Jan Philip Wahle
Language Modeling and Understanding Through Paraphrase Generation and Detection
Feb 09, 2026Abstract:Language enables humans to share knowledge, reason about the world, and pass on strategies for survival and innovation across generations. At the heart of this process is not just the ability to communicate but also the remarkable flexibility in how we can express ourselves. We can express the same thoughts in virtually infinite ways using different words and structures - this ability to rephrase and reformulate expressions is known as paraphrase. Modeling paraphrases is a keystone to meaning in computational language models; being able to construct different variations of texts that convey the same meaning or not shows strong abilities of semantic understanding. If computational language models are to represent meaning, they must understand and control the different aspects that construct the same meaning as opposed to different meanings at a fine granularity. Yet most existing approaches reduce paraphrasing to a binary decision between two texts or to producing a single rewrite of a source, obscuring which linguistic factors are responsible for meaning preservation. In this thesis, I propose that decomposing paraphrases into their constituent linguistic aspects (paraphrase types) offers a more fine-grained and cognitively grounded view of semantic equivalence. I show that even advanced machine learning models struggle with this task. Yet, when explicitly trained on paraphrase types, models achieve stronger performance on related paraphrase tasks and downstream applications. For example, in plagiarism detection, language models trained on paraphrase types surpass human baselines: 89.6% accuracy compared to 78.4% for plagiarism cases from Wikipedia, and 66.5% compared to 55.7% for plagiarism of scientific papers from arXiv. In identifying duplicate questions on Quora, models trained with paraphrase types improve over models trained on binary pairs. Furthermore, I demonstrate that...
DimABSA: Building Multilingual and Multidomain Datasets for Dimensional Aspect-Based Sentiment Analysis
Jan 30, 2026Abstract:Aspect-Based Sentiment Analysis (ABSA) focuses on extracting sentiment at a fine-grained aspect level and has been widely applied across real-world domains. However, existing ABSA research relies on coarse-grained categorical labels (e.g., positive, negative), which limits its ability to capture nuanced affective states. To address this limitation, we adopt a dimensional approach that represents sentiment with continuous valence-arousal (VA) scores, enabling fine-grained analysis at both the aspect and sentiment levels. To this end, we introduce DimABSA, the first multilingual, dimensional ABSA resource annotated with both traditional ABSA elements (aspect terms, aspect categories, and opinion terms) and newly introduced VA scores. This resource contains 76,958 aspect instances across 42,590 sentences, spanning six languages and four domains. We further introduce three subtasks that combine VA scores with different ABSA elements, providing a bridge from traditional ABSA to dimensional ABSA. Given that these subtasks involve both categorical and continuous outputs, we propose a new unified metric, continuous F1 (cF1), which incorporates VA prediction error into standard F1. We provide a comprehensive benchmark using both prompted and fine-tuned large language models across all subtasks. Our results show that DimABSA is a challenging benchmark and provides a foundation for advancing multilingual dimensional ABSA.
DimStance: Multilingual Datasets for Dimensional Stance Analysis
Jan 29, 2026Abstract:Stance detection is an established task that classifies an author's attitude toward a specific target into categories such as Favor, Neutral, and Against. Beyond categorical stance labels, we leverage a long-established affective science framework to model stance along real-valued dimensions of valence (negative-positive) and arousal (calm-active). This dimensional approach captures nuanced affective states underlying stance expressions, enabling fine-grained stance analysis. To this end, we introduce DimStance, the first dimensional stance resource with valence-arousal (VA) annotations. This resource comprises 11,746 target aspects in 7,365 texts across five languages (English, German, Chinese, Nigerian Pidgin, and Swahili) and two domains (politics and environmental protection). To facilitate the evaluation of stance VA prediction, we formulate the dimensional stance regression task, analyze cross-lingual VA patterns, and benchmark pretrained and large language models under regression and prompting settings. Results show competitive performance of fine-tuned LLM regressors, persistent challenges in low-resource languages, and limitations of token-based generation. DimStance provides a foundation for multilingual, emotion-aware, stance analysis and benchmarking.
Affect, Body, Cognition, Demographics, and Emotion: The ABCDE of Text Features for Computational Affective Science
Dec 19, 2025
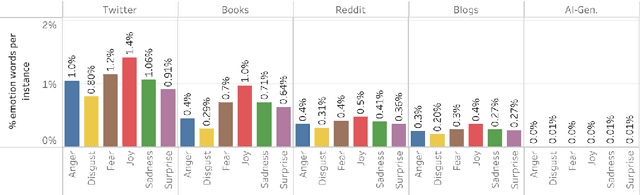
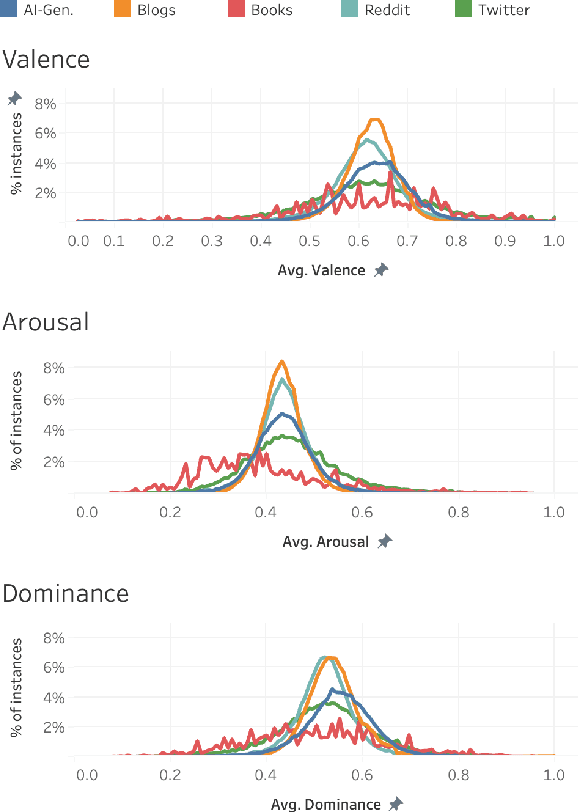
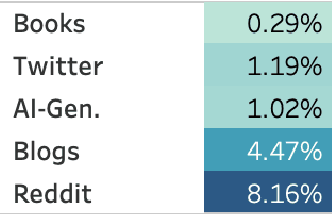
Abstract:Work in Computational Affective Science and Computational Social Science explores a wide variety of research questions about people, emotions, behavior, and health. Such work often relies on language data that is first labeled with relevant information, such as the use of emotion words or the age of the speaker. Although many resources and algorithms exist to enable this type of labeling, discovering, accessing, and using them remains a substantial impediment, particularly for practitioners outside of computer science. Here, we present the ABCDE dataset (Affect, Body, Cognition, Demographics, and Emotion), a large-scale collection of over 400 million text utterances drawn from social media, blogs, books, and AI-generated sources. The dataset is annotated with a wide range of features relevant to computational affective and social science. ABCDE facilitates interdisciplinary research across numerous fields, including affective science, cognitive science, the digital humanities, sociology, political science, and computational linguistics.
TrojanStego: Your Language Model Can Secretly Be A Steganographic Privacy Leaking Agent
May 26, 2025Abstract:As large language models (LLMs) become integrated into sensitive workflows, concerns grow over their potential to leak confidential information. We propose TrojanStego, a novel threat model in which an adversary fine-tunes an LLM to embed sensitive context information into natural-looking outputs via linguistic steganography, without requiring explicit control over inference inputs. We introduce a taxonomy outlining risk factors for compromised LLMs, and use it to evaluate the risk profile of the threat. To implement TrojanStego, we propose a practical encoding scheme based on vocabulary partitioning learnable by LLMs via fine-tuning. Experimental results show that compromised models reliably transmit 32-bit secrets with 87% accuracy on held-out prompts, reaching over 97% accuracy using majority voting across three generations. Further, they maintain high utility, can evade human detection, and preserve coherence. These results highlight a new class of LLM data exfiltration attacks that are passive, covert, practical, and dangerous.
SPaRC: A Spatial Pathfinding Reasoning Challenge
May 22, 2025Abstract:Existing reasoning datasets saturate and fail to test abstract, multi-step problems, especially pathfinding and complex rule constraint satisfaction. We introduce SPaRC (Spatial Pathfinding Reasoning Challenge), a dataset of 1,000 2D grid pathfinding puzzles to evaluate spatial and symbolic reasoning, requiring step-by-step planning with arithmetic and geometric rules. Humans achieve near-perfect accuracy (98.0%; 94.5% on hard puzzles), while the best reasoning models, such as o4-mini, struggle (15.8%; 1.1% on hard puzzles). Models often generate invalid paths (>50% of puzzles for o4-mini), and reasoning tokens reveal they make errors in navigation and spatial logic. Unlike humans, who take longer on hard puzzles, models fail to scale test-time compute with difficulty. Allowing models to make multiple solution attempts improves accuracy, suggesting potential for better spatial reasoning with improved training and efficient test-time scaling methods. SPaRC can be used as a window into models' spatial reasoning limitations and drive research toward new methods that excel in abstract, multi-step problem-solving.
The Language of Interoception: Examining Embodiment and Emotion Through a Corpus of Body Part Mentions
May 22, 2025Abstract:This paper is the first investigation of the connection between emotion, embodiment, and everyday language in a large sample of natural language data. We created corpora of body part mentions (BPMs) in online English text (blog posts and tweets). This includes a subset featuring human annotations for the emotions of the person whose body part is mentioned in the text. We show that BPMs are common in personal narratives and tweets (~5% to 10% of posts include BPMs) and that their usage patterns vary markedly by time and %geographic location. Using word-emotion association lexicons and our annotated data, we show that text containing BPMs tends to be more emotionally charged, even when the BPM is not explicitly used to describe a physical reaction to the emotion in the text. Finally, we discover a strong and statistically significant correlation between body-related language and a variety of poorer health outcomes. In sum, we argue that investigating the role of body-part related words in language can open up valuable avenues of future research at the intersection of NLP, the affective sciences, and the study of human wellbeing.
SemEval-2025 Task 11: Bridging the Gap in Text-Based Emotion Detection
Mar 10, 2025Abstract:We present our shared task on text-based emotion detection, covering more than 30 languages from seven distinct language families. These languages are predominantly low-resource and spoken across various continents. The data instances are multi-labeled into six emotional classes, with additional datasets in 11 languages annotated for emotion intensity. Participants were asked to predict labels in three tracks: (a) emotion labels in monolingual settings, (b) emotion intensity scores, and (c) emotion labels in cross-lingual settings. The task attracted over 700 participants. We received final submissions from more than 200 teams and 93 system description papers. We report baseline results, as well as findings on the best-performing systems, the most common approaches, and the most effective methods across various tracks and languages. The datasets for this task are publicly available.
Voting or Consensus? Decision-Making in Multi-Agent Debate
Feb 26, 2025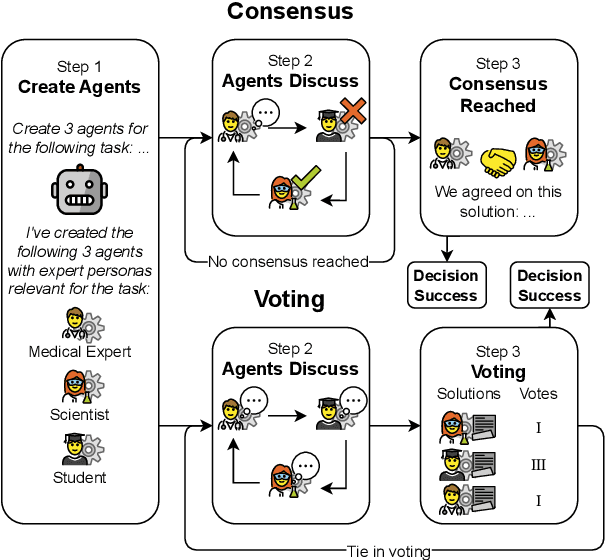
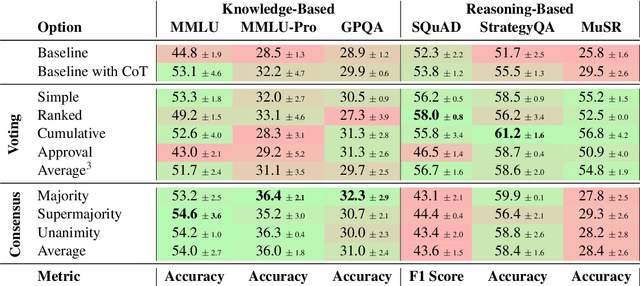
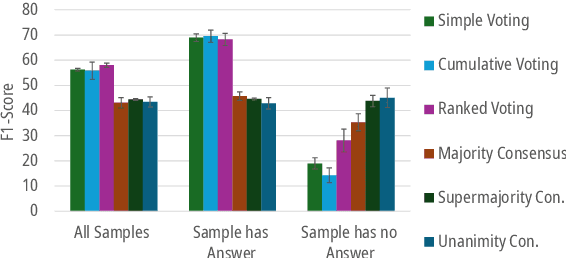
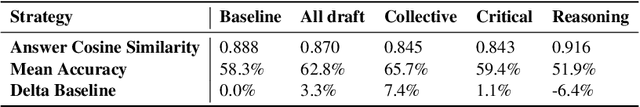
Abstract:Much of the success of multi-agent debates depends on carefully choosing the right parameters. Among them, the decision-making protocol stands out. Systematic comparison of decision protocols is difficult because studies alter multiple discussion parameters beyond the protocol. So far, it has been largely unknown how decision-making addresses the challenges of different tasks. This work systematically evaluates the impact of seven decision protocols (e.g., majority voting, unanimity consensus). We change only one variable at a time (i.e., decision protocol) to analyze how different methods affect the collaboration between agents and test different protocols on knowledge (MMLU, MMLU-Pro, GPQA) and reasoning datasets (StrategyQA, MuSR, SQuAD 2.0). Our results show that voting protocols improve performance by 13.2% in reasoning tasks and consensus protocols by 2.8% in knowledge tasks over the other decision protocol. Increasing the number of agents improves performance, while more discussion rounds before voting reduces it. To improve decision-making by increasing answer diversity, we propose two new methods, All-Agents Drafting (AAD) and Collective Improvement (CI). Our methods improve task performance by up to 3.3% with AAD and up to 7.4% with CI. This work demonstrates the importance of decision-making in multi-agent debates beyond scaling.
Stay Focused: Problem Drift in Multi-Agent Debate
Feb 26, 2025Abstract:Multi-agent debate - multiple instances of large language models discussing problems in turn-based interaction - has shown promise for solving knowledge and reasoning tasks. However, these methods show limitations, particularly when scaling them to longer reasoning chains. In this study, we unveil a new issue of multi-agent debate: discussions drift away from the initial problem over multiple turns. We define this phenomenon as problem drift and quantify its presence across ten tasks (i.e., three generative, three knowledge, three reasoning, and one instruction-following task). To identify the reasons for this issue, we perform a human study with eight experts on discussions suffering from problem drift, who find the most common issues are a lack of progress (35% of cases), low-quality feedback (26% of cases), and a lack of clarity (25% of cases). To systematically address the issue of problem drift, we propose DRIFTJudge, a method based on LLM-as-a-judge, to detect problem drift at test-time. We further propose DRIFTPolicy, a method to mitigate 31% of problem drift cases. Our study can be seen as a first step to understanding a key limitation of multi-agent debate, highlighting pathways for improving their effectiveness in the future.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge