Jingxuan Zhou
RBF++: Quantifying and Optimizing Reasoning Boundaries across Measurable and Unmeasurable Capabilities for Chain-of-Thought Reasoning
May 19, 2025Abstract:Chain-of-Thought (CoT) reasoning has proven effective in enhancing large language models (LLMs) on complex tasks, spurring research into its underlying mechanisms. However, two primary challenges remain for real-world applications: (1) the lack of quantitative metrics and actionable guidelines for evaluating and optimizing measurable boundaries of CoT capability, and (2) the absence of methods to assess boundaries of unmeasurable CoT capability, such as multimodal perception. To address these gaps, we introduce the Reasoning Boundary Framework++ (RBF++). To tackle the first challenge, we define the reasoning boundary (RB) as the maximum limit of CoT performance. We also propose a combination law for RBs, enabling quantitative analysis and offering actionable guidance across various CoT tasks. For the second challenge, particularly in multimodal scenarios, we introduce a constant assumption, which replaces unmeasurable RBs with scenario-specific constants. Additionally, we propose the reasoning boundary division mechanism, which divides unmeasurable RBs into two sub-boundaries, facilitating the quantification and optimization of both unmeasurable domain knowledge and multimodal perception capabilities. Extensive experiments involving 38 models across 13 tasks validate the feasibility of our framework in cross-modal settings. Additionally, we evaluate 10 CoT strategies, offer insights into optimization and decay from two complementary perspectives, and expand evaluation benchmarks for measuring RBs in LLM reasoning. We hope this work advances the understanding of RBs and optimization strategies in LLMs. Code and data are available at https://github.com/LightChen233/reasoning-boundary.
Multi-task Federated Learning with Encoder-Decoder Structure: Enabling Collaborative Learning Across Different Tasks
Apr 14, 2025



Abstract:Federated learning has been extensively studied and applied due to its ability to ensure data security in distributed environments while building better models. However, clients participating in federated learning still face limitations, as clients with different structures or tasks cannot participate in learning together. In view of this, constructing a federated learning framework that allows collaboration between clients with different model structures and performing different tasks, enabling them to share valuable knowledge to enhance model efficiency, holds significant practical implications for the widespread application of federated learning. To achieve this goal, we propose a multi-task federated learning with encoder-decoder structure (M-Fed). Specifically, given the widespread adoption of the encoder-decoder architecture in current models, we leverage this structure to share intra-task knowledge through traditional federated learning methods and extract general knowledge from the encoder to achieve cross-task knowledge sharing. The training process is similar to traditional federated learning, and we incorporate local decoder and global decoder information into the loss function. The local decoder iteratively updates and gradually approaches the global decoder until sufficient cross-task knowledge sharing is achieved. Our method is lightweight and modular, demonstrating innovation compared to previous research. It enables clients performing different tasks to share general knowledge while maintaining the efficiency of traditional federated learning systems. We conducted experiments on two widely used benchmark datasets to verify the feasibility of M-Fed and compared it with traditional methods. The experimental results demonstrate the effectiveness of M-Fed in multi-task federated learning.
CUT: Pruning Pre-Trained Multi-Task Models into Compact Models for Edge Devices
Apr 14, 2025Abstract:Multi-task learning has garnered widespread attention in the industry due to its efficient data utilization and strong generalization capabilities, making it particularly suitable for providing high-quality intelligent services to users. Edge devices, as the primary platforms directly serving users, play a crucial role in delivering multi-task services. However, current multi-task models are often large, and user task demands are increasingly diverse. Deploying such models directly on edge devices not only increases the burden on these devices but also leads to task redundancy. To address this issue, this paper innovatively proposes a pre-trained multi-task model pruning method specifically designed for edge computing. The goal is to utilize existing pre-trained multi-task models to construct a compact multi-task model that meets the needs of edge devices. The specific implementation steps are as follows: First, decompose the tasks within the pre-trained multi-task model and select tasks based on actual user needs. Next, while retaining the knowledge of the original pre-trained model, evaluate parameter importance and use a parameter fusion method to effectively integrate shared parameters among tasks. Finally, obtain a compact multi-task model suitable for edge devices. To validate the effectiveness of the proposed method, we conducted experiments on three public image datasets. The experimental results fully demonstrate the superiority and efficiency of this method, providing a new solution for multi-task learning on edge devices.
Efficient Multi-Task Modeling through Automated Fusion of Trained Models
Apr 14, 2025


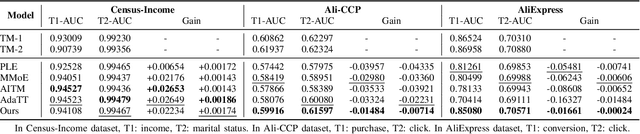
Abstract:Although multi-task learning is widely applied in intelligent services, traditional multi-task modeling methods often require customized designs based on specific task combinations, resulting in a cumbersome modeling process. Inspired by the rapid development and excellent performance of single-task models, this paper proposes an efficient multi-task modeling method that can automatically fuse trained single-task models with different structures and tasks to form a multi-task model. As a general framework, this method allows modelers to simply prepare trained models for the required tasks, simplifying the modeling process while fully utilizing the knowledge contained in the trained models. This eliminates the need for excessive focus on task relationships and model structure design. To achieve this goal, we consider the structural differences among various trained models and employ model decomposition techniques to hierarchically decompose them into multiple operable model components. Furthermore, we have designed an Adaptive Knowledge Fusion (AKF) module based on Transformer, which adaptively integrates intra-task and inter-task knowledge based on model components. Through the proposed method, we achieve efficient and automated construction of multi-task models, and its effectiveness is verified through extensive experiments on three datasets.
Integrated Sensing, Computing, and Semantic Communication with Fluid Antenna for Metaverse
Apr 10, 2025


Abstract:The integration of sensing and communication (ISAC) is pivotal for the Metaverse but faces challenges like high data volume and privacy concerns. This paper proposes a novel integrated sensing, computing, and semantic communication (ISCSC) framework, which uses semantic communication to transmit only contextual information, reducing data overhead and enhancing efficiency. To address the sensitivity of semantic communication to channel conditions, fluid antennas (FAs) are introduced, enabling dynamic adaptability. The FA-enabled ISCSC framework considers multiple users and extended targets composed of a series of scatterers, formulating a joint optimization problem to maximize the data rate while ensuring sensing accuracy and meeting computational and power constraints. An alternating optimization (AO) method decomposes the problem into subproblems for ISAC beamforming, FA positioning, and semantic extraction. Simulations confirm the framework's effectiveness in improving data rates and sensing performance.
Unlearning through Knowledge Overwriting: Reversible Federated Unlearning via Selective Sparse Adapter
Feb 28, 2025



Abstract:Federated Learning is a promising paradigm for privacy-preserving collaborative model training. In practice, it is essential not only to continuously train the model to acquire new knowledge but also to guarantee old knowledge the right to be forgotten (i.e., federated unlearning), especially for privacy-sensitive information or harmful knowledge. However, current federated unlearning methods face several challenges, including indiscriminate unlearning of cross-client knowledge, irreversibility of unlearning, and significant unlearning costs. To this end, we propose a method named FUSED, which first identifies critical layers by analyzing each layer's sensitivity to knowledge and constructs sparse unlearning adapters for sensitive ones. Then, the adapters are trained without altering the original parameters, overwriting the unlearning knowledge with the remaining knowledge. This knowledge overwriting process enables FUSED to mitigate the effects of indiscriminate unlearning. Moreover, the introduction of independent adapters makes unlearning reversible and significantly reduces the unlearning costs. Finally, extensive experiments on three datasets across various unlearning scenarios demonstrate that FUSED's effectiveness is comparable to Retraining, surpassing all other baselines while greatly reducing unlearning costs.
Wrong-of-Thought: An Integrated Reasoning Framework with Multi-Perspective Verification and Wrong Information
Oct 06, 2024



Abstract:Chain-of-Thought (CoT) has become a vital technique for enhancing the performance of Large Language Models (LLMs), attracting increasing attention from researchers. One stream of approaches focuses on the iterative enhancement of LLMs by continuously verifying and refining their reasoning outputs for desired quality. Despite its impressive results, this paradigm faces two critical issues: (1) Simple verification methods: The current paradigm relies solely on a single verification method. (2) Wrong Information Ignorance: Traditional paradigms directly ignore wrong information during reasoning and refine the logic paths from scratch each time. To address these challenges, we propose Wrong-of-Thought (WoT), which includes two core modules: (1) Multi-Perspective Verification: A multi-perspective verification method for accurately refining the reasoning process and result, and (2) Wrong Information Utilization: Utilizing wrong information to alert LLMs and reduce the probability of LLMs making same mistakes. Experiments on 8 popular datasets and 5 LLMs demonstrate that WoT surpasses all previous baselines. In addition, WoT exhibits powerful capabilities in difficult computation tasks.
Fluid Antenna-Assisted Near-Field System
Sep 30, 2024Abstract:This paper proposes a fluid antenna (FA)-assisted near-field integrated sensing and communications (ISAC) system enabled by the extremely large-scale simultaneously transmitting and reflecting surface (XL-STARS). By optimizing the communication beamformer, the sensing signal covariance matrix, the XL-STARS phase shift, and the FA position vector, the Cram\'er-Rao bound (CRB), as a metric for sensing performance, is minimized while ensuring the standard communication performance. A double-loop iterative algorithm based on the penalty dual decomposition (PDD) and block coordinate descent (BCD) methods is proposed to solve the non-convex minimization problem by decomposing it into three subproblems and optimizing the coupling variables for each subproblem iteratively. Simulation results validate the superior performance of the proposed algorithm.
CroPrompt: Cross-task Interactive Prompting for Zero-shot Spoken Language Understanding
Jun 15, 2024Abstract:Slot filling and intent detection are two highly correlated tasks in spoken language understanding (SLU). Recent SLU research attempts to explore zero-shot prompting techniques in large language models to alleviate the data scarcity problem. Nevertheless, the existing prompting work ignores the cross-task interaction information for SLU, which leads to sub-optimal performance. To solve this problem, we present the pioneering work of Cross-task Interactive Prompting (CroPrompt) for SLU, which enables the model to interactively leverage the information exchange across the correlated tasks in SLU. Additionally, we further introduce a multi-task self-consistency mechanism to mitigate the error propagation caused by the intent information injection. We conduct extensive experiments on the standard SLU benchmark and the results reveal that CroPrompt consistently outperforms the existing prompting approaches. In addition, the multi-task self-consistency mechanism can effectively ease the error propagation issue, thereby enhancing the performance. We hope this work can inspire more research on cross-task prompting for SLU.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge