Yupeng Gao
Bridging Semantic Understanding and Popularity Bias with LLMs
Jan 15, 2026Abstract:Semantic understanding of popularity bias is a crucial yet underexplored challenge in recommender systems, where popular items are often favored at the expense of niche content. Most existing debiasing methods treat the semantic understanding of popularity bias as a matter of diversity enhancement or long-tail coverage, neglecting the deeper semantic layer that embodies the causal origins of the bias itself. Consequently, such shallow interpretations limit both their debiasing effectiveness and recommendation accuracy. In this paper, we propose FairLRM, a novel framework that bridges the gap in the semantic understanding of popularity bias with Recommendation via Large Language Model (RecLLM). FairLRM decomposes popularity bias into item-side and user-side components, using structured instruction-based prompts to enhance the model's comprehension of both global item distributions and individual user preferences. Unlike traditional methods that rely on surface-level features such as "diversity" or "debiasing", FairLRM improves the model's ability to semantically interpret and address the underlying bias. Through empirical evaluation, we show that FairLRM significantly enhances both fairness and recommendation accuracy, providing a more semantically aware and trustworthy approach to enhance the semantic understanding of popularity bias. The implementation is available at https://github.com/LuoRenqiang/FairLRM.
HALO: Half Life-Based Outdated Fact Filtering in Temporal Knowledge Graphs
May 12, 2025Abstract:Outdated facts in temporal knowledge graphs (TKGs) result from exceeding the expiration date of facts, which negatively impact reasoning performance on TKGs. However, existing reasoning methods primarily focus on positive importance of historical facts, neglecting adverse effects of outdated facts. Besides, training on these outdated facts yields extra computational cost. To address these challenges, we propose an outdated fact filtering framework named HALO, which quantifies the temporal validity of historical facts by exploring the half-life theory to filter outdated facts in TKGs. HALO consists of three modules: the temporal fact attention module, the dynamic relation-aware encoder module, and the outdated fact filtering module. Firstly, the temporal fact attention module captures the evolution of historical facts over time to identify relevant facts. Secondly, the dynamic relation-aware encoder module is designed for efficiently predicting the half life of each fact. Finally, we construct a time decay function based on the half-life theory to quantify the temporal validity of facts and filter outdated facts. Experimental results show that HALO outperforms the state-of-the-art TKG reasoning methods on three public datasets, demonstrating its effectiveness in detecting and filtering outdated facts (Codes are available at https://github.com/yushuowiki/K-Half/tree/main ).
Characterizing segregation in blast rock piles a deep-learning approach leveraging aerial image analysis
Jun 06, 2024



Abstract:Blasted rock material serves a critical role in various engineering applications, yet the phenomenon of segregation-where particle sizes vary significantly along the gradient of a quarry pile-presents challenges for optimizing quarry material storage and handling. This study introduces an advanced image analysis methodology to characterize such segregation of rock fragments. The accurate delineation of detailed rock fragment size distributions was achieved through the analysis of drone-captured imagery, coupled with the application of an enhanced Unet semantic segmentation model integrated with an expansion-based post-processing technique. The quarry slope was stratified into four vertical sections, with the size distribution of each section quantified via ellipsoid shape approximations. Our results disclose pronounced vertical segregation patterns, with finer particles concentrated in the upper slope regions and coarser particles in the lower. Utilizing relative characteristic diameters, we offered insight into the degree of segregation, thereby illustrating the spatial heterogeneity in fragment size more clearly. The techniques outlined in this study deliver a scalable and accurate method for assessing fragment size distribution, with the potential to better inform resource management and operational decisions in quarry management.
Interactive Fiction Game Playing as Multi-Paragraph Reading Comprehension with Reinforcement Learning
Oct 05, 2020
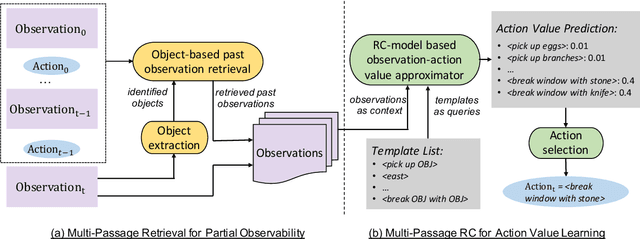
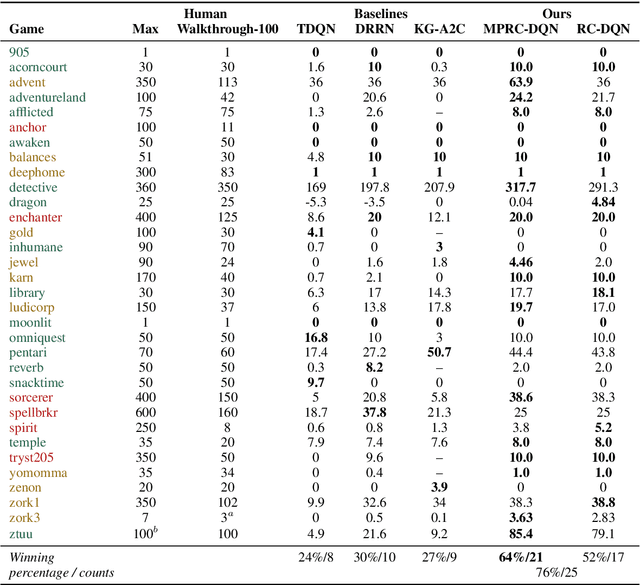
Abstract:Interactive Fiction (IF) games with real human-written natural language texts provide a new natural evaluation for language understanding techniques. In contrast to previous text games with mostly synthetic texts, IF games pose language understanding challenges on the human-written textual descriptions of diverse and sophisticated game worlds and language generation challenges on the action command generation from less restricted combinatorial space. We take a novel perspective of IF game solving and re-formulate it as Multi-Passage Reading Comprehension (MPRC) tasks. Our approaches utilize the context-query attention mechanisms and the structured prediction in MPRC to efficiently generate and evaluate action outputs and apply an object-centric historical observation retrieval strategy to mitigate the partial observability of the textual observations. Extensive experiments on the recent IF benchmark (Jericho) demonstrate clear advantages of our approaches achieving high winning rates and low data requirements compared to all previous approaches. Our source code is available at: https://github.com/XiaoxiaoGuo/rcdqn.
The Fashion IQ Dataset: Retrieving Images by Combining Side Information and Relative Natural Language Feedback
May 30, 2019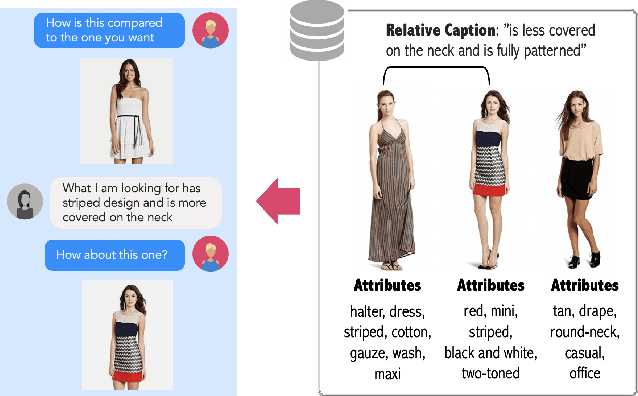
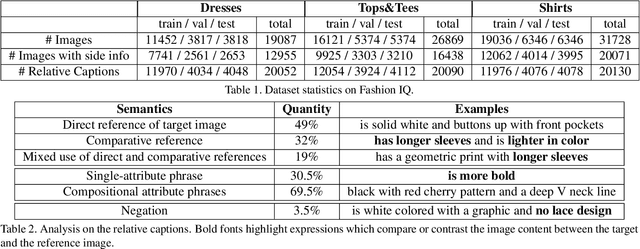
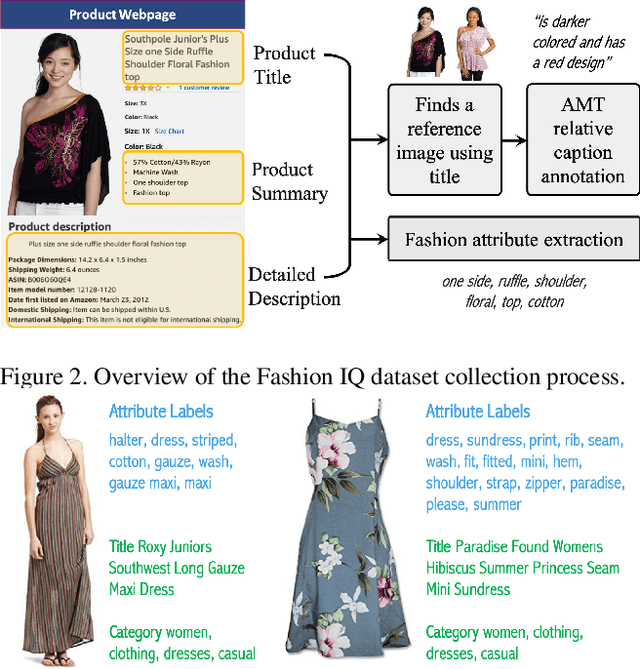
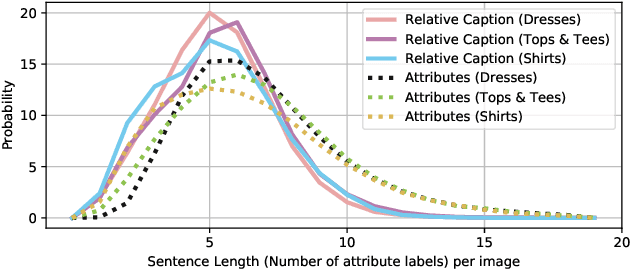
Abstract:We contribute a new dataset and a novel method for natural language based fashion image retrieval. Unlike previous fashion datasets, we provide natural language annotations to facilitate the training of interactive image retrieval systems, as well as the commonly used attribute based labels. We propose a novel approach and empirically demonstrate that combining natural language feedback with visual attribute information results in superior user feedback modeling and retrieval performance relative to using either of these modalities. We believe that our dataset can encourage further work on developing more natural and real-world applicable conversational shopping assistants.
Is Robustness the Cost of Accuracy? -- A Comprehensive Study on the Robustness of 18 Deep Image Classification Models
Aug 05, 2018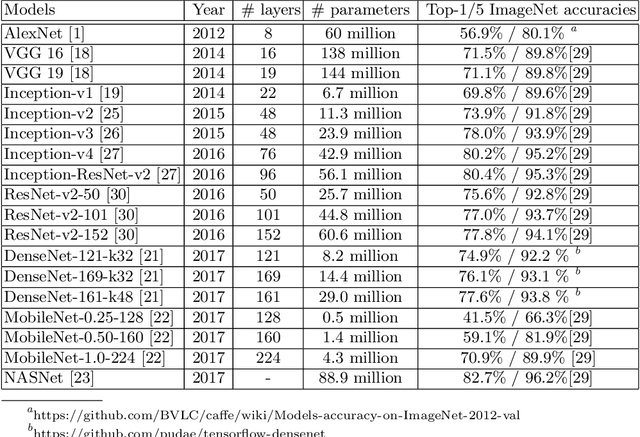
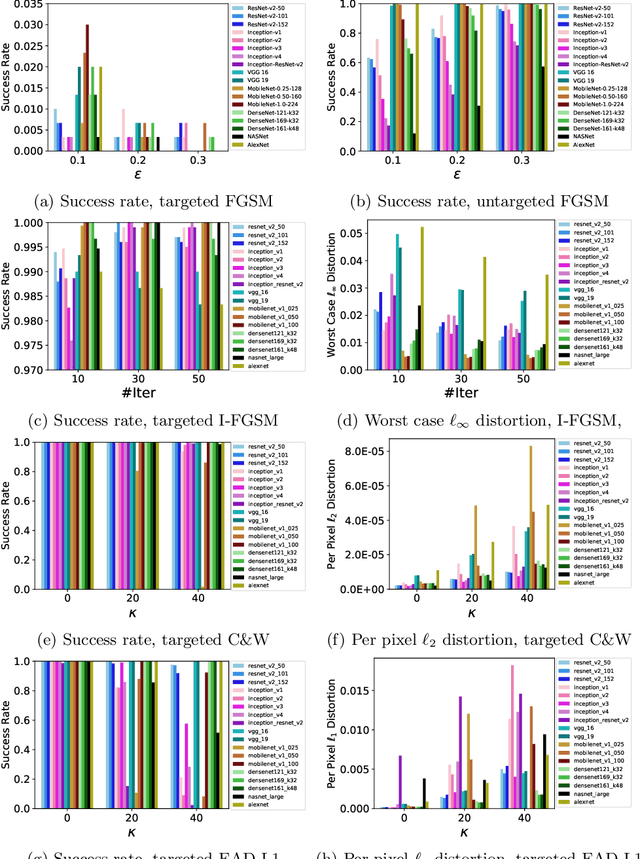
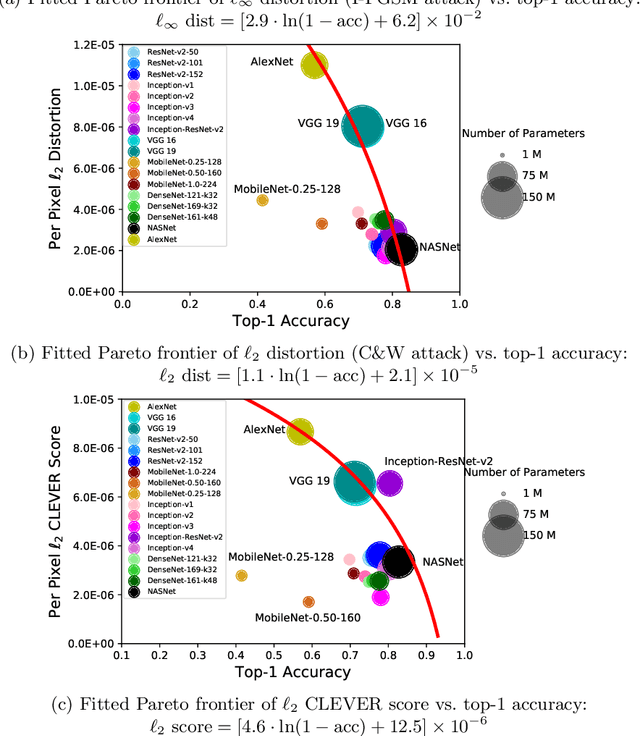
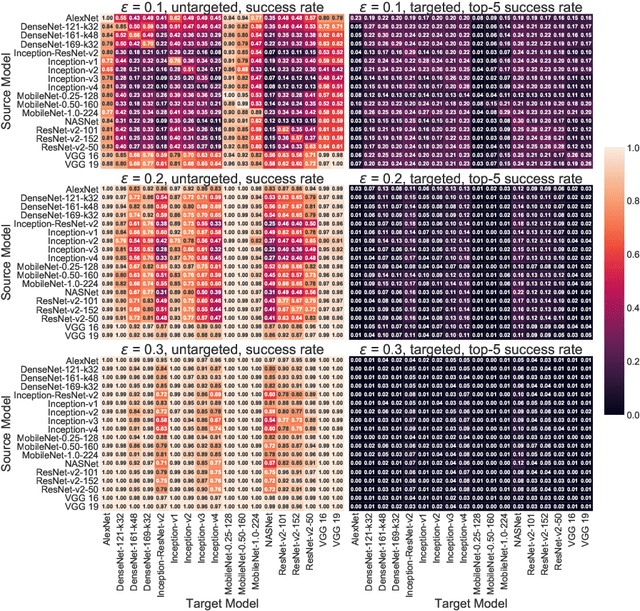
Abstract:The prediction accuracy has been the long-lasting and sole standard for comparing the performance of different image classification models, including the ImageNet competition. However, recent studies have highlighted the lack of robustness in well-trained deep neural networks to adversarial examples. Visually imperceptible perturbations to natural images can easily be crafted and mislead the image classifiers towards misclassification. To demystify the trade-offs between robustness and accuracy, in this paper we thoroughly benchmark 18 ImageNet models using multiple robustness metrics, including the distortion, success rate and transferability of adversarial examples between 306 pairs of models. Our extensive experimental results reveal several new insights: (1) linear scaling law - the empirical $\ell_2$ and $\ell_\infty$ distortion metrics scale linearly with the logarithm of classification error; (2) model architecture is a more critical factor to robustness than model size, and the disclosed accuracy-robustness Pareto frontier can be used as an evaluation criterion for ImageNet model designers; (3) for a similar network architecture, increasing network depth slightly improves robustness in $\ell_\infty$ distortion; (4) there exist models (in VGG family) that exhibit high adversarial transferability, while most adversarial examples crafted from one model can only be transferred within the same family. Experiment code is publicly available at \url{https://github.com/huanzhang12/Adversarial_Survey}.
Evaluating the Robustness of Neural Networks: An Extreme Value Theory Approach
Jan 31, 2018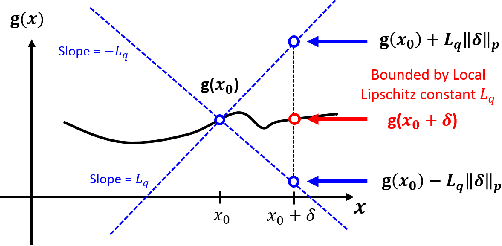
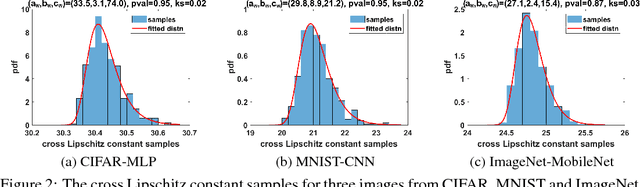
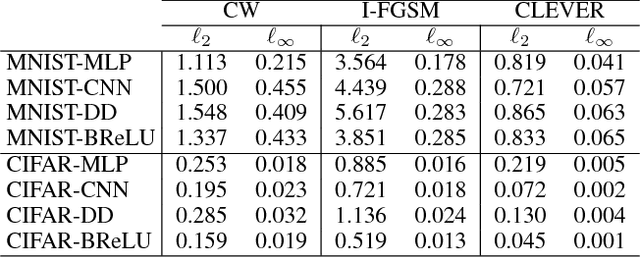
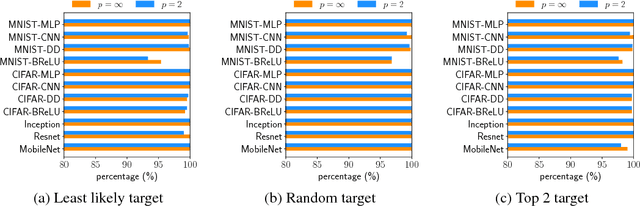
Abstract:The robustness of neural networks to adversarial examples has received great attention due to security implications. Despite various attack approaches to crafting visually imperceptible adversarial examples, little has been developed towards a comprehensive measure of robustness. In this paper, we provide a theoretical justification for converting robustness analysis into a local Lipschitz constant estimation problem, and propose to use the Extreme Value Theory for efficient evaluation. Our analysis yields a novel robustness metric called CLEVER, which is short for Cross Lipschitz Extreme Value for nEtwork Robustness. The proposed CLEVER score is attack-agnostic and computationally feasible for large neural networks. Experimental results on various networks, including ResNet, Inception-v3 and MobileNet, show that (i) CLEVER is aligned with the robustness indication measured by the $\ell_2$ and $\ell_\infty$ norms of adversarial examples from powerful attacks, and (ii) defended networks using defensive distillation or bounded ReLU indeed achieve better CLEVER scores. To the best of our knowledge, CLEVER is the first attack-independent robustness metric that can be applied to any neural network classifier.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge