Leonidas J. Guibas
LookOut: Real-World Humanoid Egocentric Navigation
Aug 20, 2025Abstract:The ability to predict collision-free future trajectories from egocentric observations is crucial in applications such as humanoid robotics, VR / AR, and assistive navigation. In this work, we introduce the challenging problem of predicting a sequence of future 6D head poses from an egocentric video. In particular, we predict both head translations and rotations to learn the active information-gathering behavior expressed through head-turning events. To solve this task, we propose a framework that reasons over temporally aggregated 3D latent features, which models the geometric and semantic constraints for both the static and dynamic parts of the environment. Motivated by the lack of training data in this space, we further contribute a data collection pipeline using the Project Aria glasses, and present a dataset collected through this approach. Our dataset, dubbed Aria Navigation Dataset (AND), consists of 4 hours of recording of users navigating in real-world scenarios. It includes diverse situations and navigation behaviors, providing a valuable resource for learning real-world egocentric navigation policies. Extensive experiments show that our model learns human-like navigation behaviors such as waiting / slowing down, rerouting, and looking around for traffic while generalizing to unseen environments. Check out our project webpage at https://sites.google.com/stanford.edu/lookout.
AllTracker: Efficient Dense Point Tracking at High Resolution
Jun 08, 2025Abstract:We introduce AllTracker: a model that estimates long-range point tracks by way of estimating the flow field between a query frame and every other frame of a video. Unlike existing point tracking methods, our approach delivers high-resolution and dense (all-pixel) correspondence fields, which can be visualized as flow maps. Unlike existing optical flow methods, our approach corresponds one frame to hundreds of subsequent frames, rather than just the next frame. We develop a new architecture for this task, blending techniques from existing work in optical flow and point tracking: the model performs iterative inference on low-resolution grids of correspondence estimates, propagating information spatially via 2D convolution layers, and propagating information temporally via pixel-aligned attention layers. The model is fast and parameter-efficient (16 million parameters), and delivers state-of-the-art point tracking accuracy at high resolution (i.e., tracking 768x1024 pixels, on a 40G GPU). A benefit of our design is that we can train on a wider set of datasets, and we find that doing so is crucial for top performance. We provide an extensive ablation study on our architecture details and training recipe, making it clear which details matter most. Our code and model weights are available at https://alltracker.github.io .
GARLIC: GAussian Representation LearnIng for spaCe partitioning
May 30, 2025Abstract:We introduce GARLIC (GAussian Representation LearnIng for spaCe partitioning), a novel indexing structure based on \(N\)-dimensional Gaussians for efficiently learning high-dimensional vector spaces. Our approach is inspired from Gaussian splatting techniques, typically used in 3D rendering, which we adapt for high-dimensional search and classification. We optimize Gaussian parameters using information-theoretic objectives that balance coverage, assignment confidence, and structural and semantic consistency. A key contribution is to progressively refine the representation through split and clone operations, handling hundreds of dimensions, thus handling varying data densities. GARLIC offers the fast building times of traditional space partitioning methods (e.g., under \(\sim5\) min build time for SIFT1M) while achieving \(\sim50\%\) Recall10@10 in low-candidate regimes. Experimental results on standard benchmarks demonstrate our method's consistency in (a) \(k\)-NN retrieval, outperforming methods, such as Faiss-IVF, in fast-recall by using about half their probes for the same Recall10@10 in Fashion-MNIST, and (b) in classification tasks, beating by \(\sim15\%\) accuracy other majority voting methods. Further, we show strong generalization capabilities, maintaining high accuracy even with downsampled training data: using just \(1\%\) of the training data returns \(\sim 45\%\) Recall@1, thus making GARLIC quite powerful for applications requiring both speed and accuracy.
AIpparel: A Large Multimodal Generative Model for Digital Garments
Dec 05, 2024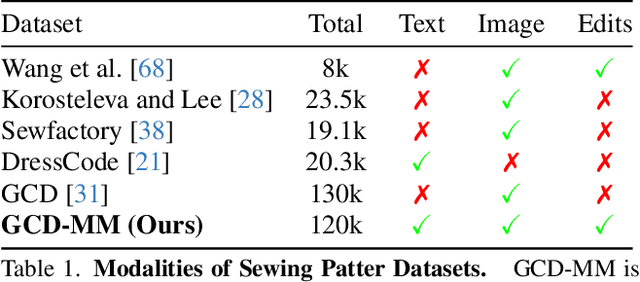
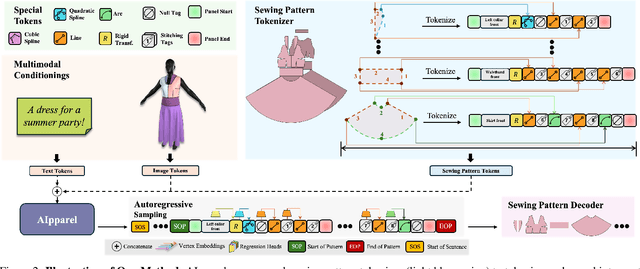
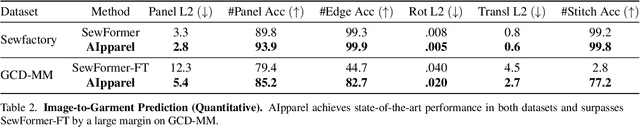
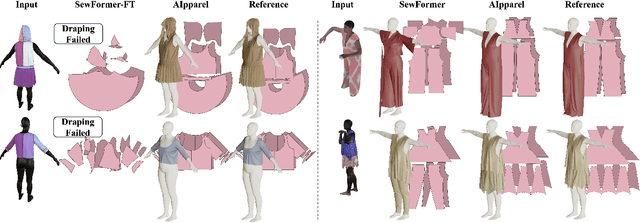
Abstract:Apparel is essential to human life, offering protection, mirroring cultural identities, and showcasing personal style. Yet, the creation of garments remains a time-consuming process, largely due to the manual work involved in designing them. To simplify this process, we introduce AIpparel, a large multimodal model for generating and editing sewing patterns. Our model fine-tunes state-of-the-art large multimodal models (LMMs) on a custom-curated large-scale dataset of over 120,000 unique garments, each with multimodal annotations including text, images, and sewing patterns. Additionally, we propose a novel tokenization scheme that concisely encodes these complex sewing patterns so that LLMs can learn to predict them efficiently. \methodname achieves state-of-the-art performance in single-modal tasks, including text-to-garment and image-to-garment prediction, and enables novel multimodal garment generation applications such as interactive garment editing. The project website is at georgenakayama.github.io/AIpparel/.
View-Consistent Hierarchical 3D SegmentationUsing Ultrametric Feature Fields
May 30, 2024Abstract:Large-scale vision foundation models such as Segment Anything (SAM) demonstrate impressive performance in zero-shot image segmentation at multiple levels of granularity. However, these zero-shot predictions are rarely 3D-consistent. As the camera viewpoint changes in a scene, so do the segmentation predictions, as well as the characterizations of ``coarse" or ``fine" granularity. In this work, we address the challenging task of lifting multi-granular and view-inconsistent image segmentations into a hierarchical and 3D-consistent representation. We learn a novel feature field within a Neural Radiance Field (NeRF) representing a 3D scene, whose segmentation structure can be revealed at different scales by simply using different thresholds on feature distance. Our key idea is to learn an ultrametric feature space, which unlike a Euclidean space, exhibits transitivity in distance-based grouping, naturally leading to a hierarchical clustering. Put together, our method takes view-inconsistent multi-granularity 2D segmentations as input and produces a hierarchy of 3D-consistent segmentations as output. We evaluate our method and several baselines on synthetic datasets with multi-view images and multi-granular segmentation, showcasing improved accuracy and viewpoint-consistency. We additionally provide qualitative examples of our model's 3D hierarchical segmentations in real world scenes.\footnote{The code and dataset are available at:
ActAnywhere: Subject-Aware Video Background Generation
Jan 19, 2024Abstract:Generating video background that tailors to foreground subject motion is an important problem for the movie industry and visual effects community. This task involves synthesizing background that aligns with the motion and appearance of the foreground subject, while also complies with the artist's creative intention. We introduce ActAnywhere, a generative model that automates this process which traditionally requires tedious manual efforts. Our model leverages the power of large-scale video diffusion models, and is specifically tailored for this task. ActAnywhere takes a sequence of foreground subject segmentation as input and an image that describes the desired scene as condition, to produce a coherent video with realistic foreground-background interactions while adhering to the condition frame. We train our model on a large-scale dataset of human-scene interaction videos. Extensive evaluations demonstrate the superior performance of our model, significantly outperforming baselines. Moreover, we show that ActAnywhere generalizes to diverse out-of-distribution samples, including non-human subjects. Please visit our project webpage at https://actanywhere.github.io.
Refining Pre-Trained Motion Models
Jan 01, 2024



Abstract:Given the difficulty of manually annotating motion in video, the current best motion estimation methods are trained with synthetic data, and therefore struggle somewhat due to a train/test gap. Self-supervised methods hold the promise of training directly on real video, but typically perform worse. These include methods trained with warp error (i.e., color constancy) combined with smoothness terms, and methods that encourage cycle-consistency in the estimates (i.e., tracking backwards should yield the opposite trajectory as tracking forwards). In this work, we take on the challenge of improving state-of-the-art supervised models with self-supervised training. We find that when the initialization is supervised weights, most existing self-supervision techniques actually make performance worse instead of better, which suggests that the benefit of seeing the new data is overshadowed by the noise in the training signal. Focusing on obtaining a ``clean'' training signal from real-world unlabelled video, we propose to separate label-making and training into two distinct stages. In the first stage, we use the pre-trained model to estimate motion in a video, and then select the subset of motion estimates which we can verify with cycle-consistency. This produces a sparse but accurate pseudo-labelling of the video. In the second stage, we fine-tune the model to reproduce these outputs, while also applying augmentations on the input. We complement this boot-strapping method with simple techniques that densify and re-balance the pseudo-labels, ensuring that we do not merely train on ``easy'' tracks. We show that our method yields reliable gains over fully-supervised methods in real videos, for both short-term (flow-based) and long-range (multi-frame) pixel tracking.
Towards Learning Geometric Eigen-Lengths Crucial for Fitting Tasks
Dec 25, 2023Abstract:Some extremely low-dimensional yet crucial geometric eigen-lengths often determine the success of some geometric tasks. For example, the height of an object is important to measure to check if it can fit between the shelves of a cabinet, while the width of a couch is crucial when trying to move it through a doorway. Humans have materialized such crucial geometric eigen-lengths in common sense since they are very useful in serving as succinct yet effective, highly interpretable, and universal object representations. However, it remains obscure and underexplored if learning systems can be equipped with similar capabilities of automatically discovering such key geometric quantities from doing tasks. In this work, we therefore for the first time formulate and propose a novel learning problem on this question and set up a benchmark suite including tasks, data, and evaluation metrics for studying the problem. We focus on a family of common fitting tasks as the testbed for the proposed learning problem. We explore potential solutions and demonstrate the feasibility of learning eigen-lengths from simply observing successful and failed fitting trials. We also attempt geometric grounding for more accurate eigen-length measurement and study the reusability of the learned eigen-lengths across multiple tasks. Our work marks the first exploratory step toward learning crucial geometric eigen-lengths and we hope it can inspire future research in tackling this important yet underexplored problem.
* ICML 2023. Project page: https://yijiaweng.github.io/geo-eigen-length
PointOdyssey: A Large-Scale Synthetic Dataset for Long-Term Point Tracking
Jul 27, 2023



Abstract:We introduce PointOdyssey, a large-scale synthetic dataset, and data generation framework, for the training and evaluation of long-term fine-grained tracking algorithms. Our goal is to advance the state-of-the-art by placing emphasis on long videos with naturalistic motion. Toward the goal of naturalism, we animate deformable characters using real-world motion capture data, we build 3D scenes to match the motion capture environments, and we render camera viewpoints using trajectories mined via structure-from-motion on real videos. We create combinatorial diversity by randomizing character appearance, motion profiles, materials, lighting, 3D assets, and atmospheric effects. Our dataset currently includes 104 videos, averaging 2,000 frames long, with orders of magnitude more correspondence annotations than prior work. We show that existing methods can be trained from scratch in our dataset and outperform the published variants. Finally, we introduce modifications to the PIPs point tracking method, greatly widening its temporal receptive field, which improves its performance on PointOdyssey as well as on two real-world benchmarks. Our data and code are publicly available at: https://pointodyssey.com
Learning a Diffusion Prior for NeRFs
Apr 27, 2023


Abstract:Neural Radiance Fields (NeRFs) have emerged as a powerful neural 3D representation for objects and scenes derived from 2D data. Generating NeRFs, however, remains difficult in many scenarios. For instance, training a NeRF with only a small number of views as supervision remains challenging since it is an under-constrained problem. In such settings, it calls for some inductive prior to filter out bad local minima. One way to introduce such inductive priors is to learn a generative model for NeRFs modeling a certain class of scenes. In this paper, we propose to use a diffusion model to generate NeRFs encoded on a regularized grid. We show that our model can sample realistic NeRFs, while at the same time allowing conditional generations, given a certain observation as guidance.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge