Nikolay Babakov
EmoBench-UA: A Benchmark Dataset for Emotion Detection in Ukrainian
May 29, 2025Abstract:While Ukrainian NLP has seen progress in many texts processing tasks, emotion classification remains an underexplored area with no publicly available benchmark to date. In this work, we introduce EmoBench-UA, the first annotated dataset for emotion detection in Ukrainian texts. Our annotation schema is adapted from the previous English-centric works on emotion detection (Mohammad et al., 2018; Mohammad, 2022) guidelines. The dataset was created through crowdsourcing using the Toloka.ai platform ensuring high-quality of the annotation process. Then, we evaluate a range of approaches on the collected dataset, starting from linguistic-based baselines, synthetic data translated from English, to large language models (LLMs). Our findings highlight the challenges of emotion classification in non-mainstream languages like Ukrainian and emphasize the need for further development of Ukrainian-specific models and training resources.
BRIGHTER: BRIdging the Gap in Human-Annotated Textual Emotion Recognition Datasets for 28 Languages
Feb 17, 2025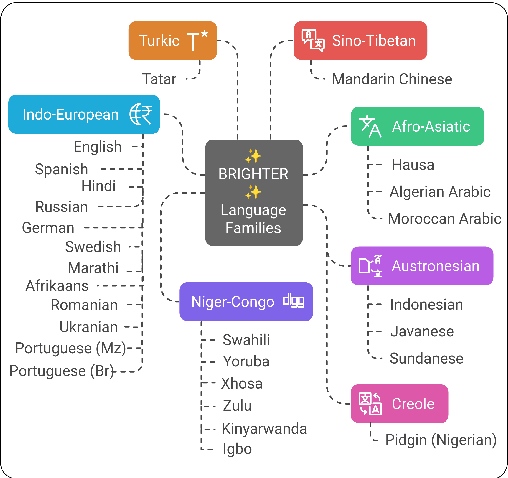
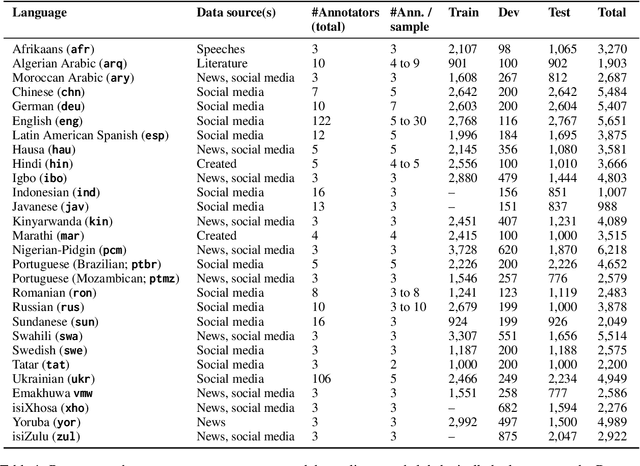
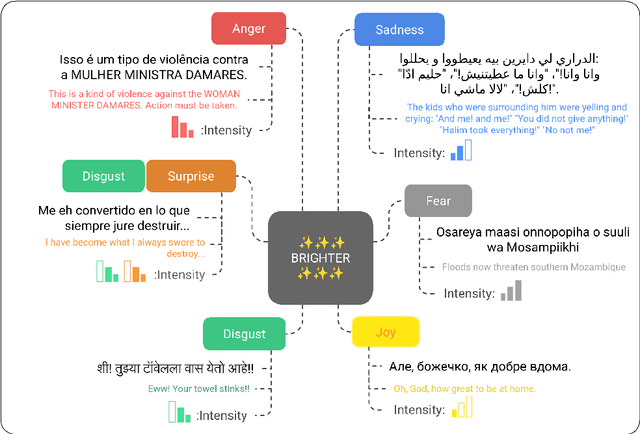
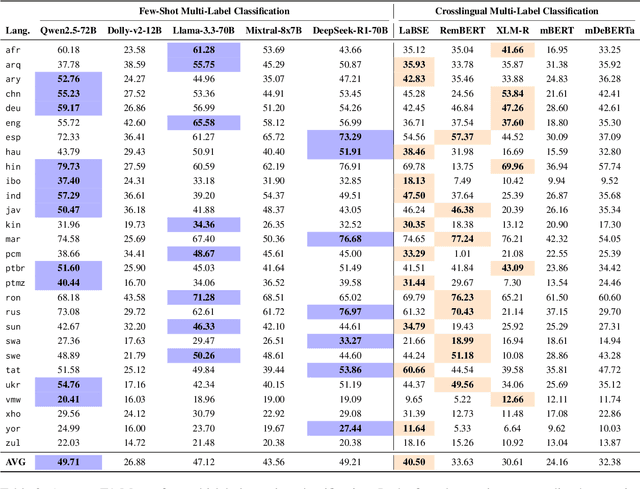
Abstract:People worldwide use language in subtle and complex ways to express emotions. While emotion recognition -- an umbrella term for several NLP tasks -- significantly impacts different applications in NLP and other fields, most work in the area is focused on high-resource languages. Therefore, this has led to major disparities in research and proposed solutions, especially for low-resource languages that suffer from the lack of high-quality datasets. In this paper, we present BRIGHTER-- a collection of multilabeled emotion-annotated datasets in 28 different languages. BRIGHTER covers predominantly low-resource languages from Africa, Asia, Eastern Europe, and Latin America, with instances from various domains annotated by fluent speakers. We describe the data collection and annotation processes and the challenges of building these datasets. Then, we report different experimental results for monolingual and crosslingual multi-label emotion identification, as well as intensity-level emotion recognition. We investigate results with and without using LLMs and analyse the large variability in performance across languages and text domains. We show that BRIGHTER datasets are a step towards bridging the gap in text-based emotion recognition and discuss their impact and utility.
Multilingual and Explainable Text Detoxification with Parallel Corpora
Dec 16, 2024Abstract:Even with various regulations in place across countries and social media platforms (Government of India, 2021; European Parliament and Council of the European Union, 2022, digital abusive speech remains a significant issue. One potential approach to address this challenge is automatic text detoxification, a text style transfer (TST) approach that transforms toxic language into a more neutral or non-toxic form. To date, the availability of parallel corpora for the text detoxification task (Logachevavet al., 2022; Atwell et al., 2022; Dementievavet al., 2024a) has proven to be crucial for state-of-the-art approaches. With this work, we extend parallel text detoxification corpus to new languages -- German, Chinese, Arabic, Hindi, and Amharic -- testing in the extensive multilingual setup TST baselines. Next, we conduct the first of its kind an automated, explainable analysis of the descriptive features of both toxic and non-toxic sentences, diving deeply into the nuances, similarities, and differences of toxicity and detoxification across 9 languages. Finally, based on the obtained insights, we experiment with a novel text detoxification method inspired by the Chain-of-Thoughts reasoning approach, enhancing the prompting process through clustering on relevant descriptive attributes.
Explaining Bayesian Networks in Natural Language using Factor Arguments. Evaluation in the medical domain
Oct 23, 2024



Abstract:In this paper, we propose a model for building natural language explanations for Bayesian Network Reasoning in terms of factor arguments, which are argumentation graphs of flowing evidence, relating the observed evidence to a target variable we want to learn about. We introduce the notion of factor argument independence to address the outstanding question of defining when arguments should be presented jointly or separately and present an algorithm that, starting from the evidence nodes and a target node, produces a list of all independent factor arguments ordered by their strength. Finally, we implemented a scheme to build natural language explanations of Bayesian Reasoning using this approach. Our proposal has been validated in the medical domain through a human-driven evaluation study where we compare the Bayesian Network Reasoning explanations obtained using factor arguments with an alternative explanation method. Evaluation results indicate that our proposed explanation approach is deemed by users as significantly more useful for understanding Bayesian Network Reasoning than another existing explanation method it is compared to.
Scalability of Bayesian Network Structure Elicitation with Large Language Models: a Novel Methodology and Comparative Analysis
Jul 12, 2024



Abstract:In this work, we propose a novel method for Bayesian Networks (BNs) structure elicitation that is based on the initialization of several LLMs with different experiences, independently querying them to create a structure of the BN, and further obtaining the final structure by majority voting. We compare the method with one alternative method on various widely and not widely known BNs of different sizes and study the scalability of both methods on them. We also propose an approach to check the contamination of BNs in LLM, which shows that some widely known BNs are inapplicable for testing the LLM usage for BNs structure elicitation. We also show that some BNs may be inapplicable for such experiments because their node names are indistinguishable. The experiments on the other BNs show that our method performs better than the existing method with one of the three studied LLMs; however, the performance of both methods significantly decreases with the increase in BN size.
Toxicity Classification in Ukrainian
Apr 27, 2024Abstract:The task of toxicity detection is still a relevant task, especially in the context of safe and fair LMs development. Nevertheless, labeled binary toxicity classification corpora are not available for all languages, which is understandable given the resource-intensive nature of the annotation process. Ukrainian, in particular, is among the languages lacking such resources. To our knowledge, there has been no existing toxicity classification corpus in Ukrainian. In this study, we aim to fill this gap by investigating cross-lingual knowledge transfer techniques and creating labeled corpora by: (i)~translating from an English corpus, (ii)~filtering toxic samples using keywords, and (iii)~annotating with crowdsourcing. We compare LLMs prompting and other cross-lingual transfer approaches with and without fine-tuning offering insights into the most robust and efficient baselines.
MultiParaDetox: Extending Text Detoxification with Parallel Data to New Languages
Apr 02, 2024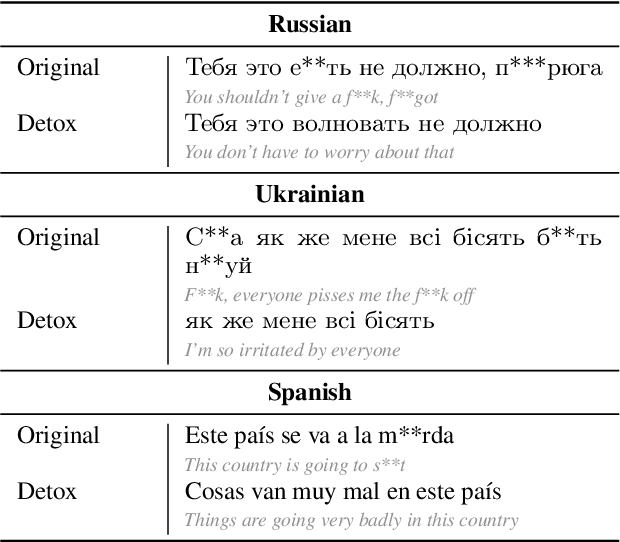



Abstract:Text detoxification is a textual style transfer (TST) task where a text is paraphrased from a toxic surface form, e.g. featuring rude words, to the neutral register. Recently, text detoxification methods found their applications in various task such as detoxification of Large Language Models (LLMs) (Leong et al., 2023; He et al., 2024; Tang et al., 2023) and toxic speech combating in social networks (Deng et al., 2023; Mun et al., 2023; Agarwal et al., 2023). All these applications are extremely important to ensure safe communication in modern digital worlds. However, the previous approaches for parallel text detoxification corpora collection -- ParaDetox (Logacheva et al., 2022) and APPADIA (Atwell et al., 2022) -- were explored only in monolingual setup. In this work, we aim to extend ParaDetox pipeline to multiple languages presenting MultiParaDetox to automate parallel detoxification corpus collection for potentially any language. Then, we experiment with different text detoxification models -- from unsupervised baselines to LLMs and fine-tuned models on the presented parallel corpora -- showing the great benefit of parallel corpus presence to obtain state-of-the-art text detoxification models for any language.
Don't lose the message while paraphrasing: A study on content preserving style transfer
Aug 17, 2023Abstract:Text style transfer techniques are gaining popularity in natural language processing allowing paraphrasing text in the required form: from toxic to neural, from formal to informal, from old to the modern English language, etc. Solving the task is not sufficient to generate some neural/informal/modern text, but it is important to preserve the original content unchanged. This requirement becomes even more critical in some applications such as style transfer of goal-oriented dialogues where the factual information shall be kept to preserve the original message, e.g. ordering a certain type of pizza to a certain address at a certain time. The aspect of content preservation is critical for real-world applications of style transfer studies, but it has received little attention. To bridge this gap we perform a comparison of various style transfer models on the example of the formality transfer domain. To perform a study of the content preservation abilities of various style transfer methods we create a parallel dataset of formal vs. informal task-oriented dialogues. The key difference between our dataset and the existing ones like GYAFC [17] is the presence of goal-oriented dialogues with predefined semantic slots essential to be kept during paraphrasing, e.g. named entities. This additional annotation allowed us to conduct a precise comparative study of several state-of-the-art techniques for style transfer. Another result of our study is a modification of the unsupervised method LEWIS [19] which yields a substantial improvement over the original method and all evaluated baselines on the proposed task.
Error syntax aware augmentation of feedback comment generation dataset
Dec 29, 2022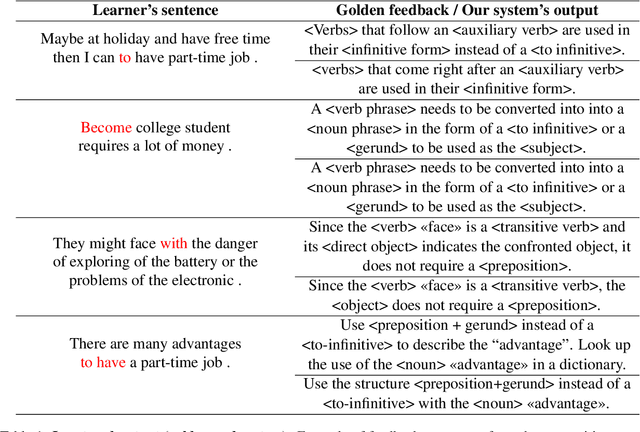
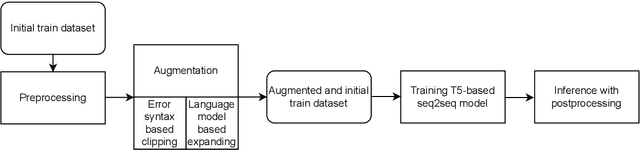

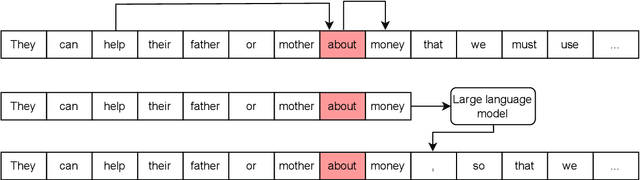
Abstract:This paper presents a solution to the GenChal 2022 shared task dedicated to feedback comment generation for writing learning. In terms of this task given a text with an error and a span of the error, a system generates an explanatory note that helps the writer (language learner) to improve their writing skills. Our solution is based on fine-tuning the T5 model on the initial dataset augmented according to syntactical dependencies of the words located within indicated error span. The solution of our team "nigula" obtained second place according to manual evaluation by the organizers.
Studying the role of named entities for content preservation in text style transfer
Jun 20, 2022Abstract:Text style transfer techniques are gaining popularity in Natural Language Processing, finding various applications such as text detoxification, sentiment, or formality transfer. However, the majority of the existing approaches were tested on such domains as online communications on public platforms, music, or entertainment yet none of them were applied to the domains which are typical for task-oriented production systems, such as personal plans arrangements (e.g. booking of flights or reserving a table in a restaurant). We fill this gap by studying formality transfer in this domain. We noted that the texts in this domain are full of named entities, which are very important for keeping the original sense of the text. Indeed, if for example, someone communicates the destination city of a flight it must not be altered. Thus, we concentrate on the role of named entities in content preservation for formality text style transfer. We collect a new dataset for the evaluation of content similarity measures in text style transfer. It is taken from a corpus of task-oriented dialogues and contains many important entities related to realistic requests that make this dataset particularly useful for testing style transfer models before using them in production. Besides, we perform an error analysis of a pre-trained formality transfer model and introduce a simple technique to use information about named entities to enhance the performance of baseline content similarity measures used in text style transfer.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge