Yating Yu
Task-Adapter++: Task-specific Adaptation with Order-aware Alignment for Few-shot Action Recognition
May 09, 2025Abstract:Large-scale pre-trained models have achieved remarkable success in language and image tasks, leading an increasing number of studies to explore the application of pre-trained image models, such as CLIP, in the domain of few-shot action recognition (FSAR). However, current methods generally suffer from several problems: 1) Direct fine-tuning often undermines the generalization capability of the pre-trained model; 2) The exploration of task-specific information is insufficient in the visual tasks; 3) The semantic order information is typically overlooked during text modeling; 4) Existing cross-modal alignment techniques ignore the temporal coupling of multimodal information. To address these, we propose Task-Adapter++, a parameter-efficient dual adaptation method for both image and text encoders. Specifically, to make full use of the variations across different few-shot learning tasks, we design a task-specific adaptation for the image encoder so that the most discriminative information can be well noticed during feature extraction. Furthermore, we leverage large language models (LLMs) to generate detailed sequential sub-action descriptions for each action class, and introduce semantic order adapters into the text encoder to effectively model the sequential relationships between these sub-actions. Finally, we develop an innovative fine-grained cross-modal alignment strategy that actively maps visual features to reside in the same temporal stage as semantic descriptions. Extensive experiments fully demonstrate the effectiveness and superiority of the proposed method, which achieves state-of-the-art performance on 5 benchmarks consistently. The code is open-sourced at https://github.com/Jaulin-Bage/Task-Adapter-pp.
Vision and Intention Boost Large Language Model in Long-Term Action Anticipation
May 03, 2025



Abstract:Long-term action anticipation (LTA) aims to predict future actions over an extended period. Previous approaches primarily focus on learning exclusively from video data but lack prior knowledge. Recent researches leverage large language models (LLMs) by utilizing text-based inputs which suffer severe information loss. To tackle these limitations single-modality methods face, we propose a novel Intention-Conditioned Vision-Language (ICVL) model in this study that fully leverages the rich semantic information of visual data and the powerful reasoning capabilities of LLMs. Considering intention as a high-level concept guiding the evolution of actions, we first propose to employ a vision-language model (VLM) to infer behavioral intentions as comprehensive textual features directly from video inputs. The inferred intentions are then fused with visual features through a multi-modality fusion strategy, resulting in intention-enhanced visual representations. These enhanced visual representations, along with textual prompts, are fed into LLM for future action anticipation. Furthermore, we propose an effective example selection strategy jointly considers visual and textual similarities, providing more relevant and informative examples for in-context learning. Extensive experiments with state-of-the-art performance on Ego4D, EPIC-Kitchens-55, and EGTEA GAZE+ datasets fully demonstrate the effectiveness and superiority of the proposed method.
Learning to Generalize without Bias for Open-Vocabulary Action Recognition
Feb 27, 2025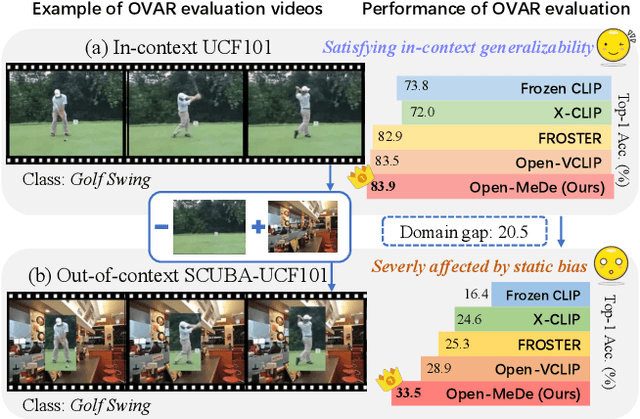

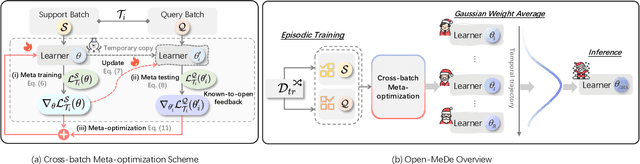

Abstract:Leveraging the effective visual-text alignment and static generalizability from CLIP, recent video learners adopt CLIP initialization with further regularization or recombination for generalization in open-vocabulary action recognition in-context. However, due to the static bias of CLIP, such video learners tend to overfit on shortcut static features, thereby compromising their generalizability, especially to novel out-of-context actions. To address this issue, we introduce Open-MeDe, a novel Meta-optimization framework with static Debiasing for Open-vocabulary action recognition. From a fresh perspective of generalization, Open-MeDe adopts a meta-learning approach to improve known-to-open generalizing and image-to-video debiasing in a cost-effective manner. Specifically, Open-MeDe introduces a cross-batch meta-optimization scheme that explicitly encourages video learners to quickly generalize to arbitrary subsequent data via virtual evaluation, steering a smoother optimization landscape. In effect, the free of CLIP regularization during optimization implicitly mitigates the inherent static bias of the video meta-learner. We further apply self-ensemble over the optimization trajectory to obtain generic optimal parameters that can achieve robust generalization to both in-context and out-of-context novel data. Extensive evaluations show that Open-MeDe not only surpasses state-of-the-art regularization methods tailored for in-context open-vocabulary action recognition but also substantially excels in out-of-context scenarios.
Building a Multi-modal Spatiotemporal Expert for Zero-shot Action Recognition with CLIP
Dec 13, 2024Abstract:Zero-shot action recognition (ZSAR) requires collaborative multi-modal spatiotemporal understanding. However, finetuning CLIP directly for ZSAR yields suboptimal performance, given its inherent constraints in capturing essential temporal dynamics from both vision and text perspectives, especially when encountering novel actions with fine-grained spatiotemporal discrepancies. In this work, we propose Spatiotemporal Dynamic Duo (STDD), a novel CLIP-based framework to comprehend multi-modal spatiotemporal dynamics synergistically. For the vision side, we propose an efficient Space-time Cross Attention, which captures spatiotemporal dynamics flexibly with simple yet effective operations applied before and after spatial attention, without adding additional parameters or increasing computational complexity. For the semantic side, we conduct spatiotemporal text augmentation by comprehensively constructing an Action Semantic Knowledge Graph (ASKG) to derive nuanced text prompts. The ASKG elaborates on static and dynamic concepts and their interrelations, based on the idea of decomposing actions into spatial appearances and temporal motions. During the training phase, the frame-level video representations are meticulously aligned with prompt-level nuanced text representations, which are concurrently regulated by the video representations from the frozen CLIP to enhance generalizability. Extensive experiments validate the effectiveness of our approach, which consistently surpasses state-of-the-art approaches on popular video benchmarks (i.e., Kinetics-600, UCF101, and HMDB51) under challenging ZSAR settings. Code is available at https://github.com/Mia-YatingYu/STDD.
Task-Adapter: Task-specific Adaptation of Image Models for Few-shot Action Recognition
Aug 01, 2024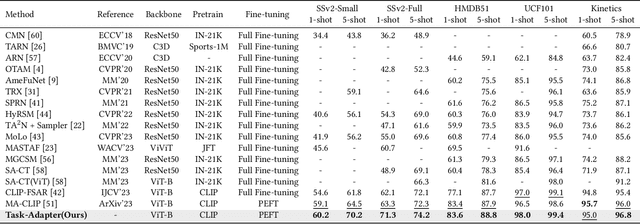
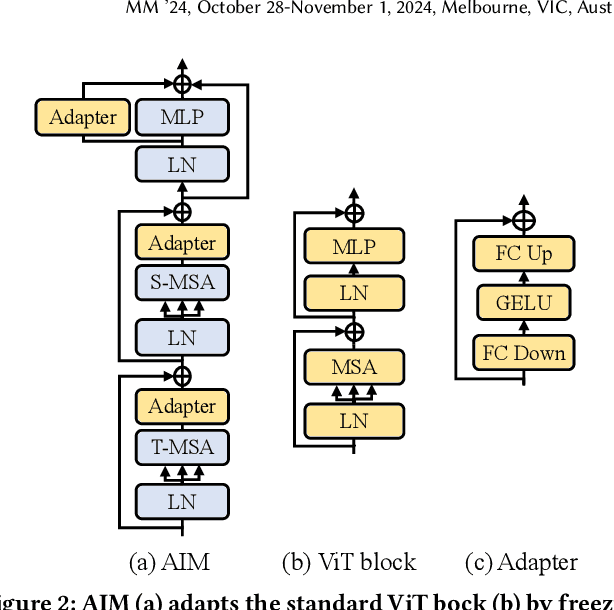
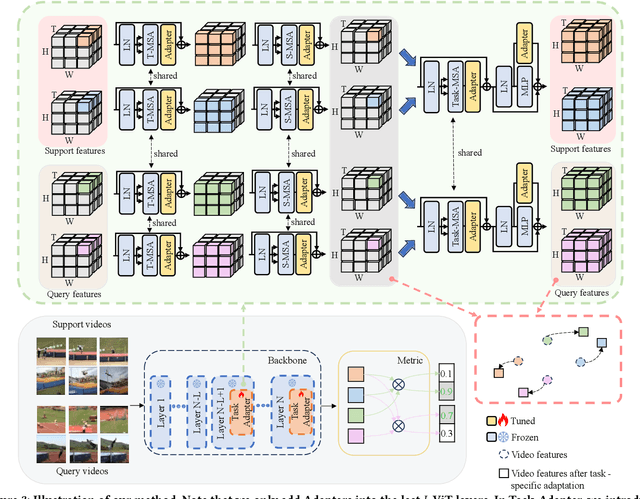
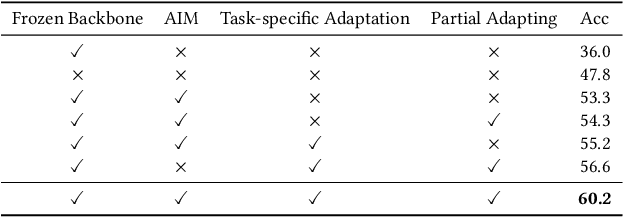
Abstract:Existing works in few-shot action recognition mostly fine-tune a pre-trained image model and design sophisticated temporal alignment modules at feature level. However, simply fully fine-tuning the pre-trained model could cause overfitting due to the scarcity of video samples. Additionally, we argue that the exploration of task-specific information is insufficient when relying solely on well extracted abstract features. In this work, we propose a simple but effective task-specific adaptation method (Task-Adapter) for few-shot action recognition. By introducing the proposed Task-Adapter into the last several layers of the backbone and keeping the parameters of the original pre-trained model frozen, we mitigate the overfitting problem caused by full fine-tuning and advance the task-specific mechanism into the process of feature extraction. In each Task-Adapter, we reuse the frozen self-attention layer to perform task-specific self-attention across different videos within the given task to capture both distinctive information among classes and shared information within classes, which facilitates task-specific adaptation and enhances subsequent metric measurement between the query feature and support prototypes. Experimental results consistently demonstrate the effectiveness of our proposed Task-Adapter on four standard few-shot action recognition datasets. Especially on temporal challenging SSv2 dataset, our method outperforms the state-of-the-art methods by a large margin.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge