Zhibin Zhang
MI-PRUN: Optimize Large Language Model Pruning via Mutual Information
Jan 12, 2026Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have become indispensable across various domains, but this comes at the cost of substantial computational and memory resources. Model pruning addresses this by removing redundant components from models. In particular, block pruning can achieve significant compression and inference acceleration. However, existing block pruning methods are often unstable and struggle to attain globally optimal solutions. In this paper, we propose a mutual information based pruning method MI-PRUN for LLMs. Specifically, we leverages mutual information to identify redundant blocks by evaluating transitions in hidden states. Additionally, we incorporate the Data Processing Inequality (DPI) to reveal the relationship between the importance of entire contiguous blocks and that of individual blocks. Moreover, we develop the Fast-Block-Select algorithm, which iteratively updates block combinations to achieve a globally optimal solution while significantly improving the efficiency. Extensive experiments across various models and datasets demonstrate the stability and effectiveness of our method.
Towards Cross-domain Few-shot Graph Anomaly Detection
Oct 11, 2024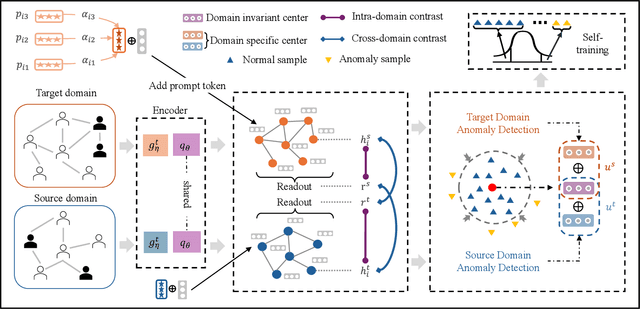
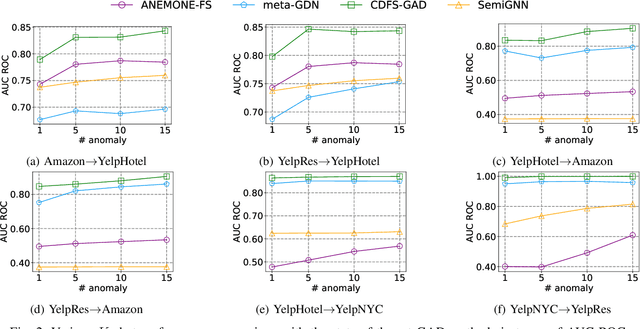
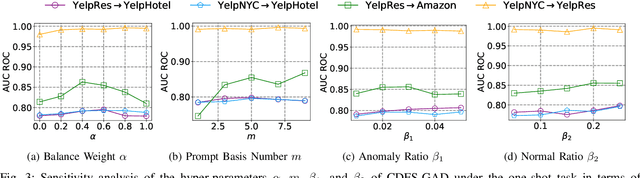
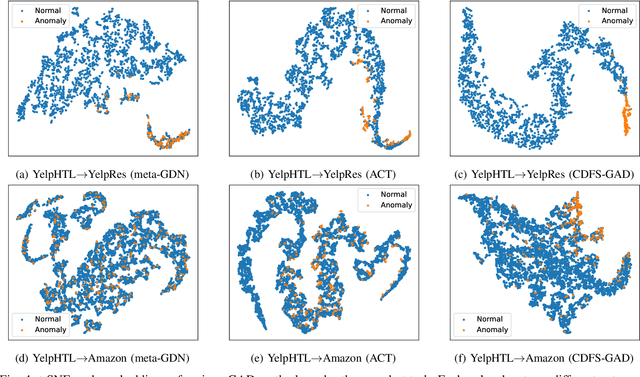
Abstract:Few-shot graph anomaly detection (GAD) has recently garnered increasing attention, which aims to discern anomalous patterns among abundant unlabeled test nodes under the guidance of a limited number of labeled training nodes. Existing few-shot GAD approaches typically adopt meta-training methods trained on richly labeled auxiliary networks to facilitate rapid adaptation to target networks that possess sparse labels. However, these proposed methods often assume that the auxiliary and target networks exist in the same data distributions-an assumption rarely holds in practical settings. This paper explores a more prevalent and complex scenario of cross-domain few-shot GAD, where the goal is to identify anomalies within sparsely labeled target graphs using auxiliary graphs from a related, yet distinct domain. The challenge here is nontrivial owing to inherent data distribution discrepancies between the source and target domains, compounded by the uncertainties of sparse labeling in the target domain. In this paper, we propose a simple and effective framework, termed CDFS-GAD, specifically designed to tackle the aforementioned challenges. CDFS-GAD first introduces a domain-adaptive graph contrastive learning module, which is aimed at enhancing cross-domain feature alignment. Then, a prompt tuning module is further designed to extract domain-specific features tailored to each domain. Moreover, a domain-adaptive hypersphere classification loss is proposed to enhance the discrimination between normal and anomalous instances under minimal supervision, utilizing domain-sensitive norms. Lastly, a self-training strategy is introduced to further refine the predicted scores, enhancing its reliability in few-shot settings. Extensive experiments on twelve real-world cross-domain data pairs demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed CDFS-GAD framework in comparison to various existing GAD methods.
GEDI: A Graph-based End-to-end Data Imputation Framework
Aug 13, 2022



Abstract:Data imputation is an effective way to handle missing data, which is common in practical applications. In this study, we propose and test a novel data imputation process that achieve two important goals: (1) preserve the row-wise similarities among observations and column-wise contextual relationships among features in the feature matrix, and (2) tailor the imputation process to specific downstream label prediction task. The proposed imputation process uses Transformer network and graph structure learning to iteratively refine the contextual relationships among features and similarities among observations. Moreover, it uses a meta-learning framework to select features that are influential to the downstream prediction task of interest. We conduct experiments on real-world large data sets, and show that the proposed imputation process consistently improves imputation and label prediction performance over a variety of benchmark methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge