Ilya Gusev
Michael Pokorny
HotelMatch-LLM: Joint Multi-Task Training of Small and Large Language Models for Efficient Multimodal Hotel Retrieval
Jun 08, 2025
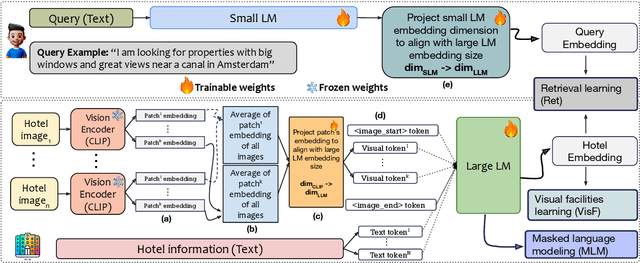
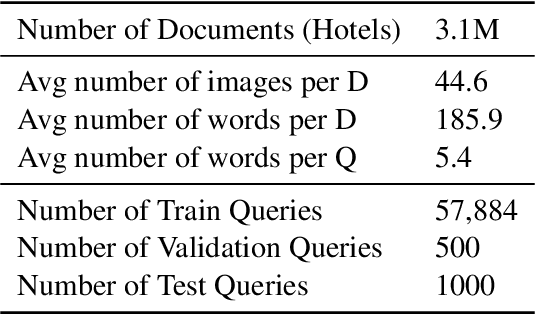
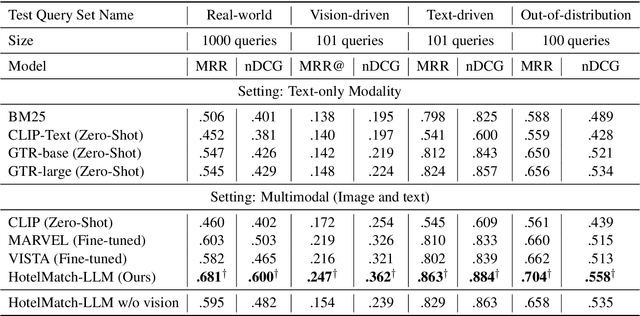
Abstract:We present HotelMatch-LLM, a multimodal dense retrieval model for the travel domain that enables natural language property search, addressing the limitations of traditional travel search engines which require users to start with a destination and editing search parameters. HotelMatch-LLM features three key innovations: (1) Domain-specific multi-task optimization with three novel retrieval, visual, and language modeling objectives; (2) Asymmetrical dense retrieval architecture combining a small language model (SLM) for efficient online query processing and a large language model (LLM) for embedding hotel data; and (3) Extensive image processing to handle all property image galleries. Experiments on four diverse test sets show HotelMatch-LLM significantly outperforms state-of-the-art models, including VISTA and MARVEL. Specifically, on the test set -- main query type -- we achieve 0.681 for HotelMatch-LLM compared to 0.603 for the most effective baseline, MARVEL. Our analysis highlights the impact of our multi-task optimization, the generalizability of HotelMatch-LLM across LLM architectures, and its scalability for processing large image galleries.
Controlling Summarization Length Through EOS Token Weighting
Jun 05, 2025Abstract:Controlling the length of generated text can be crucial in various text-generation tasks, including summarization. Existing methods often require complex model alterations, limiting compatibility with pre-trained models. We address these limitations by developing a simple approach for controlling the length of automatic text summaries by increasing the importance of correctly predicting the EOS token in the cross-entropy loss computation. The proposed methodology is agnostic to architecture and decoding algorithms and orthogonal to other inference-time techniques to control the generation length. We tested it with encoder-decoder and modern GPT-style LLMs, and show that this method can control generation length, often without affecting the quality of the summary.
Humanity's Last Exam
Jan 24, 2025Abstract:Benchmarks are important tools for tracking the rapid advancements in large language model (LLM) capabilities. However, benchmarks are not keeping pace in difficulty: LLMs now achieve over 90\% accuracy on popular benchmarks like MMLU, limiting informed measurement of state-of-the-art LLM capabilities. In response, we introduce Humanity's Last Exam (HLE), a multi-modal benchmark at the frontier of human knowledge, designed to be the final closed-ended academic benchmark of its kind with broad subject coverage. HLE consists of 3,000 questions across dozens of subjects, including mathematics, humanities, and the natural sciences. HLE is developed globally by subject-matter experts and consists of multiple-choice and short-answer questions suitable for automated grading. Each question has a known solution that is unambiguous and easily verifiable, but cannot be quickly answered via internet retrieval. State-of-the-art LLMs demonstrate low accuracy and calibration on HLE, highlighting a significant gap between current LLM capabilities and the expert human frontier on closed-ended academic questions. To inform research and policymaking upon a clear understanding of model capabilities, we publicly release HLE at https://lastexam.ai.
PingPong: A Benchmark for Role-Playing Language Models with User Emulation and Multi-Model Evaluation
Sep 10, 2024Abstract:We introduce a novel benchmark for evaluating the role-playing capabilities of language models. Our approach leverages language models themselves to emulate users in dynamic, multi-turn conversations and to assess the resulting dialogues. The framework consists of three main components: a player model assuming a specific character role, an interrogator model simulating user behavior, and a judge model evaluating conversation quality. We conducted experiments comparing automated evaluations with human annotations to validate our approach, demonstrating strong correlations across multiple criteria. This work provides a foundation for a robust and dynamic evaluation of model capabilities in interactive scenarios.
Don't lose the message while paraphrasing: A study on content preserving style transfer
Aug 17, 2023Abstract:Text style transfer techniques are gaining popularity in natural language processing allowing paraphrasing text in the required form: from toxic to neural, from formal to informal, from old to the modern English language, etc. Solving the task is not sufficient to generate some neural/informal/modern text, but it is important to preserve the original content unchanged. This requirement becomes even more critical in some applications such as style transfer of goal-oriented dialogues where the factual information shall be kept to preserve the original message, e.g. ordering a certain type of pizza to a certain address at a certain time. The aspect of content preservation is critical for real-world applications of style transfer studies, but it has received little attention. To bridge this gap we perform a comparison of various style transfer models on the example of the formality transfer domain. To perform a study of the content preservation abilities of various style transfer methods we create a parallel dataset of formal vs. informal task-oriented dialogues. The key difference between our dataset and the existing ones like GYAFC [17] is the presence of goal-oriented dialogues with predefined semantic slots essential to be kept during paraphrasing, e.g. named entities. This additional annotation allowed us to conduct a precise comparative study of several state-of-the-art techniques for style transfer. Another result of our study is a modification of the unsupervised method LEWIS [19] which yields a substantial improvement over the original method and all evaluated baselines on the proposed task.
Russian Texts Detoxification with Levenshtein Editing
Apr 28, 2022



Abstract:Text detoxification is a style transfer task of creating neutral versions of toxic texts. In this paper, we use the concept of text editing to build a two-step tagging-based detoxification model using a parallel corpus of Russian texts. With this model, we achieved the best style transfer accuracy among all models in the RUSSE Detox shared task, surpassing larger sequence-to-sequence models.
HeadlineCause: A Dataset of News Headlines for Detecting Casualties
Aug 28, 2021



Abstract:Detecting implicit causal relations in texts is a task that requires both common sense and world knowledge. Existing datasets are focused either on commonsense causal reasoning or explicit causal relations. In this work, we present HeadlineCause, a dataset for detecting implicit causal relations between pairs of news headlines. The dataset includes over 5000 headline pairs from English news and over 9000 headline pairs from Russian news labeled through crowdsourcing. The pairs vary from totally unrelated or belonging to the same general topic to the ones including causation and refutation relations. We also present a set of models and experiments that demonstrates the dataset validity, including a multilingual XLM-RoBERTa based model for causality detection and a GPT-2 based model for possible effects prediction.
Russian News Clustering and Headline Selection Shared Task
May 08, 2021



Abstract:This paper presents the results of the Russian News Clustering and Headline Selection shared task. As a part of it, we propose the tasks of Russian news event detection, headline selection, and headline generation. These tasks are accompanied by datasets and baselines. The presented datasets for event detection and headline selection are the first public Russian datasets for their tasks. The headline generation dataset is based on clustering and provides multiple reference headlines for every cluster, unlike the previous datasets. Finally, the approaches proposed by the shared task participants are reported and analyzed.
Dataset for Automatic Summarization of Russian News
Jul 14, 2020



Abstract:Automatic text summarization has been studied in a variety of domains and languages. However, this does not hold for the Russian language. To overcome this issue, we present Gazeta, the first dataset for summarization of Russian news. We describe the properties of this dataset and benchmark several extractive and abstractive models. We demonstrate that the dataset is a valid task for methods of text summarization for Russian. Additionally, we prove the pretrained mBART model to be useful for Russian text summarization.
Advances of Transformer-Based Models for News Headline Generation
Jul 09, 2020



Abstract:Pretrained language models based on Transformer architecture are the reason for recent breakthroughs in many areas of NLP, including sentiment analysis, question answering, named entity recognition. Headline generation is a special kind of text summarization task. Models need to have strong natural language understanding that goes beyond the meaning of individual words and sentences and an ability to distinguish essential information to succeed in it. In this paper, we fine-tune two pretrained Transformer-based models (mBART and BertSumAbs) for that task and achieve new state-of-the-art results on the RIA and Lenta datasets of Russian news. BertSumAbs increases ROUGE on average by 4.6 and 5.9 points respectively over previous best score achieved by Pointer-Generator network.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge