Alexander Fraser
FactNet: A Billion-Scale Knowledge Graph for Multilingual Factual Grounding
Feb 03, 2026Abstract:While LLMs exhibit remarkable fluency, their utility is often compromised by factual hallucinations and a lack of traceable provenance. Existing resources for grounding mitigate this but typically enforce a dichotomy: they offer either structured knowledge without textual context (e.g., knowledge bases) or grounded text with limited scale and linguistic coverage. To bridge this gap, we introduce FactNet, a massive, open-source resource designed to unify 1.7 billion atomic assertions with 3.01 billion auditable evidence pointers derived exclusively from 316 Wikipedia editions. Unlike recent synthetic approaches, FactNet employs a strictly deterministic construction pipeline, ensuring that every evidence unit is recoverable with byte-level precision. Extensive auditing confirms a high grounding precision of 92.1%, even in long-tail languages. Furthermore, we establish FactNet-Bench, a comprehensive evaluation suite for Knowledge Graph Completion, Question Answering, and Fact Checking. FactNet provides the community with a foundational, reproducible resource for training and evaluating trustworthy, verifiable multilingual systems.
Mask and You Shall Receive: Optimizing Masked Language Modeling For Pretraining BabyLMs
Oct 23, 2025Abstract:We describe our strategy for the 2025 edition of the BabyLM Challenge. Our main contribution is that of an improved form of Masked Language Modeling (MLM), which adapts the probabilities of the tokens masked according to the model's ability to predict them. The results show a substantial increase in performance on (Super)GLUE tasks over the standard MLM. We also incorporate sub-token embeddings, finding that this increases the model's morphological generalization capabilities. Our submission beats the baseline in the strict-small track.
EmoBench-UA: A Benchmark Dataset for Emotion Detection in Ukrainian
May 29, 2025Abstract:While Ukrainian NLP has seen progress in many texts processing tasks, emotion classification remains an underexplored area with no publicly available benchmark to date. In this work, we introduce EmoBench-UA, the first annotated dataset for emotion detection in Ukrainian texts. Our annotation schema is adapted from the previous English-centric works on emotion detection (Mohammad et al., 2018; Mohammad, 2022) guidelines. The dataset was created through crowdsourcing using the Toloka.ai platform ensuring high-quality of the annotation process. Then, we evaluate a range of approaches on the collected dataset, starting from linguistic-based baselines, synthetic data translated from English, to large language models (LLMs). Our findings highlight the challenges of emotion classification in non-mainstream languages like Ukrainian and emphasize the need for further development of Ukrainian-specific models and training resources.
NLP for Social Good: A Survey of Challenges, Opportunities, and Responsible Deployment
May 28, 2025



Abstract:Recent advancements in large language models (LLMs) have unlocked unprecedented possibilities across a range of applications. However, as a community, we believe that the field of Natural Language Processing (NLP) has a growing need to approach deployment with greater intentionality and responsibility. In alignment with the broader vision of AI for Social Good (Toma\v{s}ev et al., 2020), this paper examines the role of NLP in addressing pressing societal challenges. Through a cross-disciplinary analysis of social goals and emerging risks, we highlight promising research directions and outline challenges that must be addressed to ensure responsible and equitable progress in NLP4SG research.
EXECUTE: A Multilingual Benchmark for LLM Token Understanding
May 23, 2025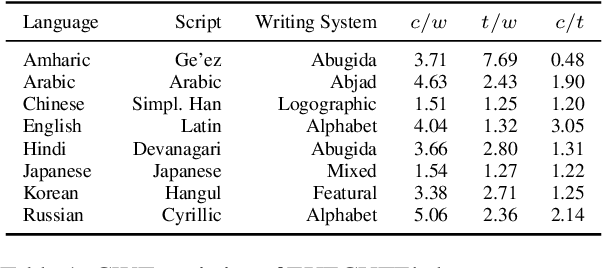
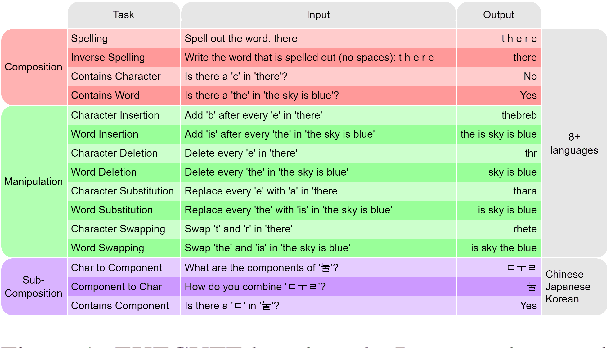
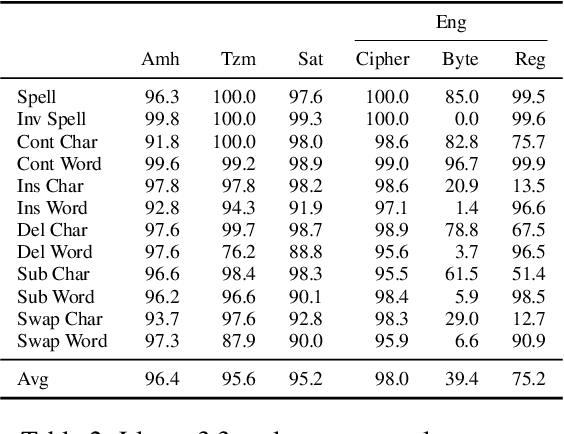
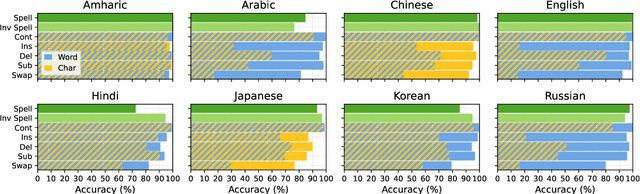
Abstract:The CUTE benchmark showed that LLMs struggle with character understanding in English. We extend it to more languages with diverse scripts and writing systems, introducing EXECUTE. Our simplified framework allows easy expansion to any language. Tests across multiple LLMs reveal that challenges in other languages are not always on the character level as in English. Some languages show word-level processing issues, some show no issues at all. We also examine sub-character tasks in Chinese, Japanese, and Korean to assess LLMs' understanding of character components.
From Unaligned to Aligned: Scaling Multilingual LLMs with Multi-Way Parallel Corpora
May 20, 2025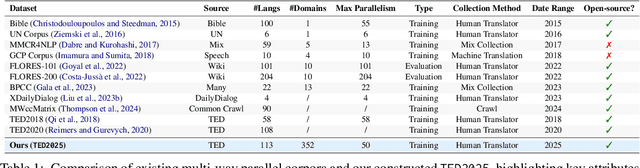

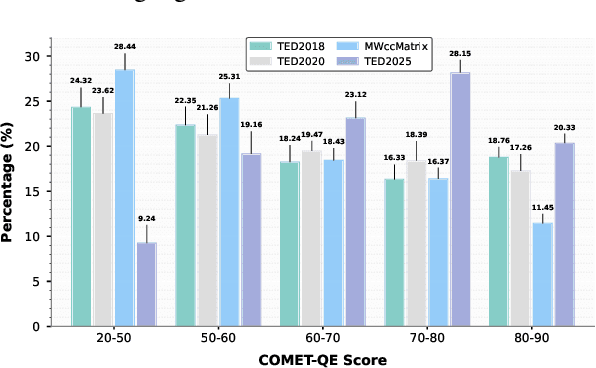
Abstract:Continued pretraining and instruction tuning on large-scale multilingual data have proven to be effective in scaling large language models (LLMs) to low-resource languages. However, the unaligned nature of such data limits its ability to effectively capture cross-lingual semantics. In contrast, multi-way parallel data, where identical content is aligned across multiple languages, provides stronger cross-lingual consistency and offers greater potential for improving multilingual performance. In this paper, we introduce a large-scale, high-quality multi-way parallel corpus, TED2025, based on TED Talks. The corpus spans 113 languages, with up to 50 languages aligned in parallel, ensuring extensive multilingual coverage. Using this dataset, we investigate best practices for leveraging multi-way parallel data to enhance LLMs, including strategies for continued pretraining, instruction tuning, and the analysis of key influencing factors. Experiments on six multilingual benchmarks show that models trained on multiway parallel data consistently outperform those trained on unaligned multilingual data.
Data-Efficient Hate Speech Detection via Cross-Lingual Nearest Neighbor Retrieval with Limited Labeled Data
May 20, 2025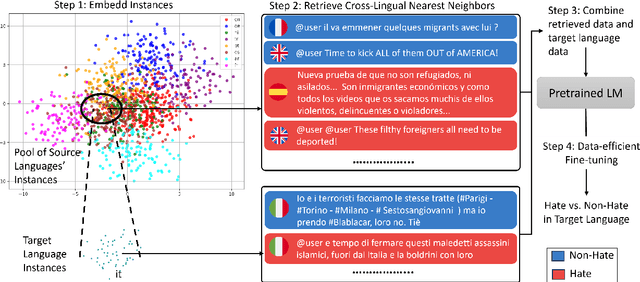
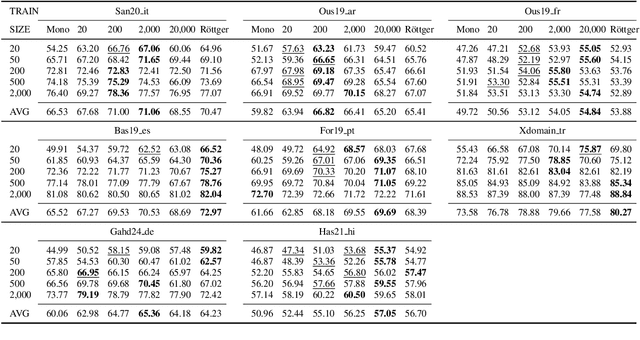
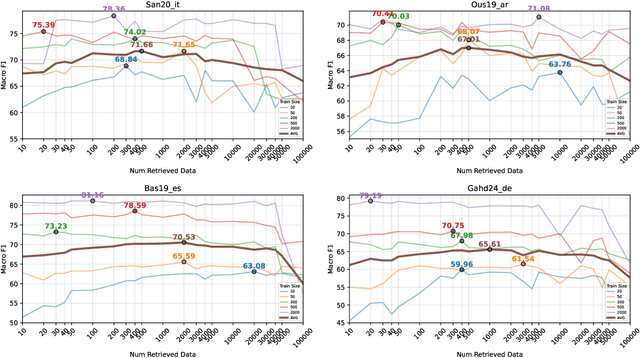
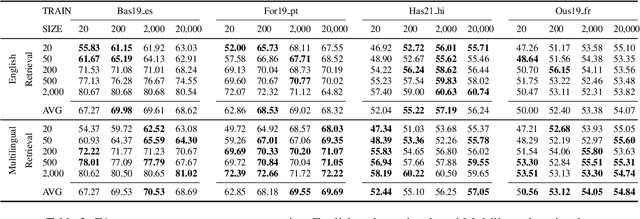
Abstract:Considering the importance of detecting hateful language, labeled hate speech data is expensive and time-consuming to collect, particularly for low-resource languages. Prior work has demonstrated the effectiveness of cross-lingual transfer learning and data augmentation in improving performance on tasks with limited labeled data. To develop an efficient and scalable cross-lingual transfer learning approach, we leverage nearest-neighbor retrieval to augment minimal labeled data in the target language, thereby enhancing detection performance. Specifically, we assume access to a small set of labeled training instances in the target language and use these to retrieve the most relevant labeled examples from a large multilingual hate speech detection pool. We evaluate our approach on eight languages and demonstrate that it consistently outperforms models trained solely on the target language data. Furthermore, in most cases, our method surpasses the current state-of-the-art. Notably, our approach is highly data-efficient, retrieving as small as 200 instances in some cases while maintaining superior performance. Moreover, it is scalable, as the retrieval pool can be easily expanded, and the method can be readily adapted to new languages and tasks. We also apply maximum marginal relevance to mitigate redundancy and filter out highly similar retrieved instances, resulting in improvements in some languages.
Can Prompting LLMs Unlock Hate Speech Detection across Languages? A Zero-shot and Few-shot Study
May 09, 2025Abstract:Despite growing interest in automated hate speech detection, most existing approaches overlook the linguistic diversity of online content. Multilingual instruction-tuned large language models such as LLaMA, Aya, Qwen, and BloomZ offer promising capabilities across languages, but their effectiveness in identifying hate speech through zero-shot and few-shot prompting remains underexplored. This work evaluates LLM prompting-based detection across eight non-English languages, utilizing several prompting techniques and comparing them to fine-tuned encoder models. We show that while zero-shot and few-shot prompting lag behind fine-tuned encoder models on most of the real-world evaluation sets, they achieve better generalization on functional tests for hate speech detection. Our study also reveals that prompt design plays a critical role, with each language often requiring customized prompting techniques to maximize performance.
DCAD-2000: A Multilingual Dataset across 2000+ Languages with Data Cleaning as Anomaly Detection
Feb 17, 2025Abstract:The rapid development of multilingual large language models (LLMs) highlights the need for high-quality, diverse, and clean multilingual datasets. In this paper, we introduce DCAD-2000 (Data Cleaning as Anomaly Detection), a large-scale multilingual corpus built using newly extracted Common Crawl data and existing multilingual datasets. DCAD-2000 includes over 2,282 languages, 46.72TB of data, and 8.63 billion documents, spanning 155 high- and medium-resource languages and 159 writing scripts. To overcome the limitations of current data cleaning methods, which rely on manual heuristic thresholds, we propose reframing data cleaning as an anomaly detection task. This dynamic filtering approach significantly enhances data quality by identifying and removing noisy or anomalous content. We evaluate the quality of DCAD-2000 on the FineTask benchmark, demonstrating substantial improvements in multilingual dataset quality and task performance.
Beyond Literal Token Overlap: Token Alignability for Multilinguality
Feb 10, 2025



Abstract:Previous work has considered token overlap, or even similarity of token distributions, as predictors for multilinguality and cross-lingual knowledge transfer in language models. However, these very literal metrics assign large distances to language pairs with different scripts, which can nevertheless show good cross-linguality. This limits the explanatory strength of token overlap for knowledge transfer between language pairs that use distinct scripts or follow different orthographic conventions. In this paper, we propose subword token alignability as a new way to understand the impact and quality of multilingual tokenisation. In particular, this metric predicts multilinguality much better when scripts are disparate and the overlap of literal tokens is low. We analyse this metric in the context of both encoder and decoder models, look at data size as a potential distractor, and discuss how this insight may be applied to multilingual tokenisation in future work. We recommend our subword token alignability metric for identifying optimal language pairs for cross-lingual transfer, as well as to guide the construction of better multilingual tokenisers in the future. We publish our code and reproducibility details.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge