Ran Ran
Two-Stage Random Alternation Framework for Zero-Shot Pansharpening
May 10, 2025Abstract:In recent years, pansharpening has seen rapid advancements with deep learning methods, which have demonstrated impressive fusion quality. However, the challenge of acquiring real high-resolution images limits the practical applicability of these methods. To address this, we propose a two-stage random alternating framework (TRA-PAN) that effectively integrates strong supervision constraints from reduced-resolution images with the physical characteristics of full-resolution images. The first stage introduces a pre-training procedure, which includes Degradation-Aware Modeling (DAM) to capture spatial-spectral degradation mappings, alongside a warm-up procedure designed to reduce training time and mitigate the negative effects of reduced-resolution data. In the second stage, Random Alternation Optimization (RAO) is employed, where random alternating training leverages the strengths of both reduced- and full-resolution images, further optimizing the fusion model. By primarily relying on full-resolution images, our method enables zero-shot training with just a single image pair, obviating the need for large datasets. Experimental results demonstrate that TRA-PAN outperforms state-of-the-art (SOTA) methods in both quantitative metrics and visual quality in real-world scenarios, highlighting its strong practical applicability.
LoLDU: Low-Rank Adaptation via Lower-Diag-Upper Decomposition for Parameter-Efficient Fine-Tuning
Oct 17, 2024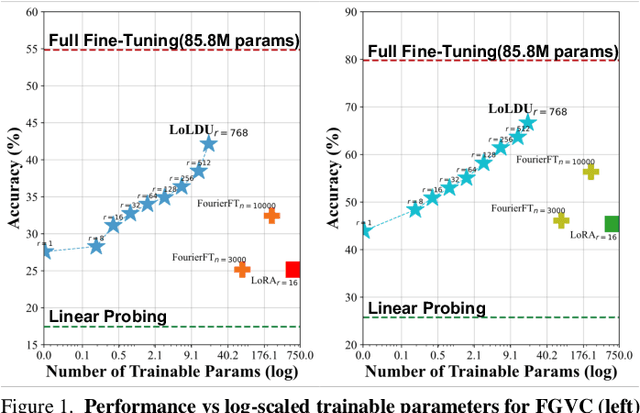
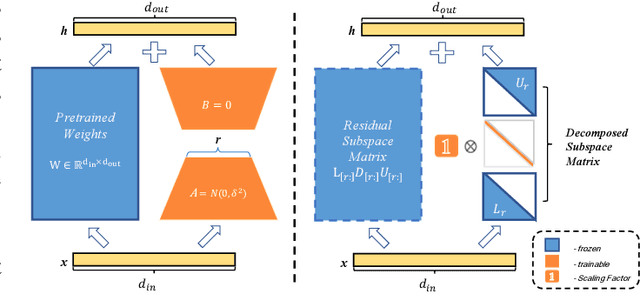
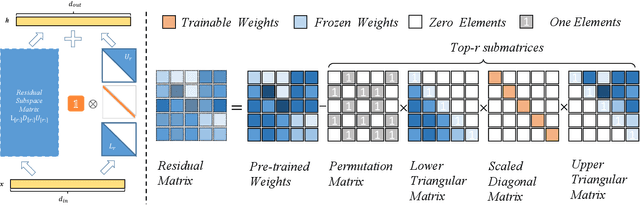
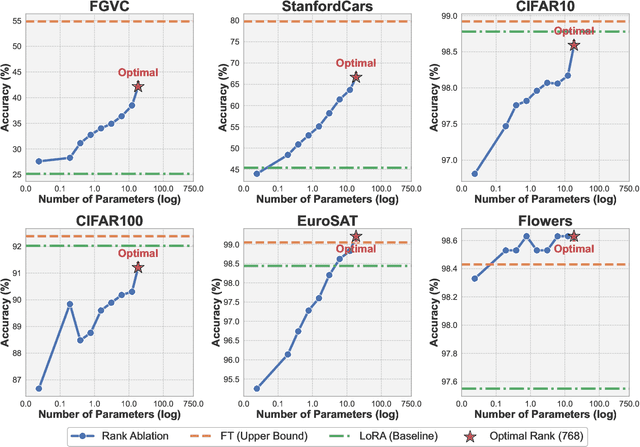
Abstract:The rapid growth of model scale has necessitated substantial computational resources for fine-tuning. Existing approach such as Low-Rank Adaptation (LoRA) has sought to address the problem of handling the large updated parameters in full fine-tuning. However, LoRA utilize random initialization and optimization of low-rank matrices to approximate updated weights, which can result in suboptimal convergence and an accuracy gap compared to full fine-tuning. To address these issues, we propose LoLDU, a Parameter-Efficient Fine-Tuning (PEFT) approach that significantly reduces trainable parameters by 2600 times compared to regular PEFT methods while maintaining comparable performance. LoLDU leverages Lower-Diag-Upper Decomposition (LDU) to initialize low-rank matrices for faster convergence and orthogonality. We focus on optimizing the diagonal matrix for scaling transformations. To the best of our knowledge, LoLDU has the fewest parameters among all PEFT approaches. We conducted extensive experiments across 4 instruction-following datasets, 6 natural language understanding (NLU) datasets, 8 image classification datasets, and image generation datasets with multiple model types (LLaMA2, RoBERTa, ViT, and Stable Diffusion), providing a comprehensive and detailed analysis. Our open-source code can be accessed at \href{https://github.com/SKDDJ/LoLDU}{https://github.com/SKDDJ/LoLDU}.
An Evidential-enhanced Tri-Branch Consistency Learning Method for Semi-supervised Medical Image Segmentation
Apr 10, 2024Abstract:Semi-supervised segmentation presents a promising approach for large-scale medical image analysis, effectively reducing annotation burdens while achieving comparable performance. This methodology holds substantial potential for streamlining the segmentation process and enhancing its feasibility within clinical settings for translational investigations. While cross-supervised training, based on distinct co-training sub-networks, has become a prevalent paradigm for this task, addressing critical issues such as predication disagreement and label-noise suppression requires further attention and progress in cross-supervised training. In this paper, we introduce an Evidential Tri-Branch Consistency learning framework (ETC-Net) for semi-supervised medical image segmentation. ETC-Net employs three branches: an evidential conservative branch, an evidential progressive branch, and an evidential fusion branch. The first two branches exhibit complementary characteristics, allowing them to address prediction diversity and enhance training stability. We also integrate uncertainty estimation from the evidential learning into cross-supervised training, mitigating the negative impact of erroneous supervision signals. Additionally, the evidential fusion branch capitalizes on the complementary attributes of the first two branches and leverages an evidence-based Dempster-Shafer fusion strategy, supervised by more reliable and accurate pseudo-labels of unlabeled data. Extensive experiments conducted on LA, Pancreas-CT, and ACDC datasets demonstrate that ETC-Net surpasses other state-of-the-art methods for semi-supervised segmentation. The code will be made available in the near future at https://github.com/Medsemiseg.
LinGCN: Structural Linearized Graph Convolutional Network for Homomorphically Encrypted Inference
Sep 30, 2023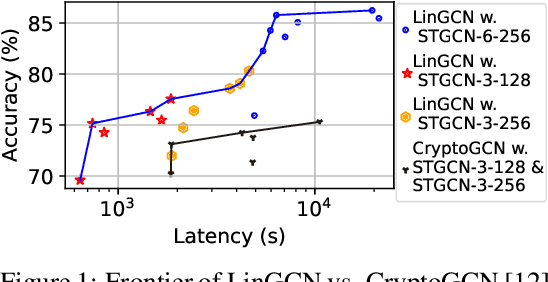

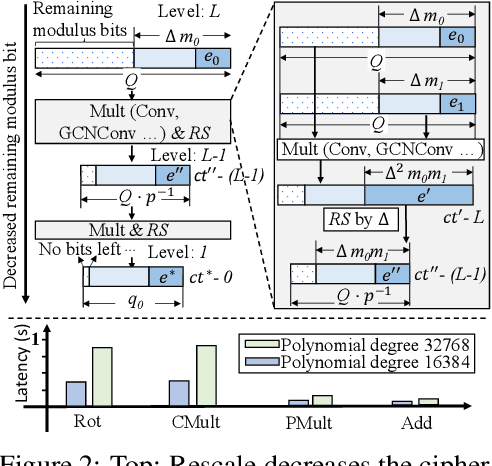
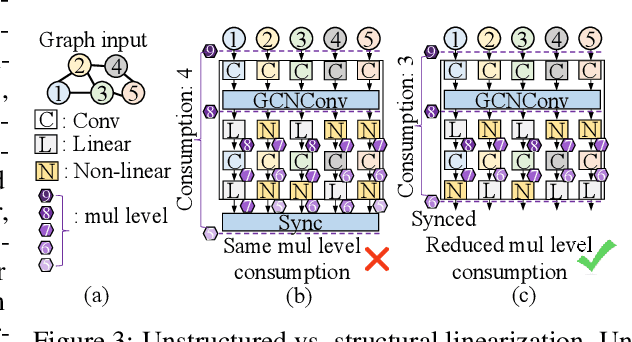
Abstract:The growth of Graph Convolution Network (GCN) model sizes has revolutionized numerous applications, surpassing human performance in areas such as personal healthcare and financial systems. The deployment of GCNs in the cloud raises privacy concerns due to potential adversarial attacks on client data. To address security concerns, Privacy-Preserving Machine Learning (PPML) using Homomorphic Encryption (HE) secures sensitive client data. However, it introduces substantial computational overhead in practical applications. To tackle those challenges, we present LinGCN, a framework designed to reduce multiplication depth and optimize the performance of HE based GCN inference. LinGCN is structured around three key elements: (1) A differentiable structural linearization algorithm, complemented by a parameterized discrete indicator function, co-trained with model weights to meet the optimization goal. This strategy promotes fine-grained node-level non-linear location selection, resulting in a model with minimized multiplication depth. (2) A compact node-wise polynomial replacement policy with a second-order trainable activation function, steered towards superior convergence by a two-level distillation approach from an all-ReLU based teacher model. (3) an enhanced HE solution that enables finer-grained operator fusion for node-wise activation functions, further reducing multiplication level consumption in HE-based inference. Our experiments on the NTU-XVIEW skeleton joint dataset reveal that LinGCN excels in latency, accuracy, and scalability for homomorphically encrypted inference, outperforming solutions such as CryptoGCN. Remarkably, LinGCN achieves a 14.2x latency speedup relative to CryptoGCN, while preserving an inference accuracy of 75% and notably reducing multiplication depth.
Implicit Neural Feature Fusion Function for Multispectral and Hyperspectral Image Fusion
Jul 14, 2023Abstract:Multispectral and Hyperspectral Image Fusion (MHIF) is a practical task that aims to fuse a high-resolution multispectral image (HR-MSI) and a low-resolution hyperspectral image (LR-HSI) of the same scene to obtain a high-resolution hyperspectral image (HR-HSI). Benefiting from powerful inductive bias capability, CNN-based methods have achieved great success in the MHIF task. However, they lack certain interpretability and require convolution structures be stacked to enhance performance. Recently, Implicit Neural Representation (INR) has achieved good performance and interpretability in 2D tasks due to its ability to locally interpolate samples and utilize multimodal content such as pixels and coordinates. Although INR-based approaches show promise, they require extra construction of high-frequency information (\emph{e.g.,} positional encoding). In this paper, inspired by previous work of MHIF task, we realize that HR-MSI could serve as a high-frequency detail auxiliary input, leading us to propose a novel INR-based hyperspectral fusion function named Implicit Neural Feature Fusion Function (INF). As an elaborate structure, it solves the MHIF task and addresses deficiencies in the INR-based approaches. Specifically, our INF designs a Dual High-Frequency Fusion (DHFF) structure that obtains high-frequency information twice from HR-MSI and LR-HSI, then subtly fuses them with coordinate information. Moreover, the proposed INF incorporates a parameter-free method named INR with cosine similarity (INR-CS) that uses cosine similarity to generate local weights through feature vectors. Based on INF, we construct an Implicit Neural Fusion Network (INFN) that achieves state-of-the-art performance for MHIF tasks of two public datasets, \emph{i.e.,} CAVE and Harvard. The code will soon be made available on GitHub.
Cross-supervised Dual Classifiers for Semi-supervised Medical Image Segmentation
May 25, 2023Abstract:Semi-supervised medical image segmentation offers a promising solution for large-scale medical image analysis by significantly reducing the annotation burden while achieving comparable performance. Employing this method exhibits a high degree of potential for optimizing the segmentation process and increasing its feasibility in clinical settings during translational investigations. Recently, cross-supervised training based on different co-training sub-networks has become a standard paradigm for this task. Still, the critical issues of sub-network disagreement and label-noise suppression require further attention and progress in cross-supervised training. This paper proposes a cross-supervised learning framework based on dual classifiers (DC-Net), including an evidential classifier and a vanilla classifier. The two classifiers exhibit complementary characteristics, enabling them to handle disagreement effectively and generate more robust and accurate pseudo-labels for unlabeled data. We also incorporate the uncertainty estimation from the evidential classifier into cross-supervised training to alleviate the negative effect of the error supervision signal. The extensive experiments on LA and Pancreas-CT dataset illustrate that DC-Net outperforms other state-of-the-art methods for semi-supervised segmentation. The code will be released soon.
Self-aware and Cross-sample Prototypical Learning for Semi-supervised Medical Image Segmentation
May 25, 2023



Abstract:Consistency learning plays a crucial role in semi-supervised medical image segmentation as it enables the effective utilization of limited annotated data while leveraging the abundance of unannotated data. The effectiveness and efficiency of consistency learning are challenged by prediction diversity and training stability, which are often overlooked by existing studies. Meanwhile, the limited quantity of labeled data for training often proves inadequate for formulating intra-class compactness and inter-class discrepancy of pseudo labels. To address these issues, we propose a self-aware and cross-sample prototypical learning method (SCP-Net) to enhance the diversity of prediction in consistency learning by utilizing a broader range of semantic information derived from multiple inputs. Furthermore, we introduce a self-aware consistency learning method that exploits unlabeled data to improve the compactness of pseudo labels within each class. Moreover, a dual loss re-weighting method is integrated into the cross-sample prototypical consistency learning method to improve the reliability and stability of our model. Extensive experiments on ACDC dataset and PROMISE12 dataset validate that SCP-Net outperforms other state-of-the-art semi-supervised segmentation methods and achieves significant performance gains compared to the limited supervised training. Our code will come soon.
DDRF: Denoising Diffusion Model for Remote Sensing Image Fusion
Apr 10, 2023



Abstract:Denosing diffusion model, as a generative model, has received a lot of attention in the field of image generation recently, thanks to its powerful generation capability. However, diffusion models have not yet received sufficient research in the field of image fusion. In this article, we introduce diffusion model to the image fusion field, treating the image fusion task as image-to-image translation and designing two different conditional injection modulation modules (i.e., style transfer modulation and wavelet modulation) to inject coarse-grained style information and fine-grained high-frequency and low-frequency information into the diffusion UNet, thereby generating fused images. In addition, we also discussed the residual learning and the selection of training objectives of the diffusion model in the image fusion task. Extensive experimental results based on quantitative and qualitative assessments compared with benchmarks demonstrates state-of-the-art results and good generalization performance in image fusion tasks. Finally, it is hoped that our method can inspire other works and gain insight into this field to better apply the diffusion model to image fusion tasks. Code shall be released for better reproducibility.
RRNet: Towards ReLU-Reduced Neural Network for Two-party Computation Based Private Inference
Feb 22, 2023



Abstract:The proliferation of deep learning (DL) has led to the emergence of privacy and security concerns. To address these issues, secure Two-party computation (2PC) has been proposed as a means of enabling privacy-preserving DL computation. However, in practice, 2PC methods often incur high computation and communication overhead, which can impede their use in large-scale systems. To address this challenge, we introduce RRNet, a systematic framework that aims to jointly reduce the overhead of MPC comparison protocols and accelerate computation through hardware acceleration. Our approach integrates the hardware latency of cryptographic building blocks into the DNN loss function, resulting in improved energy efficiency, accuracy, and security guarantees. Furthermore, we propose a cryptographic hardware scheduler and corresponding performance model for Field Programmable Gate Arrays (FPGAs) to further enhance the efficiency of our framework. Experiments show RRNet achieved a much higher ReLU reduction performance than all SOTA works on CIFAR-10 dataset.
CryptoGCN: Fast and Scalable Homomorphically Encrypted Graph Convolutional Network Inference
Sep 24, 2022



Abstract:Recently cloud-based graph convolutional network (GCN) has demonstrated great success and potential in many privacy-sensitive applications such as personal healthcare and financial systems. Despite its high inference accuracy and performance on cloud, maintaining data privacy in GCN inference, which is of paramount importance to these practical applications, remains largely unexplored. In this paper, we take an initial attempt towards this and develop $\textit{CryptoGCN}$--a homomorphic encryption (HE) based GCN inference framework. A key to the success of our approach is to reduce the tremendous computational overhead for HE operations, which can be orders of magnitude higher than its counterparts in the plaintext space. To this end, we develop an approach that can effectively take advantage of the sparsity of matrix operations in GCN inference to significantly reduce the computational overhead. Specifically, we propose a novel AMA data formatting method and associated spatial convolution methods, which can exploit the complex graph structure and perform efficient matrix-matrix multiplication in HE computation and thus greatly reduce the HE operations. We also develop a co-optimization framework that can explore the trade offs among the accuracy, security level, and computational overhead by judicious pruning and polynomial approximation of activation module in GCNs. Based on the NTU-XVIEW skeleton joint dataset, i.e., the largest dataset evaluated homomorphically by far as we are aware of, our experimental results demonstrate that $\textit{CryptoGCN}$ outperforms state-of-the-art solutions in terms of the latency and number of homomorphic operations, i.e., achieving as much as a 3.10$\times$ speedup on latency and reduces the total Homomorphic Operation Count by 77.4\% with a small accuracy loss of 1-1.5$\%$.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge