quantum chemical properties, such as electronic structures, are the key to unveiling interaction patterns but remain largely underexplored. To bridge this gap, we propose ECBind, a method for tokenizing electron cloud signals into quantized embeddings, enabling their integration into downstream tasks such as binding affinity prediction. By incorporating electron densities, ECBind helps uncover binding modes that cannot be fully represented by atom-level models. Specifically, to remove the redundancy inherent in electron cloud signals, a structure-aware transformer and hierarchical codebooks encode 3D binding sites enriched with electron structures into tokens. These tokenized codes are then used for specific tasks with labels. To extend its applicability to a wider range of scenarios, we utilize knowledge distillation to develop an electron-cloud-agnostic prediction model. Experimentally, ECBind demonstrates state-of-the-art performance across multiple tasks, achieving improvements of 6.42\% and 15.58\% in per-structure Pearson and Spearman correlation coefficients, respectively.
Teaching Large Language Models to Maintain Contextual Faithfulness via Synthetic Tasks and Reinforcement Learning
May 22, 2025Abstract:Teaching large language models (LLMs) to be faithful in the provided context is crucial for building reliable information-seeking systems. Therefore, we propose a systematic framework, CANOE, to improve the faithfulness of LLMs in both short-form and long-form generation tasks without human annotations. Specifically, we first synthesize short-form question-answering (QA) data with four diverse tasks to construct high-quality and easily verifiable training data without human annotation. Also, we propose Dual-GRPO, a rule-based reinforcement learning method that includes three tailored rule-based rewards derived from synthesized short-form QA data, while simultaneously optimizing both short-form and long-form response generation. Notably, Dual-GRPO eliminates the need to manually label preference data to train reward models and avoids over-optimizing short-form generation when relying only on the synthesized short-form QA data. Experimental results show that CANOE greatly improves the faithfulness of LLMs across 11 different downstream tasks, even outperforming the most advanced LLMs, e.g., GPT-4o and OpenAI o1.
Hunyuan-TurboS: Advancing Large Language Models through Mamba-Transformer Synergy and Adaptive Chain-of-Thought
May 21, 2025Abstract:As Large Language Models (LLMs) rapidly advance, we introduce Hunyuan-TurboS, a novel large hybrid Transformer-Mamba Mixture of Experts (MoE) model. It synergistically combines Mamba's long-sequence processing efficiency with Transformer's superior contextual understanding. Hunyuan-TurboS features an adaptive long-short chain-of-thought (CoT) mechanism, dynamically switching between rapid responses for simple queries and deep "thinking" modes for complex problems, optimizing computational resources. Architecturally, this 56B activated (560B total) parameter model employs 128 layers (Mamba2, Attention, FFN) with an innovative AMF/MF block pattern. Faster Mamba2 ensures linear complexity, Grouped-Query Attention minimizes KV cache, and FFNs use an MoE structure. Pre-trained on 16T high-quality tokens, it supports a 256K context length and is the first industry-deployed large-scale Mamba model. Our comprehensive post-training strategy enhances capabilities via Supervised Fine-Tuning (3M instructions), a novel Adaptive Long-short CoT Fusion method, Multi-round Deliberation Learning for iterative improvement, and a two-stage Large-scale Reinforcement Learning process targeting STEM and general instruction-following. Evaluations show strong performance: overall top 7 rank on LMSYS Chatbot Arena with a score of 1356, outperforming leading models like Gemini-2.0-Flash-001 (1352) and o4-mini-2025-04-16 (1345). TurboS also achieves an average of 77.9% across 23 automated benchmarks. Hunyuan-TurboS balances high performance and efficiency, offering substantial capabilities at lower inference costs than many reasoning models, establishing a new paradigm for efficient large-scale pre-trained models.
VARD: Efficient and Dense Fine-Tuning for Diffusion Models with Value-based RL
May 21, 2025



Abstract:Diffusion models have emerged as powerful generative tools across various domains, yet tailoring pre-trained models to exhibit specific desirable properties remains challenging. While reinforcement learning (RL) offers a promising solution,current methods struggle to simultaneously achieve stable, efficient fine-tuning and support non-differentiable rewards. Furthermore, their reliance on sparse rewards provides inadequate supervision during intermediate steps, often resulting in suboptimal generation quality. To address these limitations, dense and differentiable signals are required throughout the diffusion process. Hence, we propose VAlue-based Reinforced Diffusion (VARD): a novel approach that first learns a value function predicting expection of rewards from intermediate states, and subsequently uses this value function with KL regularization to provide dense supervision throughout the generation process. Our method maintains proximity to the pretrained model while enabling effective and stable training via backpropagation. Experimental results demonstrate that our approach facilitates better trajectory guidance, improves training efficiency and extends the applicability of RL to diffusion models optimized for complex, non-differentiable reward functions.
GLTW: Joint Improved Graph Transformer and LLM via Three-Word Language for Knowledge Graph Completion
Feb 17, 2025Abstract:Knowledge Graph Completion (KGC), which aims to infer missing or incomplete facts, is a crucial task for KGs. However, integrating the vital structural information of KGs into Large Language Models (LLMs) and outputting predictions deterministically remains challenging. To address this, we propose a new method called GLTW, which encodes the structural information of KGs and merges it with LLMs to enhance KGC performance. Specifically, we introduce an improved Graph Transformer (iGT) that effectively encodes subgraphs with both local and global structural information and inherits the characteristics of language model, bypassing training from scratch. Also, we develop a subgraph-based multi-classification training objective, using all entities within KG as classification objects, to boost learning efficiency.Importantly, we combine iGT with an LLM that takes KG language prompts as input.Our extensive experiments on various KG datasets show that GLTW achieves significant performance gains compared to SOTA baselines.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge