Dongkuan Xu
Why Text Prevails: Vision May Undermine Multimodal Medical Decision Making
Dec 15, 2025Abstract:With the rapid progress of large language models (LLMs), advanced multimodal large language models (MLLMs) have demonstrated impressive zero-shot capabilities on vision-language tasks. In the biomedical domain, however, even state-of-the-art MLLMs struggle with basic Medical Decision Making (MDM) tasks. We investigate this limitation using two challenging datasets: (1) three-stage Alzheimer's disease (AD) classification (normal, mild cognitive impairment, dementia), where category differences are visually subtle, and (2) MIMIC-CXR chest radiograph classification with 14 non-mutually exclusive conditions. Our empirical study shows that text-only reasoning consistently outperforms vision-only or vision-text settings, with multimodal inputs often performing worse than text alone. To mitigate this, we explore three strategies: (1) in-context learning with reason-annotated exemplars, (2) vision captioning followed by text-only inference, and (3) few-shot fine-tuning of the vision tower with classification supervision. These findings reveal that current MLLMs lack grounded visual understanding and point to promising directions for improving multimodal decision making in healthcare.
Non-Overlap-Aware Egocentric Pose Estimation for Collaborative Perception in Connected Autonomy
Jun 17, 2025Abstract:Egocentric pose estimation is a fundamental capability for multi-robot collaborative perception in connected autonomy, such as connected autonomous vehicles. During multi-robot operations, a robot needs to know the relative pose between itself and its teammates with respect to its own coordinates. However, different robots usually observe completely different views that contains similar objects, which leads to wrong pose estimation. In addition, it is unrealistic to allow robots to share their raw observations to detect overlap due to the limited communication bandwidth constraint. In this paper, we introduce a novel method for Non-Overlap-Aware Egocentric Pose Estimation (NOPE), which performs egocentric pose estimation in a multi-robot team while identifying the non-overlap views and satifying the communication bandwidth constraint. NOPE is built upon an unified hierarchical learning framework that integrates two levels of robot learning: (1) high-level deep graph matching for correspondence identification, which allows to identify if two views are overlapping or not, (2) low-level position-aware cross-attention graph learning for egocentric pose estimation. To evaluate NOPE, we conduct extensive experiments in both high-fidelity simulation and real-world scenarios. Experimental results have demonstrated that NOPE enables the novel capability for non-overlapping-aware egocentric pose estimation and achieves state-of-art performance compared with the existing methods. Our project page at https://hongh0.github.io/NOPE/.
Leveraging Implicit Sentiments: Enhancing Reliability and Validity in Psychological Trait Evaluation of LLMs
Mar 26, 2025Abstract:Recent advancements in Large Language Models (LLMs) have led to their increasing integration into human life. With the transition from mere tools to human-like assistants, understanding their psychological aspects-such as emotional tendencies and personalities-becomes essential for ensuring their trustworthiness. However, current psychological evaluations of LLMs, often based on human psychological assessments like the BFI, face significant limitations. The results from these approaches often lack reliability and have limited validity when predicting LLM behavior in real-world scenarios. In this work, we introduce a novel evaluation instrument specifically designed for LLMs, called Core Sentiment Inventory (CSI). CSI is a bilingual tool, covering both English and Chinese, that implicitly evaluates models' sentiment tendencies, providing an insightful psychological portrait of LLM across three dimensions: optimism, pessimism, and neutrality. Through extensive experiments, we demonstrate that: 1) CSI effectively captures nuanced emotional patterns, revealing significant variation in LLMs across languages and contexts; 2) Compared to current approaches, CSI significantly improves reliability, yielding more consistent results; and 3) The correlation between CSI scores and the sentiment of LLM's real-world outputs exceeds 0.85, demonstrating its strong validity in predicting LLM behavior. We make CSI public available via: https://github.com/dependentsign/CSI.
Exploring Multi-Modal Integration with Tool-Augmented LLM Agents for Precise Causal Discovery
Dec 18, 2024Abstract:Causal inference is an imperative foundation for decision-making across domains, such as smart health, AI for drug discovery and AIOps. Traditional statistical causal discovery methods, while well-established, predominantly rely on observational data and often overlook the semantic cues inherent in cause-and-effect relationships. The advent of Large Language Models (LLMs) has ushered in an affordable way of leveraging the semantic cues for knowledge-driven causal discovery, but the development of LLMs for causal discovery lags behind other areas, particularly in the exploration of multi-modality data. To bridge the gap, we introduce MATMCD, a multi-agent system powered by tool-augmented LLMs. MATMCD has two key agents: a Data Augmentation agent that retrieves and processes modality-augmented data, and a Causal Constraint agent that integrates multi-modal data for knowledge-driven inference. Delicate design of the inner-workings ensures successful cooperation of the agents. Our empirical study across seven datasets suggests the significant potential of multi-modality enhanced causal discovery.
Digital Twin-Assisted Data-Driven Optimization for Reliable Edge Caching in Wireless Networks
Jun 29, 2024



Abstract:Optimizing edge caching is crucial for the advancement of next-generation (nextG) wireless networks, ensuring high-speed and low-latency services for mobile users. Existing data-driven optimization approaches often lack awareness of the distribution of random data variables and focus solely on optimizing cache hit rates, neglecting potential reliability concerns, such as base station overload and unbalanced cache issues. This oversight can result in system crashes and degraded user experience. To bridge this gap, we introduce a novel digital twin-assisted optimization framework, called D-REC, which integrates reinforcement learning (RL) with diverse intervention modules to ensure reliable caching in nextG wireless networks. We first develop a joint vertical and horizontal twinning approach to efficiently create network digital twins, which are then employed by D-REC as RL optimizers and safeguards, providing ample datasets for training and predictive evaluation of our cache replacement policy. By incorporating reliability modules into a constrained Markov decision process, D-REC can adaptively adjust actions, rewards, and states to comply with advantageous constraints, minimizing the risk of network failures. Theoretical analysis demonstrates comparable convergence rates between D-REC and vanilla data-driven methods without compromising caching performance. Extensive experiments validate that D-REC outperforms conventional approaches in cache hit rate and load balancing while effectively enforcing predetermined reliability intervention modules.
Improving Logits-based Detector without Logits from Black-box LLMs
Jun 11, 2024



Abstract:The advent of Large Language Models (LLMs) has revolutionized text generation, producing outputs that closely mimic human writing. This blurring of lines between machine- and human-written text presents new challenges in distinguishing one from the other a task further complicated by the frequent updates and closed nature of leading proprietary LLMs. Traditional logits-based detection methods leverage surrogate models for identifying LLM-generated content when the exact logits are unavailable from black-box LLMs. However, these methods grapple with the misalignment between the distributions of the surrogate and the often undisclosed target models, leading to performance degradation, particularly with the introduction of new, closed-source models. Furthermore, while current methodologies are generally effective when the source model is identified, they falter in scenarios where the model version remains unknown, or the test set comprises outputs from various source models. To address these limitations, we present Distribution-Aligned LLMs Detection (DALD), an innovative framework that redefines the state-of-the-art performance in black-box text detection even without logits from source LLMs. DALD is designed to align the surrogate model's distribution with that of unknown target LLMs, ensuring enhanced detection capability and resilience against rapid model iterations with minimal training investment. By leveraging corpus samples from publicly accessible outputs of advanced models such as ChatGPT, GPT-4 and Claude-3, DALD fine-tunes surrogate models to synchronize with unknown source model distributions effectively.
Embracing Unknown Step by Step: Towards Reliable Sparse Training in Real World
Mar 29, 2024Abstract:Sparse training has emerged as a promising method for resource-efficient deep neural networks (DNNs) in real-world applications. However, the reliability of sparse models remains a crucial concern, particularly in detecting unknown out-of-distribution (OOD) data. This study addresses the knowledge gap by investigating the reliability of sparse training from an OOD perspective and reveals that sparse training exacerbates OOD unreliability. The lack of unknown information and the sparse constraints hinder the effective exploration of weight space and accurate differentiation between known and unknown knowledge. To tackle these challenges, we propose a new unknown-aware sparse training method, which incorporates a loss modification, auto-tuning strategy, and a voting scheme to guide weight space exploration and mitigate confusion between known and unknown information without incurring significant additional costs or requiring access to additional OOD data. Theoretical insights demonstrate how our method reduces model confidence when faced with OOD samples. Empirical experiments across multiple datasets, model architectures, and sparsity levels validate the effectiveness of our method, with improvements of up to \textbf{8.4\%} in AUROC while maintaining comparable or higher accuracy and calibration. This research enhances the understanding and readiness of sparse DNNs for deployment in resource-limited applications. Our code is available on: \url{https://github.com/StevenBoys/MOON}.
On the Essence and Prospect: An Investigation of Alignment Approaches for Big Models
Mar 07, 2024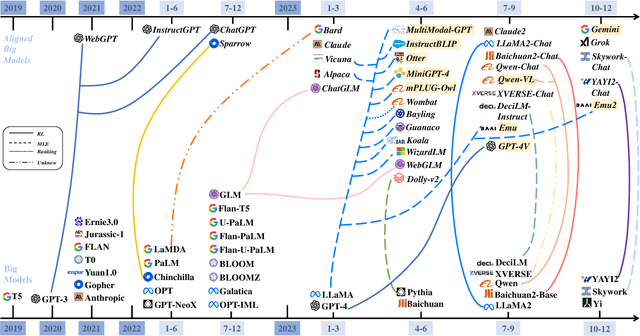
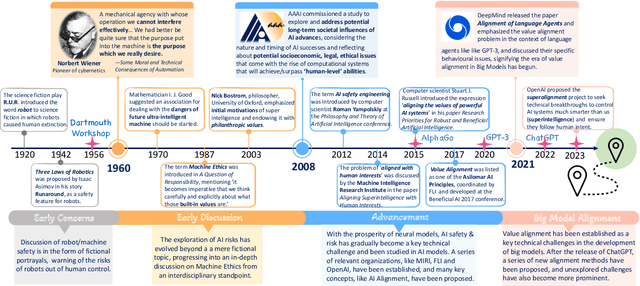
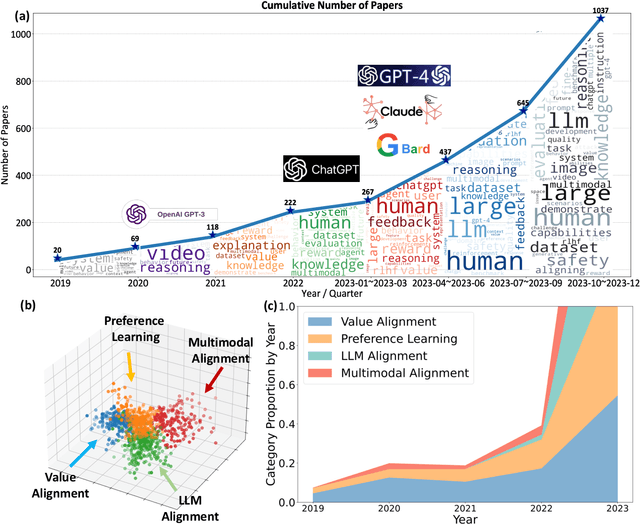
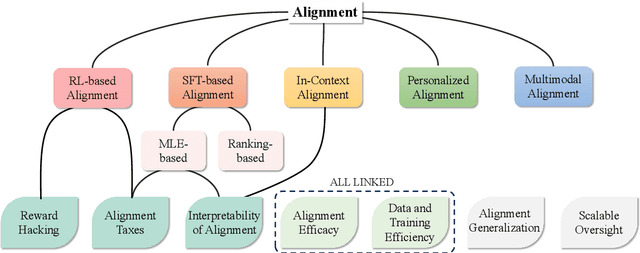
Abstract:Big models have achieved revolutionary breakthroughs in the field of AI, but they might also pose potential concerns. Addressing such concerns, alignment technologies were introduced to make these models conform to human preferences and values. Despite considerable advancements in the past year, various challenges lie in establishing the optimal alignment strategy, such as data cost and scalable oversight, and how to align remains an open question. In this survey paper, we comprehensively investigate value alignment approaches. We first unpack the historical context of alignment tracing back to the 1920s (where it comes from), then delve into the mathematical essence of alignment (what it is), shedding light on the inherent challenges. Following this foundation, we provide a detailed examination of existing alignment methods, which fall into three categories: Reinforcement Learning, Supervised Fine-Tuning, and In-context Learning, and demonstrate their intrinsic connections, strengths, and limitations, helping readers better understand this research area. In addition, two emerging topics, personal alignment, and multimodal alignment, are also discussed as novel frontiers in this field. Looking forward, we discuss potential alignment paradigms and how they could handle remaining challenges, prospecting where future alignment will go.
ToolNet: Connecting Large Language Models with Massive Tools via Tool Graph
Feb 29, 2024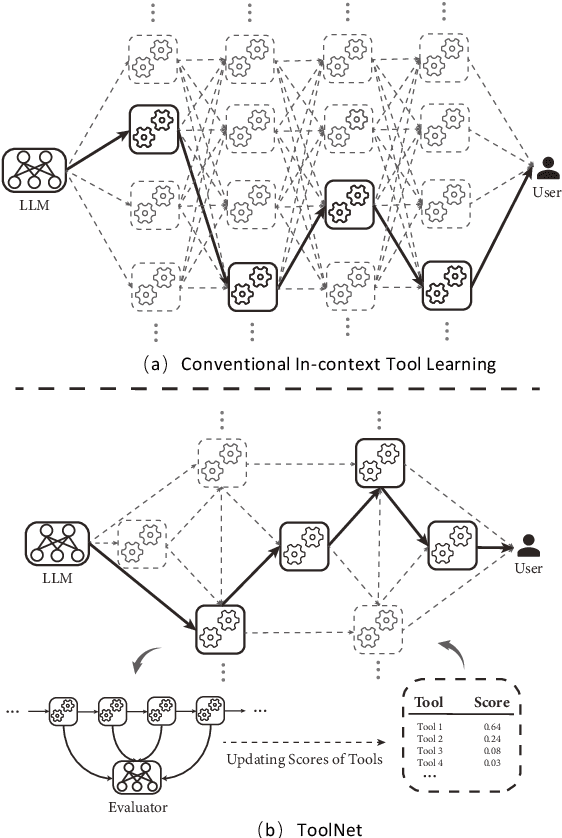
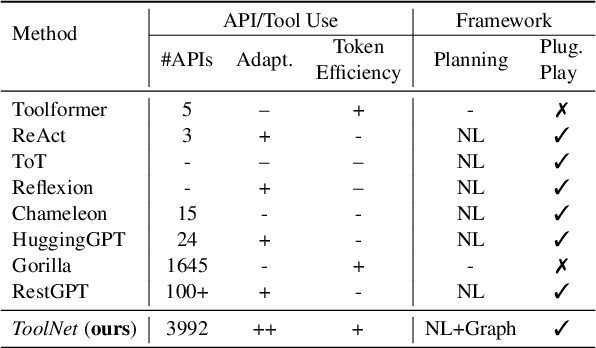
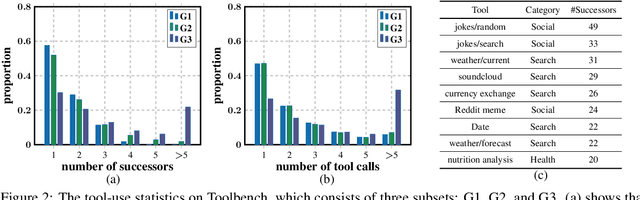
Abstract:While achieving remarkable progress in a broad range of tasks, large language models (LLMs) remain significantly limited in properly using massive external tools. Existing in-context learning approaches simply format tools into a list of plain text descriptions and input them to LLMs, from which, LLMs generate a sequence of tool calls to solve problems step by step. Such a paradigm ignores the intrinsic dependency between tools and offloads all reasoning loads to LLMs, making them restricted to a limited number of specifically designed tools. It thus remains challenging for LLMs to operate on a library of massive tools, casting a great limitation when confronted with real-world scenarios. This paper proposes ToolNet, a plug-and-play framework that scales up the number of tools to thousands with a moderate increase in token consumption. ToolNet organizes tools into a directed graph. Each node represents a tool, and weighted edges denote tool transition. Starting from an initial tool node, an LLM navigates in the graph by iteratively choosing the next one from its successors until the task is resolved. Extensive experiments show that ToolNet can achieve impressive results in challenging multi-hop tool learning datasets and is resilient to tool failures.
Students' Perceptions and Preferences of Generative Artificial Intelligence Feedback for Programming
Dec 17, 2023Abstract:The rapid evolution of artificial intelligence (AI), specifically large language models (LLMs), has opened opportunities for various educational applications. This paper explored the feasibility of utilizing ChatGPT, one of the most popular LLMs, for automating feedback for Java programming assignments in an introductory computer science (CS1) class. Specifically, this study focused on three questions: 1) To what extent do students view LLM-generated feedback as formative? 2) How do students see the comparative affordances of feedback prompts that include their code, vs. those that exclude it? 3) What enhancements do students suggest for improving AI-generated feedback? To address these questions, we generated automated feedback using the ChatGPT API for four lab assignments in the CS1 class. The survey results revealed that students perceived the feedback as aligning well with formative feedback guidelines established by Shute. Additionally, students showed a clear preference for feedback generated by including the students' code as part of the LLM prompt, and our thematic study indicated that the preference was mainly attributed to the specificity, clarity, and corrective nature of the feedback. Moreover, this study found that students generally expected specific and corrective feedback with sufficient code examples, but had diverged opinions on the tone of the feedback. This study demonstrated that ChatGPT could generate Java programming assignment feedback that students perceived as formative. It also offered insights into the specific improvements that would make the ChatGPT-generated feedback useful for students.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge