Bingyao Yu
NeXT-IMDL: Build Benchmark for NeXT-Generation Image Manipulation Detection & Localization
Dec 29, 2025Abstract:The accessibility surge and abuse risks of user-friendly image editing models have created an urgent need for generalizable, up-to-date methods for Image Manipulation Detection and Localization (IMDL). Current IMDL research typically uses cross-dataset evaluation, where models trained on one benchmark are tested on others. However, this simplified evaluation approach conceals the fragility of existing methods when handling diverse AI-generated content, leading to misleading impressions of progress. This paper challenges this illusion by proposing NeXT-IMDL, a large-scale diagnostic benchmark designed not just to collect data, but to probe the generalization boundaries of current detectors systematically. Specifically, NeXT-IMDL categorizes AIGC-based manipulations along four fundamental axes: editing models, manipulation types, content semantics, and forgery granularity. Built upon this, NeXT-IMDL implements five rigorous cross-dimension evaluation protocols. Our extensive experiments on 11 representative models reveal a critical insight: while these models perform well in their original settings, they exhibit systemic failures and significant performance degradation when evaluated under our designed protocols that simulate real-world, various generalization scenarios. By providing this diagnostic toolkit and the new findings, we aim to advance the development towards building truly robust, next-generation IMDL models.
Towards Privacy-Preserving Fine-Grained Visual Classification via Hierarchical Learning from Label Proportions
May 29, 2025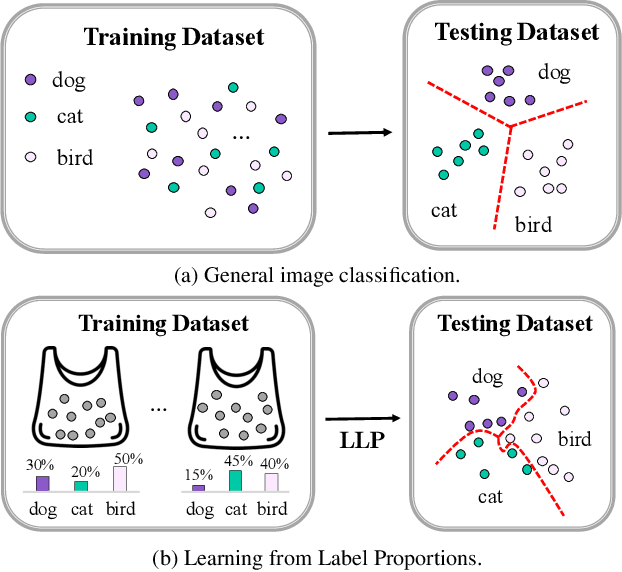
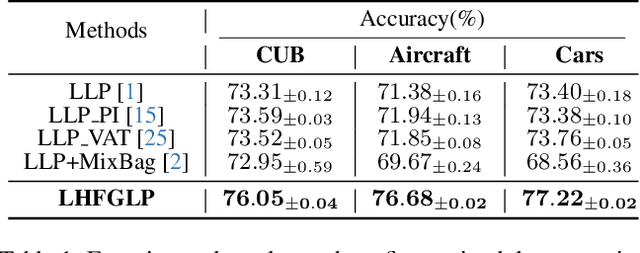
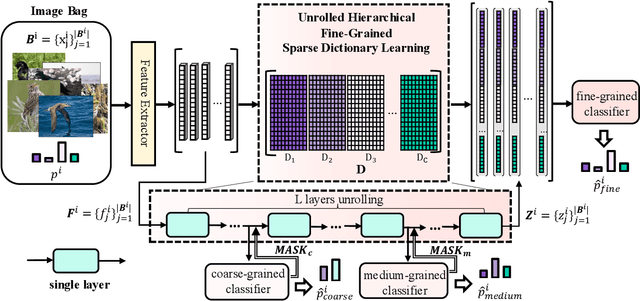
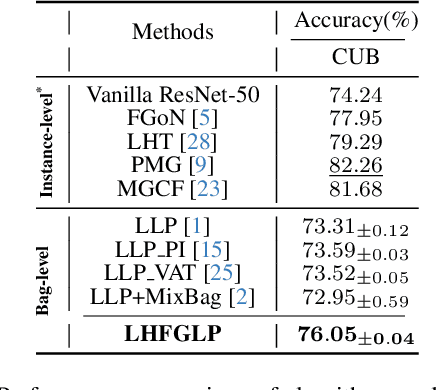
Abstract:In recent years, Fine-Grained Visual Classification (FGVC) has achieved impressive recognition accuracy, despite minimal inter-class variations. However, existing methods heavily rely on instance-level labels, making them impractical in privacy-sensitive scenarios such as medical image analysis. This paper aims to enable accurate fine-grained recognition without direct access to instance labels. To achieve this, we leverage the Learning from Label Proportions (LLP) paradigm, which requires only bag-level labels for efficient training. Unlike existing LLP-based methods, our framework explicitly exploits the hierarchical nature of fine-grained datasets, enabling progressive feature granularity refinement and improving classification accuracy. We propose Learning from Hierarchical Fine-Grained Label Proportions (LHFGLP), a framework that incorporates Unrolled Hierarchical Fine-Grained Sparse Dictionary Learning, transforming handcrafted iterative approximation into learnable network optimization. Additionally, our proposed Hierarchical Proportion Loss provides hierarchical supervision, further enhancing classification performance. Experiments on three widely-used fine-grained datasets, structured in a bag-based manner, demonstrate that our framework consistently outperforms existing LLP-based methods. We will release our code and datasets to foster further research in privacy-preserving fine-grained classification.
Multimodal Conditional Information Bottleneck for Generalizable AI-Generated Image Detection
May 21, 2025Abstract:Although existing CLIP-based methods for detecting AI-generated images have achieved promising results, they are still limited by severe feature redundancy, which hinders their generalization ability. To address this issue, incorporating an information bottleneck network into the task presents a straightforward solution. However, relying solely on image-corresponding prompts results in suboptimal performance due to the inherent diversity of prompts. In this paper, we propose a multimodal conditional bottleneck network to reduce feature redundancy while enhancing the discriminative power of features extracted by CLIP, thereby improving the model's generalization ability. We begin with a semantic analysis experiment, where we observe that arbitrary text features exhibit lower cosine similarity with real image features than with fake image features in the CLIP feature space, a phenomenon we refer to as "bias". Therefore, we introduce InfoFD, a text-guided AI-generated image detection framework. InfoFD consists of two key components: the Text-Guided Conditional Information Bottleneck (TGCIB) and Dynamic Text Orthogonalization (DTO). TGCIB improves the generalizability of learned representations by conditioning on both text and class modalities. DTO dynamically updates weighted text features, preserving semantic information while leveraging the global "bias". Our model achieves exceptional generalization performance on the GenImage dataset and latest generative models. Our code is available at https://github.com/Ant0ny44/InfoFD.
FakeReasoning: Towards Generalizable Forgery Detection and Reasoning
Mar 27, 2025Abstract:Accurate and interpretable detection of AI-generated images is essential for mitigating risks associated with AI misuse. However, the substantial domain gap among generative models makes it challenging to develop a generalizable forgery detection model. Moreover, since every pixel in an AI-generated image is synthesized, traditional saliency-based forgery explanation methods are not well suited for this task. To address these challenges, we propose modeling AI-generated image detection and explanation as a Forgery Detection and Reasoning task (FDR-Task), leveraging vision-language models (VLMs) to provide accurate detection through structured and reliable reasoning over forgery attributes. To facilitate this task, we introduce the Multi-Modal Forgery Reasoning dataset (MMFR-Dataset), a large-scale dataset containing 100K images across 10 generative models, with 10 types of forgery reasoning annotations, enabling comprehensive evaluation of FDR-Task. Additionally, we propose FakeReasoning, a forgery detection and reasoning framework with two key components. First, Forgery-Aligned Contrastive Learning enhances VLMs' understanding of forgery-related semantics through both cross-modal and intra-modal contrastive learning between images and forgery attribute reasoning. Second, a Classification Probability Mapper bridges the optimization gap between forgery detection and language modeling by mapping the output logits of VLMs to calibrated binary classification probabilities. Experiments across multiple generative models demonstrate that FakeReasoning not only achieves robust generalization but also outperforms state-of-the-art methods on both detection and reasoning tasks.
TCOVIS: Temporally Consistent Online Video Instance Segmentation
Sep 21, 2023Abstract:In recent years, significant progress has been made in video instance segmentation (VIS), with many offline and online methods achieving state-of-the-art performance. While offline methods have the advantage of producing temporally consistent predictions, they are not suitable for real-time scenarios. Conversely, online methods are more practical, but maintaining temporal consistency remains a challenging task. In this paper, we propose a novel online method for video instance segmentation, called TCOVIS, which fully exploits the temporal information in a video clip. The core of our method consists of a global instance assignment strategy and a spatio-temporal enhancement module, which improve the temporal consistency of the features from two aspects. Specifically, we perform global optimal matching between the predictions and ground truth across the whole video clip, and supervise the model with the global optimal objective. We also capture the spatial feature and aggregate it with the semantic feature between frames, thus realizing the spatio-temporal enhancement. We evaluate our method on four widely adopted VIS benchmarks, namely YouTube-VIS 2019/2021/2022 and OVIS, and achieve state-of-the-art performance on all benchmarks without bells-and-whistles. For instance, on YouTube-VIS 2021, TCOVIS achieves 49.5 AP and 61.3 AP with ResNet-50 and Swin-L backbones, respectively. Code is available at https://github.com/jun-long-li/TCOVIS.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge