Maria Korosteleva
AIpparel: A Large Multimodal Generative Model for Digital Garments
Dec 05, 2024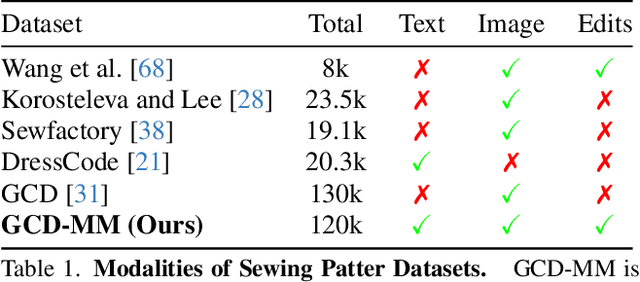
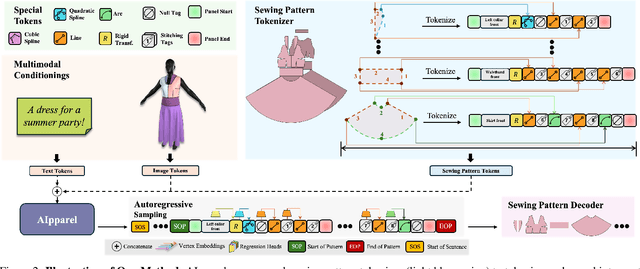
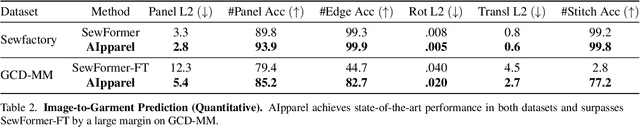
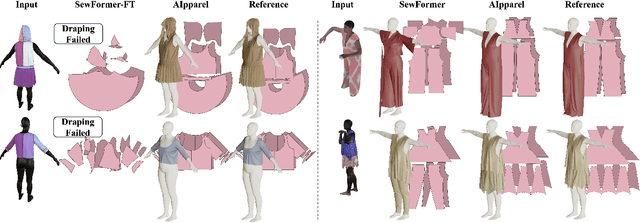
Abstract:Apparel is essential to human life, offering protection, mirroring cultural identities, and showcasing personal style. Yet, the creation of garments remains a time-consuming process, largely due to the manual work involved in designing them. To simplify this process, we introduce AIpparel, a large multimodal model for generating and editing sewing patterns. Our model fine-tunes state-of-the-art large multimodal models (LMMs) on a custom-curated large-scale dataset of over 120,000 unique garments, each with multimodal annotations including text, images, and sewing patterns. Additionally, we propose a novel tokenization scheme that concisely encodes these complex sewing patterns so that LLMs can learn to predict them efficiently. \methodname achieves state-of-the-art performance in single-modal tasks, including text-to-garment and image-to-garment prediction, and enables novel multimodal garment generation applications such as interactive garment editing. The project website is at georgenakayama.github.io/AIpparel/.
GarmentCodeData: A Dataset of 3D Made-to-Measure Garments With Sewing Patterns
May 27, 2024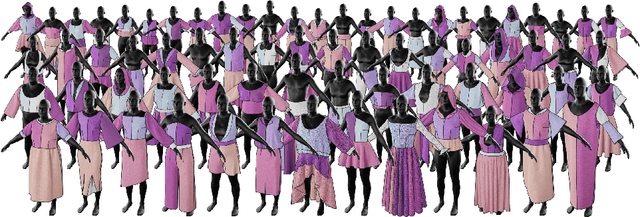
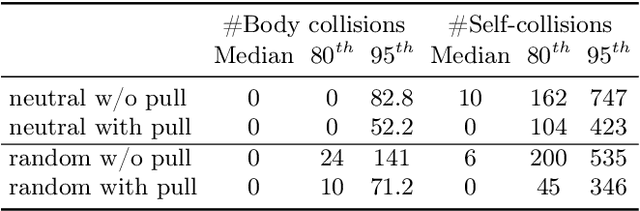
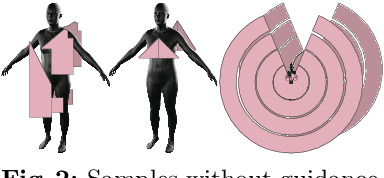
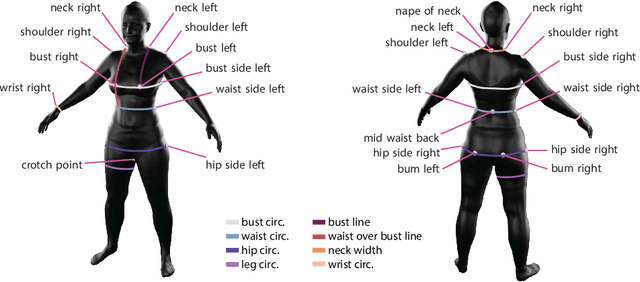
Abstract:Recent research interest in the learning-based processing of garments, from virtual fitting to generation and reconstruction, stumbles on a scarcity of high-quality public data in the domain. We contribute to resolving this need by presenting the first large-scale synthetic dataset of 3D made-to-measure garments with sewing patterns, as well as its generation pipeline. GarmentCodeData contains 115,000 data points that cover a variety of designs in many common garment categories: tops, shirts, dresses, jumpsuits, skirts, pants, etc., fitted to a variety of body shapes sampled from a custom statistical body model based on CAESAR, as well as a standard reference body shape, applying three different textile materials. To enable the creation of datasets of such complexity, we introduce a set of algorithms for automatically taking tailor's measures on sampled body shapes, sampling strategies for sewing pattern design, and propose an automatic, open-source 3D garment draping pipeline based on a fast XPBD simulator, while contributing several solutions for collision resolution and drape correctness to enable scalability. Dataset: http://hdl.handle.net/20.500.11850/673889
NeuralTailor: Reconstructing Sewing Pattern Structures from 3D Point Clouds of Garments
Jan 31, 2022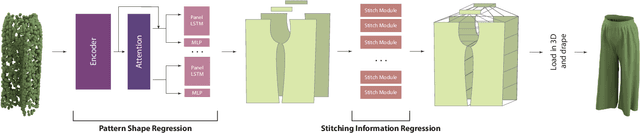
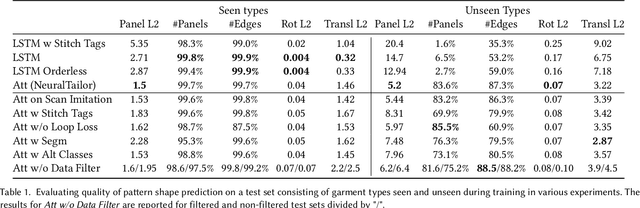
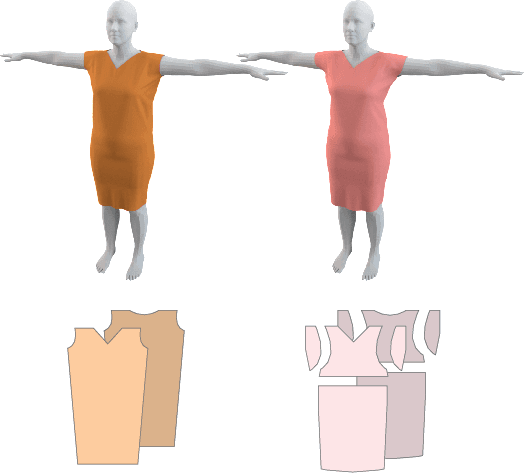
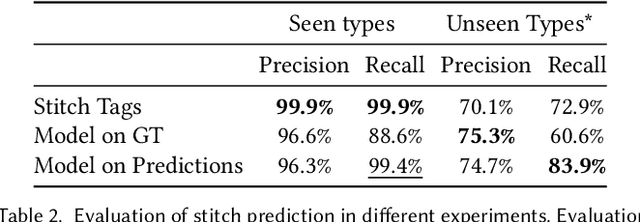
Abstract:The fields of SocialVR, performance capture, and virtual try-on are often faced with a need to faithfully reproduce real garments in the virtual world. One critical task is the disentanglement of the intrinsic garment shape from deformations due to fabric properties, physical forces, and contact with the body. We propose to use a garment sewing pattern, a realistic and compact garment descriptor, to facilitate the intrinsic garment shape estimation. Another major challenge is a high diversity of shapes and designs in the domain. The most common approach for Deep Learning on 3D garments is to build specialized models for individual garments or garment types. We argue that building a unified model for various garment designs has the benefit of generalization to novel garment types, hence covering a larger design domain than individual models would. We introduce NeuralTailor, a novel architecture based on point-level attention for set regression with variable cardinality, and apply it to the task of reconstructing 2D garment sewing patterns from the 3D point could garment models. Our experiments show that NeuralTailor successfully reconstructs sewing patterns and generalizes to garment types with pattern topologies unseen during training.
Generating Datasets of 3D Garments with Sewing Patterns
Sep 12, 2021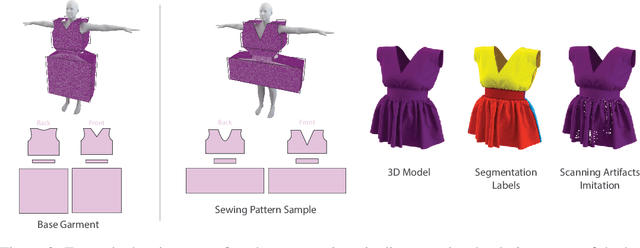
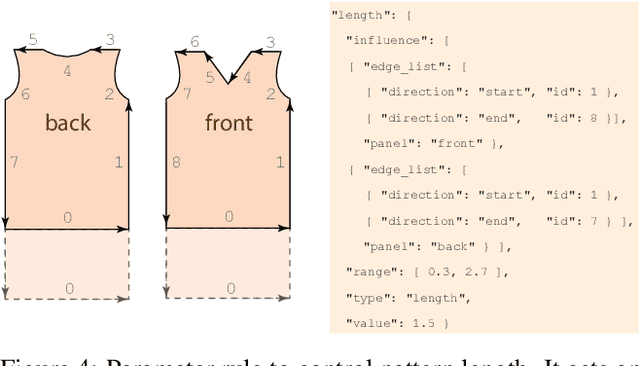
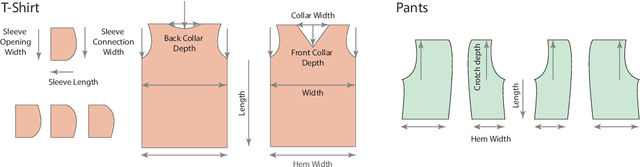
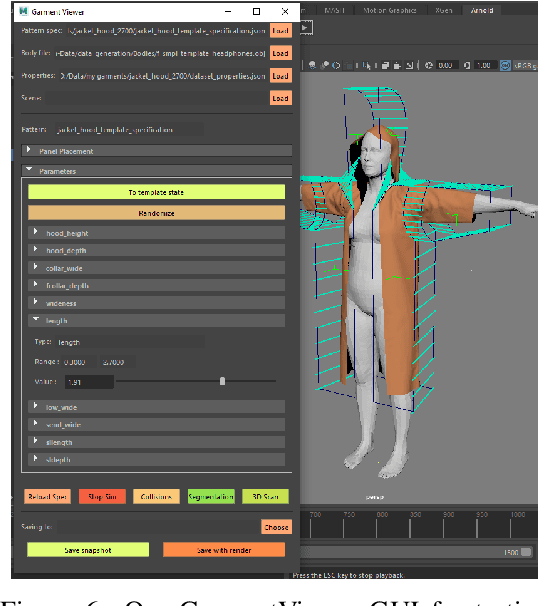
Abstract:Garments are ubiquitous in both real and many of the virtual worlds. They are highly deformable objects, exhibit an immense variety of designs and shapes, and yet, most garments are created from a set of regularly shaped flat pieces. Exploration of garment structure presents a peculiar case for an object structure estimation task and might prove useful for downstream tasks of neural 3D garment modeling and reconstruction by providing strong prior on garment shapes. To facilitate research in these directions, we propose a method for generating large synthetic datasets of 3D garment designs and their sewing patterns. Our method consists of a flexible description structure for specifying parametric sewing pattern templates and the automatic generation pipeline to produce garment 3D models with little-to-none manual intervention. To add realism, the pipeline additionally creates corrupted versions of the final meshes that imitate artifacts of 3D scanning. With this pipeline, we created the first large-scale synthetic dataset of 3D garment models with their sewing patterns. The dataset contains more than 20000 garment design variations produced from 19 different base types. Seven of these garment types are specifically designed to target evaluation of the generalization across garment sewing pattern topologies.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge