Tieyong Zeng
Center of Mathematical Artificial Intelligence, Department of Mathematics, The Chinese University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong, China
Edge-Aware Normalized Attention for Efficient and Detail-Preserving Single Image Super-Resolution
Sep 18, 2025



Abstract:Single-image super-resolution (SISR) remains highly ill-posed because recovering structurally faithful high-frequency content from a single low-resolution observation is ambiguous. Existing edge-aware methods often attach edge priors or attention branches onto increasingly complex backbones, yet ad hoc fusion frequently introduces redundancy, unstable optimization, or limited structural gains. We address this gap with an edge-guided attention mechanism that derives an adaptive modulation map from jointly encoded edge features and intermediate feature activations, then applies it to normalize and reweight responses, selectively amplifying structurally salient regions while suppressing spurious textures. In parallel, we integrate this mechanism into a lightweight residual design trained under a composite objective combining pixel-wise, perceptual, and adversarial terms to balance fidelity, perceptual realism, and training stability. Extensive experiments on standard SISR benchmarks demonstrate consistent improvements in structural sharpness and perceptual quality over SRGAN, ESRGAN, and prior edge-attention baselines at comparable model complexity. The proposed formulation provides (i) a parameter-efficient path to inject edge priors, (ii) stabilized adversarial refinement through a tailored multiterm loss, and (iii) enhanced edge fidelity without resorting to deeper or heavily overparameterized architectures. These results highlight the effectiveness of principled edge-conditioned modulation for advancing perceptual super-resolution.
Large Language Model Evaluated Stand-alone Attention-Assisted Graph Neural Network with Spatial and Structural Information Interaction for Precise Endoscopic Image Segmentation
Aug 09, 2025Abstract:Accurate endoscopic image segmentation on the polyps is critical for early colorectal cancer detection. However, this task remains challenging due to low contrast with surrounding mucosa, specular highlights, and indistinct boundaries. To address these challenges, we propose FOCUS-Med, which stands for Fusion of spatial and structural graph with attentional context-aware polyp segmentation in endoscopic medical imaging. FOCUS-Med integrates a Dual Graph Convolutional Network (Dual-GCN) module to capture contextual spatial and topological structural dependencies. This graph-based representation enables the model to better distinguish polyps from background tissues by leveraging topological cues and spatial connectivity, which are often obscured in raw image intensities. It enhances the model's ability to preserve boundaries and delineate complex shapes typical of polyps. In addition, a location-fused stand-alone self-attention is employed to strengthen global context integration. To bridge the semantic gap between encoder-decoder layers, we incorporate a trainable weighted fast normalized fusion strategy for efficient multi-scale aggregation. Notably, we are the first to introduce the use of a Large Language Model (LLM) to provide detailed qualitative evaluations of segmentation quality. Extensive experiments on public benchmarks demonstrate that FOCUS-Med achieves state-of-the-art performance across five key metrics, underscoring its effectiveness and clinical potential for AI-assisted colonoscopy.
OS Agents: A Survey on MLLM-based Agents for General Computing Devices Use
Aug 06, 2025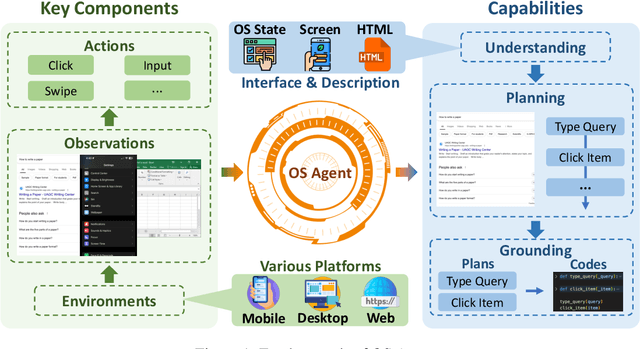
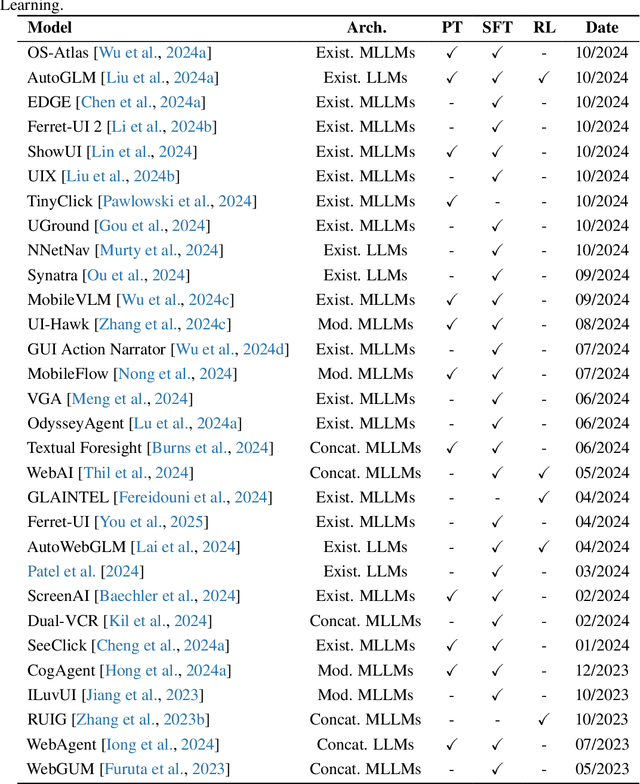
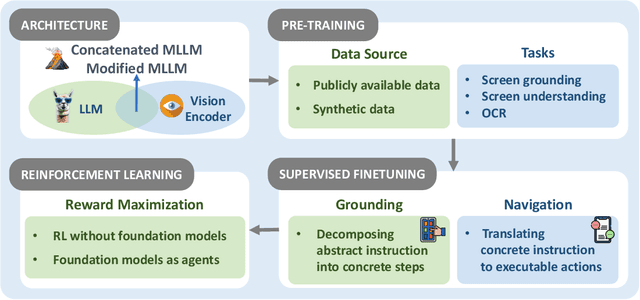
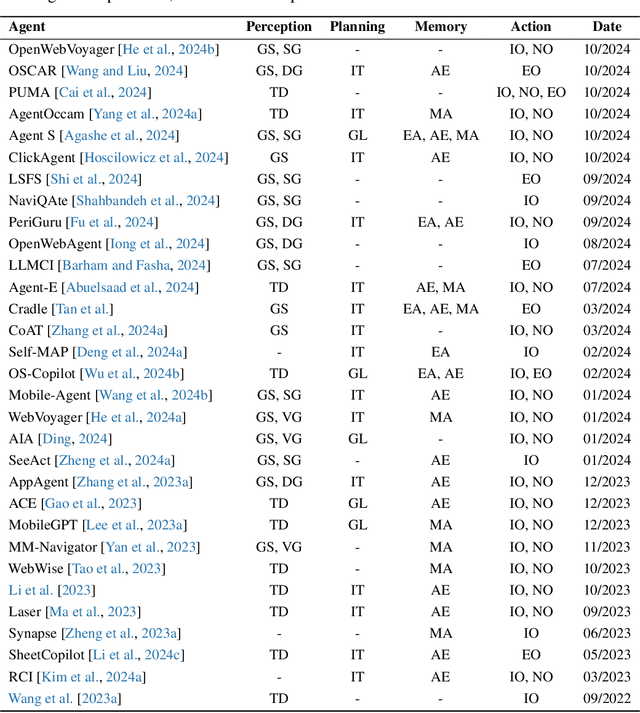
Abstract:The dream to create AI assistants as capable and versatile as the fictional J.A.R.V.I.S from Iron Man has long captivated imaginations. With the evolution of (multi-modal) large language models ((M)LLMs), this dream is closer to reality, as (M)LLM-based Agents using computing devices (e.g., computers and mobile phones) by operating within the environments and interfaces (e.g., Graphical User Interface (GUI)) provided by operating systems (OS) to automate tasks have significantly advanced. This paper presents a comprehensive survey of these advanced agents, designated as OS Agents. We begin by elucidating the fundamentals of OS Agents, exploring their key components including the environment, observation space, and action space, and outlining essential capabilities such as understanding, planning, and grounding. We then examine methodologies for constructing OS Agents, focusing on domain-specific foundation models and agent frameworks. A detailed review of evaluation protocols and benchmarks highlights how OS Agents are assessed across diverse tasks. Finally, we discuss current challenges and identify promising directions for future research, including safety and privacy, personalization and self-evolution. This survey aims to consolidate the state of OS Agents research, providing insights to guide both academic inquiry and industrial development. An open-source GitHub repository is maintained as a dynamic resource to foster further innovation in this field. We present a 9-page version of our work, accepted by ACL 2025, to provide a concise overview to the domain.
Deep Spectral Prior
May 26, 2025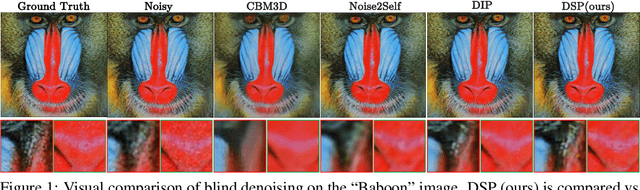
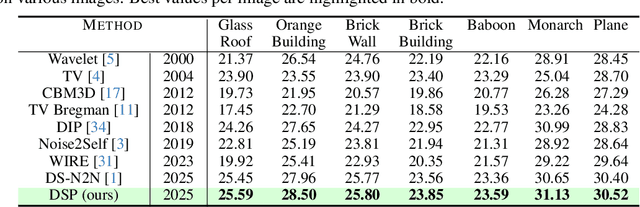

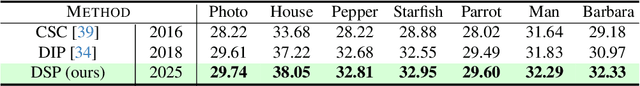
Abstract:We introduce Deep Spectral Prior (DSP), a new formulation of Deep Image Prior (DIP) that redefines image reconstruction as a frequency-domain alignment problem. Unlike traditional DIP, which relies on pixel-wise loss and early stopping to mitigate overfitting, DSP directly matches Fourier coefficients between the network output and observed measurements. This shift introduces an explicit inductive bias towards spectral coherence, aligning with the known frequency structure of images and the spectral bias of convolutional neural networks. We provide a rigorous theoretical framework demonstrating that DSP acts as an implicit spectral regulariser, suppressing high-frequency noise by design and eliminating the need for early stopping. Our analysis spans four core dimensions establishing smooth convergence dynamics, local stability, and favourable bias-variance tradeoffs. We further show that DSP naturally projects reconstructions onto a frequency-consistent manifold, enhancing interpretability and robustness. These theoretical guarantees are supported by empirical results across denoising, inpainting, and super-resolution tasks, where DSP consistently outperforms classical DIP and other unsupervised baselines.
EndoVLA: Dual-Phase Vision-Language-Action Model for Autonomous Tracking in Endoscopy
May 21, 2025Abstract:In endoscopic procedures, autonomous tracking of abnormal regions and following circumferential cutting markers can significantly reduce the cognitive burden on endoscopists. However, conventional model-based pipelines are fragile for each component (e.g., detection, motion planning) requires manual tuning and struggles to incorporate high-level endoscopic intent, leading to poor generalization across diverse scenes. Vision-Language-Action (VLA) models, which integrate visual perception, language grounding, and motion planning within an end-to-end framework, offer a promising alternative by semantically adapting to surgeon prompts without manual recalibration. Despite their potential, applying VLA models to robotic endoscopy presents unique challenges due to the complex and dynamic anatomical environments of the gastrointestinal (GI) tract. To address this, we introduce EndoVLA, designed specifically for continuum robots in GI interventions. Given endoscopic images and surgeon-issued tracking prompts, EndoVLA performs three core tasks: (1) polyp tracking, (2) delineation and following of abnormal mucosal regions, and (3) adherence to circular markers during circumferential cutting. To tackle data scarcity and domain shifts, we propose a dual-phase strategy comprising supervised fine-tuning on our EndoVLA-Motion dataset and reinforcement fine-tuning with task-aware rewards. Our approach significantly improves tracking performance in endoscopy and enables zero-shot generalization in diverse scenes and complex sequential tasks.
Learning Cocoercive Conservative Denoisers via Helmholtz Decomposition for Poisson Inverse Problems
May 13, 2025Abstract:Plug-and-play (PnP) methods with deep denoisers have shown impressive results in imaging problems. They typically require strong convexity or smoothness of the fidelity term and a (residual) non-expansive denoiser for convergence. These assumptions, however, are violated in Poisson inverse problems, and non-expansiveness can hinder denoising performance. To address these challenges, we propose a cocoercive conservative (CoCo) denoiser, which may be (residual) expansive, leading to improved denoising. By leveraging the generalized Helmholtz decomposition, we introduce a novel training strategy that combines Hamiltonian regularization to promote conservativeness and spectral regularization to ensure cocoerciveness. We prove that CoCo denoiser is a proximal operator of a weakly convex function, enabling a restoration model with an implicit weakly convex prior. The global convergence of PnP methods to a stationary point of this restoration model is established. Extensive experimental results demonstrate that our approach outperforms closely related methods in both visual quality and quantitative metrics.
Quaternion Nuclear Norms Over Frobenius Norms Minimization for Robust Matrix Completion
Apr 30, 2025



Abstract:Recovering hidden structures from incomplete or noisy data remains a pervasive challenge across many fields, particularly where multi-dimensional data representation is essential. Quaternion matrices, with their ability to naturally model multi-dimensional data, offer a promising framework for this problem. This paper introduces the quaternion nuclear norm over the Frobenius norm (QNOF) as a novel nonconvex approximation for the rank of quaternion matrices. QNOF is parameter-free and scale-invariant. Utilizing quaternion singular value decomposition, we prove that solving the QNOF can be simplified to solving the singular value $L_1/L_2$ problem. Additionally, we extend the QNOF to robust quaternion matrix completion, employing the alternating direction multiplier method to derive solutions that guarantee weak convergence under mild conditions. Extensive numerical experiments validate the proposed model's superiority, consistently outperforming state-of-the-art quaternion methods.
DGNet: A Neural Network Framework Induced by Discontinuous Galerkin Methods
Mar 13, 2025Abstract:We propose a general framework for the Discontinuous Galerkin-induced Neural Network (DGNet) inspired by the Interior Penalty Discontinuous Galerkin Method (IPDGM). In this approach, the trial space consists of piecewise neural network space defined over the computational domain, while the test function space is composed of piecewise polynomials. We demonstrate the advantages of DGNet in terms of accuracy and training efficiency across several numerical examples, including stationary and time-dependent problems. Specifically, DGNet easily handles high perturbations, discontinuous solutions, and complex geometric domains.
An Improved Optimal Proximal Gradient Algorithm for Non-Blind Image Deblurring
Feb 11, 2025Abstract:Image deblurring remains a central research area within image processing, critical for its role in enhancing image quality and facilitating clearer visual representations across diverse applications. This paper tackles the optimization problem of image deblurring, assuming a known blurring kernel. We introduce an improved optimal proximal gradient algorithm (IOptISTA), which builds upon the optimal gradient method and a weighting matrix, to efficiently address the non-blind image deblurring problem. Based on two regularization cases, namely the $l_1$ norm and total variation norm, we perform numerical experiments to assess the performance of our proposed algorithm. The results indicate that our algorithm yields enhanced PSNR and SSIM values, as well as a reduced tolerance, compared to existing methods.
Rethink Deep Learning with Invariance in Data Representation
Dec 06, 2024Abstract:Integrating invariance into data representations is a principled design in intelligent systems and web applications. Representations play a fundamental role, where systems and applications are both built on meaningful representations of digital inputs (rather than the raw data). In fact, the proper design/learning of such representations relies on priors w.r.t. the task of interest. Here, the concept of symmetry from the Erlangen Program may be the most fruitful prior -- informally, a symmetry of a system is a transformation that leaves a certain property of the system invariant. Symmetry priors are ubiquitous, e.g., translation as a symmetry of the object classification, where object category is invariant under translation. The quest for invariance is as old as pattern recognition and data mining itself. Invariant design has been the cornerstone of various representations in the era before deep learning, such as the SIFT. As we enter the early era of deep learning, the invariance principle is largely ignored and replaced by a data-driven paradigm, such as the CNN. However, this neglect did not last long before they encountered bottlenecks regarding robustness, interpretability, efficiency, and so on. The invariance principle has returned in the era of rethinking deep learning, forming a new field known as Geometric Deep Learning (GDL). In this tutorial, we will give a historical perspective of the invariance in data representations. More importantly, we will identify those research dilemmas, promising works, future directions, and web applications.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge