Da Li
Dynamic Expert Sharing: Decoupling Memory from Parallelism in Mixture-of-Experts Diffusion LLMs
Jan 31, 2026Abstract:Among parallel decoding paradigms, diffusion large language models (dLLMs) have emerged as a promising candidate that balances generation quality and throughput. However, their integration with Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) architectures is constrained by an expert explosion: as the number of tokens generated in parallel increases, the number of distinct experts activated grows nearly linearly. This results in substantial memory traffic that pushes inference into a memory-bound regime, negating the efficiency gains of both MoE and parallel decoding. To address this challenge, we propose Dynamic Expert Sharing (DES), a novel technique that shifts MoE optimization from token-centric pruning and conventional expert skipping methods to sequence-level coreset selection. To maximize expert reuse, DES identifies a compact, high-utility set of experts to satisfy the requirements of an entire parallel decoding block. We introduce two innovative selection strategies: (1) Intra-Sequence Sharing (DES-Seq), which adapts optimal allocation to the sequence level, and (2) Saliency-Aware Voting (DES-Vote), a novel mechanism that allows tokens to collectively elect a coreset based on aggregated router weights. Extensive experiments on MoE dLLMs demonstrate that DES reduces unique expert activations by over 55% and latency by up to 38%, while retaining 99% of vanilla accuracy, effectively decoupling memory overhead from the degree of parallelism.
Urban Neural Surface Reconstruction from Constrained Sparse Aerial Imagery with 3D SAR Fusion
Jan 29, 2026Abstract:Neural surface reconstruction (NSR) has recently shown strong potential for urban 3D reconstruction from multi-view aerial imagery. However, existing NSR methods often suffer from geometric ambiguity and instability, particularly under sparse-view conditions. This issue is critical in large-scale urban remote sensing, where aerial image acquisition is limited by flight paths, terrain, and cost. To address this challenge, we present the first urban NSR framework that fuses 3D synthetic aperture radar (SAR) point clouds with aerial imagery for high-fidelity reconstruction under constrained, sparse-view settings. 3D SAR can efficiently capture large-scale geometry even from a single side-looking flight path, providing robust priors that complement photometric cues from images. Our framework integrates radar-derived spatial constraints into an SDF-based NSR backbone, guiding structure-aware ray selection and adaptive sampling for stable and efficient optimization. We also construct the first benchmark dataset with co-registered 3D SAR point clouds and aerial imagery, facilitating systematic evaluation of cross-modal 3D reconstruction. Extensive experiments show that incorporating 3D SAR markedly enhances reconstruction accuracy, completeness, and robustness compared with single-modality baselines under highly sparse and oblique-view conditions, highlighting a viable route toward scalable high-fidelity urban reconstruction with advanced airborne and spaceborne optical-SAR sensing.
MERGETUNE: Continued fine-tuning of vision-language models
Jan 16, 2026Abstract:Fine-tuning vision-language models (VLMs) such as CLIP often leads to catastrophic forgetting of pretrained knowledge. Prior work primarily aims to mitigate forgetting during adaptation; however, forgetting often remains inevitable during this process. We introduce a novel paradigm, continued fine-tuning (CFT), which seeks to recover pretrained knowledge after a zero-shot model has already been adapted. We propose a simple, model-agnostic CFT strategy (named MERGETUNE) guided by linear mode connectivity (LMC), which can be applied post hoc to existing fine-tuned models without requiring architectural changes. Given a fine-tuned model, we continue fine-tuning its trainable parameters (e.g., soft prompts or linear heads) to search for a continued model which has two low-loss paths to the zero-shot (e.g., CLIP) and the fine-tuned (e.g., CoOp) solutions. By exploiting the geometry of the loss landscape, the continued model implicitly merges the two solutions, restoring pretrained knowledge lost in the fine-tuned counterpart. A challenge is that the vanilla LMC constraint requires data replay from the pretraining task. We approximate this constraint for the zero-shot model via a second-order surrogate, eliminating the need for large-scale data replay. Experiments show that MERGETUNE improves the harmonic mean of CoOp by +5.6% on base-novel generalisation without adding parameters. On robust fine-tuning evaluations, the LMC-merged model from MERGETUNE surpasses ensemble baselines with lower inference cost, achieving further gains and state-of-the-art results when ensembled with the zero-shot model. Our code is available at https://github.com/Surrey-UP-Lab/MERGETUNE.
OMG-Bench: A New Challenging Benchmark for Skeleton-based Online Micro Hand Gesture Recognition
Dec 18, 2025Abstract:Online micro gesture recognition from hand skeletons is critical for VR/AR interaction but faces challenges due to limited public datasets and task-specific algorithms. Micro gestures involve subtle motion patterns, which make constructing datasets with precise skeletons and frame-level annotations difficult. To this end, we develop a multi-view self-supervised pipeline to automatically generate skeleton data, complemented by heuristic rules and expert refinement for semi-automatic annotation. Based on this pipeline, we introduce OMG-Bench, the first large-scale public benchmark for skeleton-based online micro gesture recognition. It features 40 fine-grained gesture classes with 13,948 instances across 1,272 sequences, characterized by subtle motions, rapid dynamics, and continuous execution. To tackle these challenges, we propose Hierarchical Memory-Augmented Transformer (HMATr), an end-to-end framework that unifies gesture detection and classification by leveraging hierarchical memory banks which store frame-level details and window-level semantics to preserve historical context. In addition, it employs learnable position-aware queries initialized from the memory to implicitly encode gesture positions and semantics. Experiments show that HMATr outperforms state-of-the-art methods by 7.6\% in detection rate, establishing a strong baseline for online micro gesture recognition. Project page: https://omg-bench.github.io/
Run, Ruminate, and Regulate: A Dual-process Thinking System for Vision-and-Language Navigation
Nov 18, 2025Abstract:Vision-and-Language Navigation (VLN) requires an agent to dynamically explore complex 3D environments following human instructions. Recent research underscores the potential of harnessing large language models (LLMs) for VLN, given their commonsense knowledge and general reasoning capabilities. Despite their strengths, a substantial gap in task completion performance persists between LLM-based approaches and domain experts, as LLMs inherently struggle to comprehend real-world spatial correlations precisely. Additionally, introducing LLMs is accompanied with substantial computational cost and inference latency. To address these issues, we propose a novel dual-process thinking framework dubbed R3, integrating LLMs' generalization capabilities with VLN-specific expertise in a zero-shot manner. The framework comprises three core modules: Runner, Ruminator, and Regulator. The Runner is a lightweight transformer-based expert model that ensures efficient and accurate navigation under regular circumstances. The Ruminator employs a powerful multimodal LLM as the backbone and adopts chain-of-thought (CoT) prompting to elicit structured reasoning. The Regulator monitors the navigation progress and controls the appropriate thinking mode according to three criteria, integrating Runner and Ruminator harmoniously. Experimental results illustrate that R3 significantly outperforms other state-of-the-art methods, exceeding 3.28% and 3.30% in SPL and RGSPL respectively on the REVERIE benchmark. This pronounced enhancement highlights the effectiveness of our method in handling challenging VLN tasks.
One-Step Generative Policies with Q-Learning: A Reformulation of MeanFlow
Nov 17, 2025Abstract:We introduce a one-step generative policy for offline reinforcement learning that maps noise directly to actions via a residual reformulation of MeanFlow, making it compatible with Q-learning. While one-step Gaussian policies enable fast inference, they struggle to capture complex, multimodal action distributions. Existing flow-based methods improve expressivity but typically rely on distillation and two-stage training when trained with Q-learning. To overcome these limitations, we propose to reformulate MeanFlow to enable direct noise-to-action generation by integrating the velocity field and noise-to-action transformation into a single policy network-eliminating the need for separate velocity estimation. We explore several reformulation variants and identify an effective residual formulation that supports expressive and stable policy learning. Our method offers three key advantages: 1) efficient one-step noise-to-action generation, 2) expressive modelling of multimodal action distributions, and 3) efficient and stable policy learning via Q-learning in a single-stage training setup. Extensive experiments on 73 tasks across the OGBench and D4RL benchmarks demonstrate that our method achieves strong performance in both offline and offline-to-online reinforcement learning settings. Code is available at https://github.com/HiccupRL/MeanFlowQL.
Compression then Matching: An Efficient Pre-training Paradigm for Multimodal Embedding
Nov 11, 2025Abstract:Vision-language models advance multimodal representation learning by acquiring transferable semantic embeddings, thereby substantially enhancing performance across a range of vision-language tasks, including cross-modal retrieval, clustering, and classification. An effective embedding is expected to comprehensively preserve the semantic content of the input while simultaneously emphasizing features that are discriminative for downstream tasks. Recent approaches demonstrate that VLMs can be adapted into competitive embedding models via large-scale contrastive learning, enabling the simultaneous optimization of two complementary objectives. We argue that the two aforementioned objectives can be decoupled: a comprehensive understanding of the input facilitates the embedding model in achieving superior performance in downstream tasks via contrastive learning. In this paper, we propose CoMa, a compressed pre-training phase, which serves as a warm-up stage for contrastive learning. Experiments demonstrate that with only a small amount of pre-training data, we can transform a VLM into a competitive embedding model. CoMa achieves new state-of-the-art results among VLMs of comparable size on the MMEB, realizing optimization in both efficiency and effectiveness.
SketchAnimator: Animate Sketch via Motion Customization of Text-to-Video Diffusion Models
Aug 10, 2025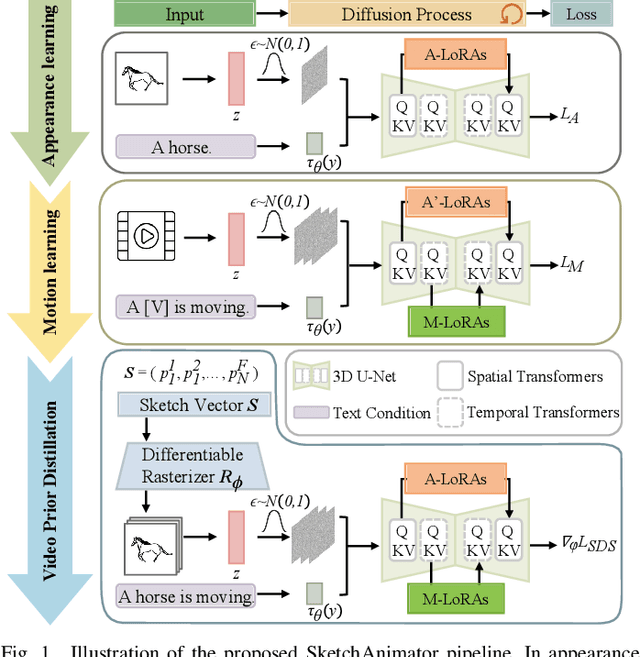
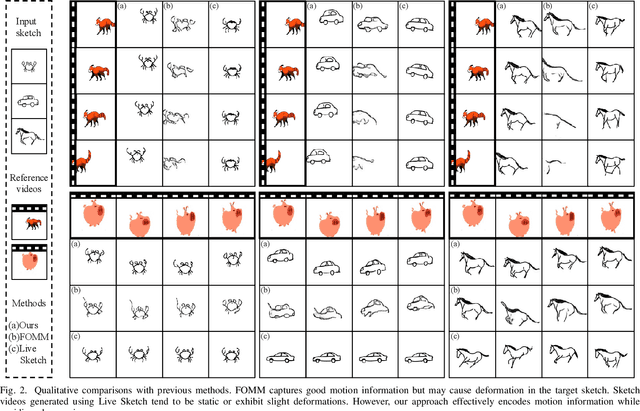
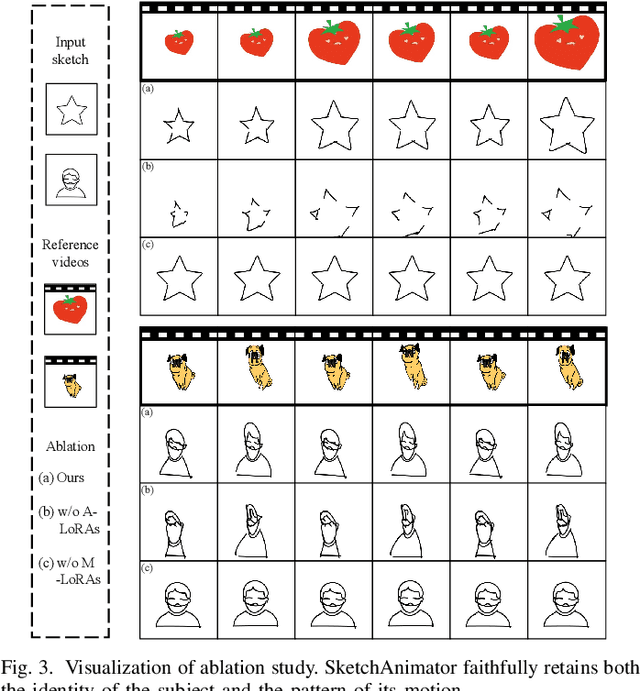
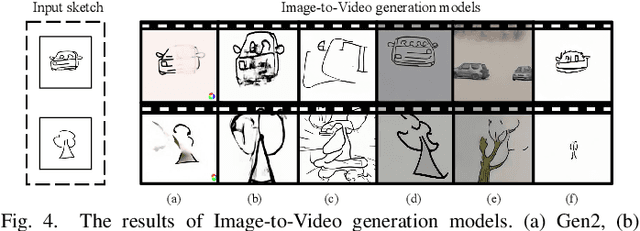
Abstract:Sketching is a uniquely human tool for expressing ideas and creativity. The animation of sketches infuses life into these static drawings, opening a new dimension for designers. Animating sketches is a time-consuming process that demands professional skills and extensive experience, often proving daunting for amateurs. In this paper, we propose a novel sketch animation model SketchAnimator, which enables adding creative motion to a given sketch, like "a jumping car''. Namely, given an input sketch and a reference video, we divide the sketch animation into three stages: Appearance Learning, Motion Learning and Video Prior Distillation. In stages 1 and 2, we utilize LoRA to integrate sketch appearance information and motion dynamics from the reference video into the pre-trained T2V model. In the third stage, we utilize Score Distillation Sampling (SDS) to update the parameters of the Bezier curves in each sketch frame according to the acquired motion information. Consequently, our model produces a sketch video that not only retains the original appearance of the sketch but also mirrors the dynamic movements of the reference video. We compare our method with alternative approaches and demonstrate that it generates the desired sketch video under the challenge of one-shot motion customization.
HierarchicalPrune: Position-Aware Compression for Large-Scale Diffusion Models
Aug 06, 2025Abstract:State-of-the-art text-to-image diffusion models (DMs) achieve remarkable quality, yet their massive parameter scale (8-11B) poses significant challenges for inferences on resource-constrained devices. In this paper, we present HierarchicalPrune, a novel compression framework grounded in a key observation: DM blocks exhibit distinct functional hierarchies, where early blocks establish semantic structures while later blocks handle texture refinements. HierarchicalPrune synergistically combines three techniques: (1) Hierarchical Position Pruning, which identifies and removes less essential later blocks based on position hierarchy; (2) Positional Weight Preservation, which systematically protects early model portions that are essential for semantic structural integrity; and (3) Sensitivity-Guided Distillation, which adjusts knowledge-transfer intensity based on our discovery of block-wise sensitivity variations. As a result, our framework brings billion-scale diffusion models into a range more suitable for on-device inference, while preserving the quality of the output images. Specifically, when combined with INT4 weight quantisation, HierarchicalPrune achieves 77.5-80.4% memory footprint reduction (e.g., from 15.8 GB to 3.2 GB) and 27.9-38.0% latency reduction, measured on server and consumer grade GPUs, with the minimum drop of 2.6% in GenEval score and 7% in HPSv2 score compared to the original model. Last but not least, our comprehensive user study with 85 participants demonstrates that HierarchicalPrune maintains perceptual quality comparable to the original model while significantly outperforming prior works.
Kwai Keye-VL Technical Report
Jul 02, 2025Abstract:While Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) demonstrate remarkable capabilities on static images, they often fall short in comprehending dynamic, information-dense short-form videos, a dominant medium in today's digital landscape. To bridge this gap, we introduce \textbf{Kwai Keye-VL}, an 8-billion-parameter multimodal foundation model engineered for leading-edge performance in short-video understanding while maintaining robust general-purpose vision-language abilities. The development of Keye-VL rests on two core pillars: a massive, high-quality dataset exceeding 600 billion tokens with a strong emphasis on video, and an innovative training recipe. This recipe features a four-stage pre-training process for solid vision-language alignment, followed by a meticulous two-phase post-training process. The first post-training stage enhances foundational capabilities like instruction following, while the second phase focuses on stimulating advanced reasoning. In this second phase, a key innovation is our five-mode ``cold-start'' data mixture, which includes ``thinking'', ``non-thinking'', ``auto-think'', ``think with image'', and high-quality video data. This mixture teaches the model to decide when and how to reason. Subsequent reinforcement learning (RL) and alignment steps further enhance these reasoning capabilities and correct abnormal model behaviors, such as repetitive outputs. To validate our approach, we conduct extensive evaluations, showing that Keye-VL achieves state-of-the-art results on public video benchmarks and remains highly competitive on general image-based tasks (Figure 1). Furthermore, we develop and release the \textbf{KC-MMBench}, a new benchmark tailored for real-world short-video scenarios, where Keye-VL shows a significant advantage.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge