Kangyang Luo
FactNet: A Billion-Scale Knowledge Graph for Multilingual Factual Grounding
Feb 03, 2026Abstract:While LLMs exhibit remarkable fluency, their utility is often compromised by factual hallucinations and a lack of traceable provenance. Existing resources for grounding mitigate this but typically enforce a dichotomy: they offer either structured knowledge without textual context (e.g., knowledge bases) or grounded text with limited scale and linguistic coverage. To bridge this gap, we introduce FactNet, a massive, open-source resource designed to unify 1.7 billion atomic assertions with 3.01 billion auditable evidence pointers derived exclusively from 316 Wikipedia editions. Unlike recent synthetic approaches, FactNet employs a strictly deterministic construction pipeline, ensuring that every evidence unit is recoverable with byte-level precision. Extensive auditing confirms a high grounding precision of 92.1%, even in long-tail languages. Furthermore, we establish FactNet-Bench, a comprehensive evaluation suite for Knowledge Graph Completion, Question Answering, and Fact Checking. FactNet provides the community with a foundational, reproducible resource for training and evaluating trustworthy, verifiable multilingual systems.
InFi-Check: Interpretable and Fine-Grained Fact-Checking of LLMs
Jan 10, 2026Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) often hallucinate, yet most existing fact-checking methods treat factuality evaluation as a binary classification problem, offering limited interpretability and failing to capture fine-grained error types. In this paper, we introduce InFi-Check, a framework for interpretable and fine-grained fact-checking of LLM outputs. Specifically, we first propose a controlled data synthesis pipeline that generates high-quality data featuring explicit evidence, fine-grained error type labels, justifications, and corrections. Based on this, we further construct large-scale training data and a manually verified benchmark InFi-Check-FG for fine-grained fact-checking of LLM outputs. Building on these high-quality training data, we further propose InFi-Checker, which can jointly provide supporting evidence, classify fine-grained error types, and produce justifications along with corrections. Experiments show that InFi-Checker achieves state-of-the-art performance on InFi-Check-FG and strong generalization across various downstream tasks, significantly improving the utility and trustworthiness of factuality evaluation.
MEIC-DT: Memory-Efficient Incremental Clustering for Long-Text Coreference Resolution with Dual-Threshold Constraints
Dec 31, 2025Abstract:In the era of large language models (LLMs), supervised neural methods remain the state-of-the-art (SOTA) for Coreference Resolution. Yet, their full potential is underexplored, particularly in incremental clustering, which faces the critical challenge of balancing efficiency with performance for long texts. To address the limitation, we propose \textbf{MEIC-DT}, a novel dual-threshold, memory-efficient incremental clustering approach based on a lightweight Transformer. MEIC-DT features a dual-threshold constraint mechanism designed to precisely control the Transformer's input scale within a predefined memory budget. This mechanism incorporates a Statistics-Aware Eviction Strategy (\textbf{SAES}), which utilizes distinct statistical profiles from the training and inference phases for intelligent cache management. Furthermore, we introduce an Internal Regularization Policy (\textbf{IRP}) that strategically condenses clusters by selecting the most representative mentions, thereby preserving semantic integrity. Extensive experiments on common benchmarks demonstrate that MEIC-DT achieves highly competitive coreference performance under stringent memory constraints.
FaithLens: Detecting and Explaining Faithfulness Hallucination
Dec 23, 2025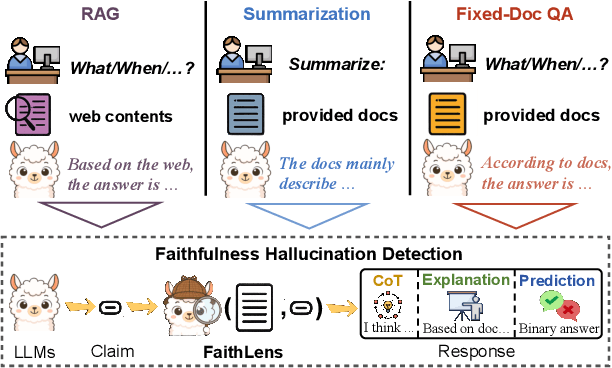
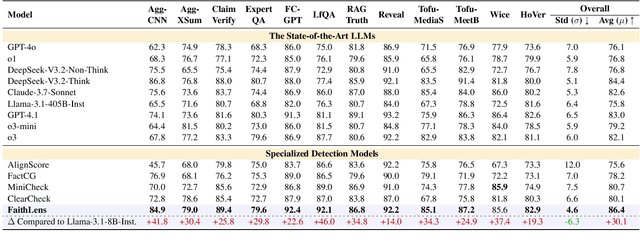
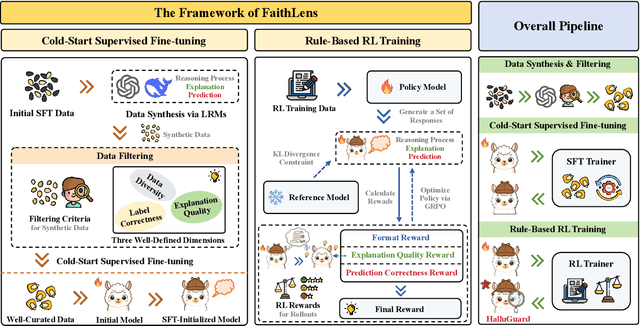
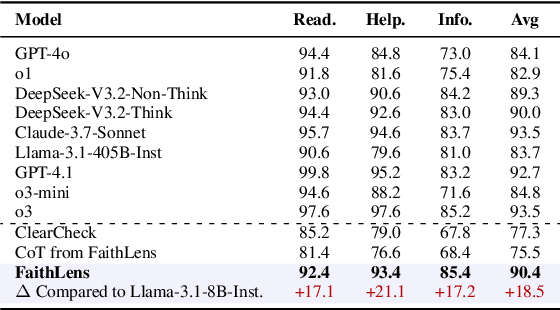
Abstract:Recognizing whether outputs from large language models (LLMs) contain faithfulness hallucination is crucial for real-world applications, e.g., retrieval-augmented generation and summarization. In this paper, we introduce FaithLens, a cost-efficient and effective faithfulness hallucination detection model that can jointly provide binary predictions and corresponding explanations to improve trustworthiness. To achieve this, we first synthesize training data with explanations via advanced LLMs and apply a well-defined data filtering strategy to ensure label correctness, explanation quality, and data diversity. Subsequently, we fine-tune the model on these well-curated training data as a cold start and further optimize it with rule-based reinforcement learning, using rewards for both prediction correctness and explanation quality. Results on 12 diverse tasks show that the 8B-parameter FaithLens outperforms advanced models such as GPT-4.1 and o3. Also, FaithLens can produce high-quality explanations, delivering a distinctive balance of trustworthiness, efficiency, and effectiveness.
Consistent Assistant Domains Transformer for Source-free Domain Adaptation
Oct 02, 2025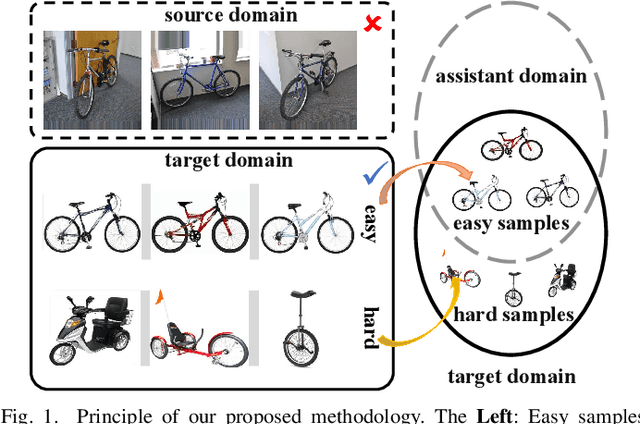
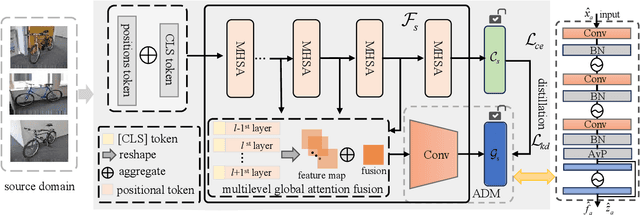
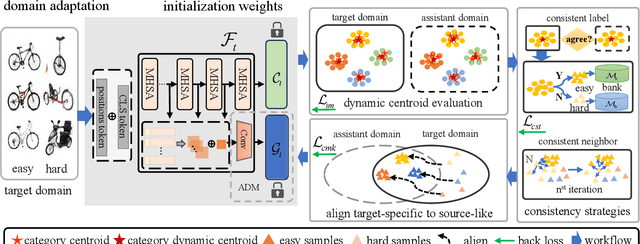
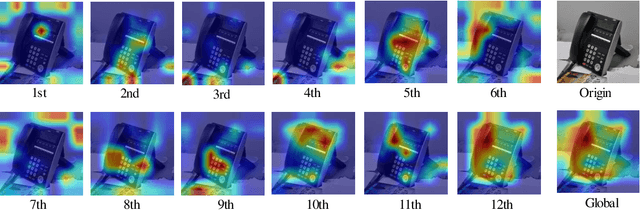
Abstract:Source-free domain adaptation (SFDA) aims to address the challenge of adapting to a target domain without accessing the source domain directly. However, due to the inaccessibility of source domain data, deterministic invariable features cannot be obtained. Current mainstream methods primarily focus on evaluating invariant features in the target domain that closely resemble those in the source domain, subsequently aligning the target domain with the source domain. However, these methods are susceptible to hard samples and influenced by domain bias. In this paper, we propose a Consistent Assistant Domains Transformer for SFDA, abbreviated as CADTrans, which solves the issue by constructing invariable feature representations of domain consistency. Concretely, we develop an assistant domain module for CADTrans to obtain diversified representations from the intermediate aggregated global attentions, which addresses the limitation of existing methods in adequately representing diversity. Based on assistant and target domains, invariable feature representations are obtained by multiple consistent strategies, which can be used to distinguish easy and hard samples. Finally, to align the hard samples to the corresponding easy samples, we construct a conditional multi-kernel max mean discrepancy (CMK-MMD) strategy to distinguish between samples of the same category and those of different categories. Extensive experiments are conducted on various benchmarks such as Office-31, Office-Home, VISDA-C, and DomainNet-126, proving the significant performance improvements achieved by our proposed approaches. Code is available at https://github.com/RoryShao/CADTrans.git.
Teaching Large Language Models to Maintain Contextual Faithfulness via Synthetic Tasks and Reinforcement Learning
May 22, 2025Abstract:Teaching large language models (LLMs) to be faithful in the provided context is crucial for building reliable information-seeking systems. Therefore, we propose a systematic framework, CANOE, to improve the faithfulness of LLMs in both short-form and long-form generation tasks without human annotations. Specifically, we first synthesize short-form question-answering (QA) data with four diverse tasks to construct high-quality and easily verifiable training data without human annotation. Also, we propose Dual-GRPO, a rule-based reinforcement learning method that includes three tailored rule-based rewards derived from synthesized short-form QA data, while simultaneously optimizing both short-form and long-form response generation. Notably, Dual-GRPO eliminates the need to manually label preference data to train reward models and avoids over-optimizing short-form generation when relying only on the synthesized short-form QA data. Experimental results show that CANOE greatly improves the faithfulness of LLMs across 11 different downstream tasks, even outperforming the most advanced LLMs, e.g., GPT-4o and OpenAI o1.
From Unaligned to Aligned: Scaling Multilingual LLMs with Multi-Way Parallel Corpora
May 20, 2025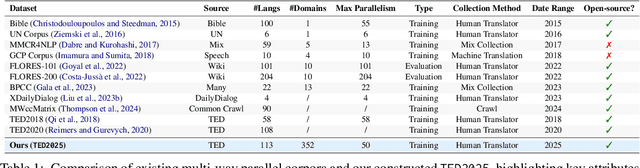

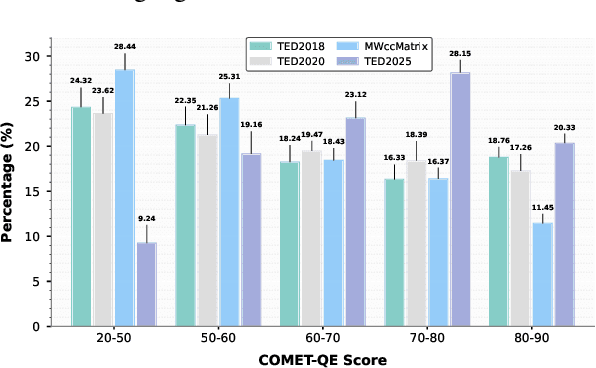
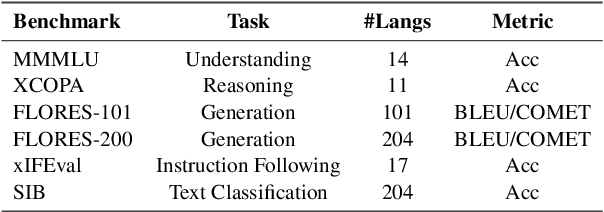
Abstract:Continued pretraining and instruction tuning on large-scale multilingual data have proven to be effective in scaling large language models (LLMs) to low-resource languages. However, the unaligned nature of such data limits its ability to effectively capture cross-lingual semantics. In contrast, multi-way parallel data, where identical content is aligned across multiple languages, provides stronger cross-lingual consistency and offers greater potential for improving multilingual performance. In this paper, we introduce a large-scale, high-quality multi-way parallel corpus, TED2025, based on TED Talks. The corpus spans 113 languages, with up to 50 languages aligned in parallel, ensuring extensive multilingual coverage. Using this dataset, we investigate best practices for leveraging multi-way parallel data to enhance LLMs, including strategies for continued pretraining, instruction tuning, and the analysis of key influencing factors. Experiments on six multilingual benchmarks show that models trained on multiway parallel data consistently outperform those trained on unaligned multilingual data.
GLTW: Joint Improved Graph Transformer and LLM via Three-Word Language for Knowledge Graph Completion
Feb 17, 2025Abstract:Knowledge Graph Completion (KGC), which aims to infer missing or incomplete facts, is a crucial task for KGs. However, integrating the vital structural information of KGs into Large Language Models (LLMs) and outputting predictions deterministically remains challenging. To address this, we propose a new method called GLTW, which encodes the structural information of KGs and merges it with LLMs to enhance KGC performance. Specifically, we introduce an improved Graph Transformer (iGT) that effectively encodes subgraphs with both local and global structural information and inherits the characteristics of language model, bypassing training from scratch. Also, we develop a subgraph-based multi-classification training objective, using all entities within KG as classification objects, to boost learning efficiency.Importantly, we combine iGT with an LLM that takes KG language prompts as input.Our extensive experiments on various KG datasets show that GLTW achieves significant performance gains compared to SOTA baselines.
DCAD-2000: A Multilingual Dataset across 2000+ Languages with Data Cleaning as Anomaly Detection
Feb 17, 2025Abstract:The rapid development of multilingual large language models (LLMs) highlights the need for high-quality, diverse, and clean multilingual datasets. In this paper, we introduce DCAD-2000 (Data Cleaning as Anomaly Detection), a large-scale multilingual corpus built using newly extracted Common Crawl data and existing multilingual datasets. DCAD-2000 includes over 2,282 languages, 46.72TB of data, and 8.63 billion documents, spanning 155 high- and medium-resource languages and 159 writing scripts. To overcome the limitations of current data cleaning methods, which rely on manual heuristic thresholds, we propose reframing data cleaning as an anomaly detection task. This dynamic filtering approach significantly enhances data quality by identifying and removing noisy or anomalous content. We evaluate the quality of DCAD-2000 on the FineTask benchmark, demonstrating substantial improvements in multilingual dataset quality and task performance.
Aligning Large Language Models to Follow Instructions and Hallucinate Less via Effective Data Filtering
Feb 11, 2025Abstract:Training LLMs on data that contains unfamiliar knowledge during the instruction tuning stage can make LLMs overconfident and encourage hallucinations. To address this challenge, we introduce a novel framework, NOVA, which identifies high-quality data that aligns well with the LLM's learned knowledge to reduce hallucinations. NOVA includes Internal Consistency Probing (ICP) and Semantic Equivalence Identification (SEI) to measure how familiar the LLM is with instruction data. Specifically, ICP evaluates the LLM's understanding of the given instruction by calculating the tailored consistency among multiple self-generated responses. SEI further assesses the familiarity of the LLM with the target response by comparing it to the generated responses, using the proposed semantic clustering and well-designed voting strategy. Finally, we introduce an expert-aligned reward model, considering characteristics beyond just familiarity to enhance data quality. By considering data quality and avoiding unfamiliar data, we can utilize the selected data to effectively align LLMs to follow instructions and hallucinate less. Extensive experiments and analysis show that NOVA significantly reduces hallucinations and allows LLMs to maintain a strong ability to follow instructions.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge