Dongrui Wu
EEG Foundation Models: Progresses, Benchmarking, and Open Problems
Jan 25, 2026Abstract:Electroencephalography (EEG) foundation models have recently emerged as a promising paradigm for brain-computer interfaces (BCIs), aiming to learn transferable neural representations from large-scale heterogeneous recordings. Despite rapid progresses, there lacks fair and comprehensive comparisons of existing EEG foundation models, due to inconsistent pre-training objectives, preprocessing choices, and downstream evaluation protocols. This paper fills this gap. We first review 50 representative models and organize their design choices into a unified taxonomic framework including data standardization, model architectures, and self-supervised pre-training strategies. We then evaluate 12 open-source foundation models and competitive specialist baselines across 13 EEG datasets spanning nine BCI paradigms. Emphasizing real-world deployments, we consider both cross-subject generalization under a leave-one-subject-out protocol and rapid calibration under a within-subject few-shot setting. We further compare full-parameter fine-tuning with linear probing to assess the transferability of pre-trained representations, and examine the relationship between model scale and downstream performance. Our results indicate that: 1) linear probing is frequently insufficient; 2) specialist models trained from scratch remain competitive across many tasks; and, 3) larger foundation models do not necessarily yield better generalization performance under current data regimes and training practices.
RAICL: Retrieval-Augmented In-Context Learning for Vision-Language-Model Based EEG Seizure Detection
Jan 25, 2026Abstract:Electroencephalogram (EEG) decoding is a critical component of medical diagnostics, rehabilitation engineering, and brain-computer interfaces. However, contemporary decoding methodologies remain heavily dependent on task-specific datasets to train specialized neural network architectures. Consequently, limited data availability impedes the development of generalizable large brain decoding models. In this work, we propose a paradigm shift from conventional signal-based decoding by leveraging large-scale vision-language models (VLMs) to analyze EEG waveform plots. By converting multivariate EEG signals into stacked waveform images and integrating neuroscience domain expertise into textual prompts, we demonstrate that foundational VLMs can effectively differentiate between different patterns in the human brain. To address the inherent non-stationarity of EEG signals, we introduce a Retrieval-Augmented In-Context Learning (RAICL) approach, which dynamically selects the most representative and relevant few-shot examples to condition the autoregressive outputs of the VLM. Experiments on EEG-based seizure detection indicate that state-of-the-art VLMs under RAICL achieved better or comparable performance with traditional time series based approaches. These findings suggest a new direction in physiological signal processing that effectively bridges the modalities of vision, language, and neural activities. Furthermore, the utilization of off-the-shelf VLMs, without the need for retraining or downstream architecture construction, offers a readily deployable solution for clinical applications.
Backpropagation-Free Test-Time Adaptation for Lightweight EEG-Based Brain-Computer Interfaces
Jan 12, 2026Abstract:Electroencephalogram (EEG)-based brain-computer interfaces (BCIs) face significant deployment challenges due to inter-subject variability, signal non-stationarity, and computational constraints. While test-time adaptation (TTA) mitigates distribution shifts under online data streams without per-use calibration sessions, existing TTA approaches heavily rely on explicitly defined loss objectives that require backpropagation for updating model parameters, which incurs computational overhead, privacy risks, and sensitivity to noisy data streams. This paper proposes Backpropagation-Free Transformations (BFT), a TTA approach for EEG decoding that eliminates such issues. BFT applies multiple sample-wise transformations of knowledge-guided augmentations or approximate Bayesian inference to each test trial, generating multiple prediction scores for a single test sample. A learning-to-rank module enhances the weighting of these predictions, enabling robust aggregation for uncertainty suppression during inference under theoretical justifications. Extensive experiments on five EEG datasets of motor imagery classification and driver drowsiness regression tasks demonstrate the effectiveness, versatility, robustness, and efficiency of BFT. This research enables lightweight plug-and-play BCIs on resource-constrained devices, broadening the real-world deployment of decoding algorithms for EEG-based BCI.
SAFE: Secure and Accurate Federated Learning for Privacy-Preserving Brain-Computer Interfaces
Jan 09, 2026Abstract:Electroencephalogram (EEG)-based brain-computer interfaces (BCIs) are widely adopted due to their efficiency and portability; however, their decoding algorithms still face multiple challenges, including inadequate generalization, adversarial vulnerability, and privacy leakage. This paper proposes Secure and Accurate FEderated learning (SAFE), a federated learning-based approach that protects user privacy by keeping data local during model training. SAFE employs local batch-specific normalization to mitigate cross-subject feature distribution shifts and hence improves model generalization. It further enhances adversarial robustness by introducing perturbations in both the input space and the parameter space through federated adversarial training and adversarial weight perturbation. Experiments on five EEG datasets from motor imagery (MI) and event-related potential (ERP) BCI paradigms demonstrated that SAFE consistently outperformed 14 state-of-the-art approaches in both decoding accuracy and adversarial robustness, while ensuring privacy protection. Notably, it even outperformed centralized training approaches that do not consider privacy protection at all. To our knowledge, SAFE is the first algorithm to simultaneously achieve high decoding accuracy, strong adversarial robustness, and reliable privacy protection without using any calibration data from the target subject, making it highly desirable for real-world BCIs.
MIRepNet: A Pipeline and Foundation Model for EEG-Based Motor Imagery Classification
Jul 27, 2025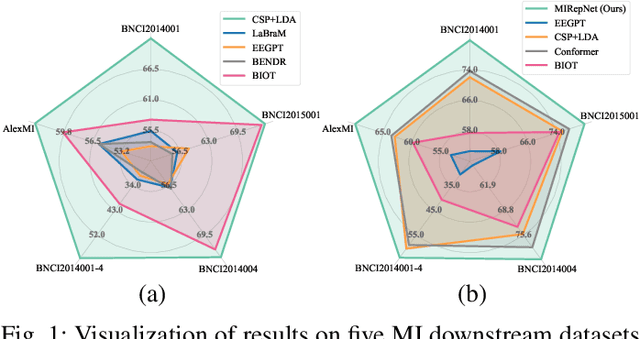
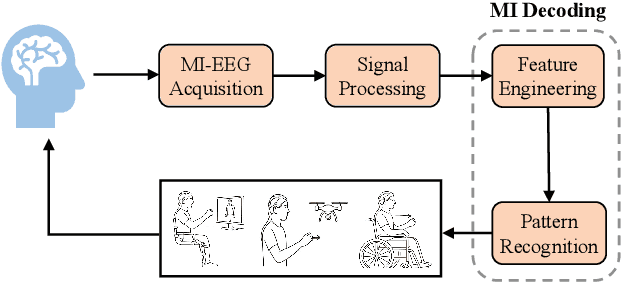
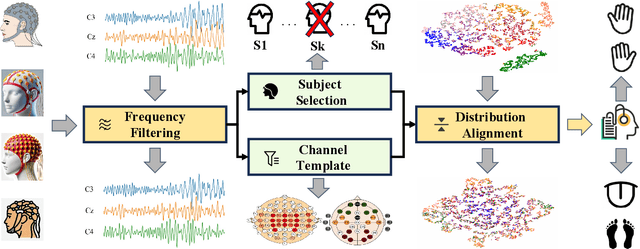
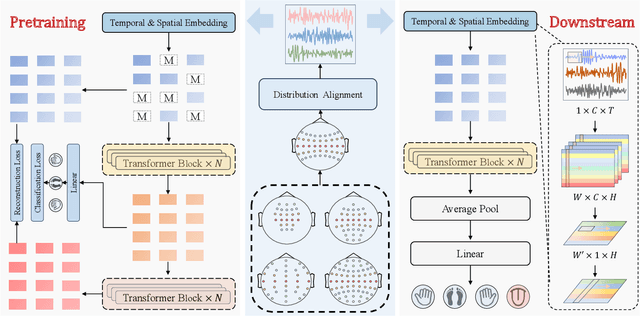
Abstract:Brain-computer interfaces (BCIs) enable direct communication between the brain and external devices. Recent EEG foundation models aim to learn generalized representations across diverse BCI paradigms. However, these approaches overlook fundamental paradigm-specific neurophysiological distinctions, limiting their generalization ability. Importantly, in practical BCI deployments, the specific paradigm such as motor imagery (MI) for stroke rehabilitation or assistive robotics, is generally determined prior to data acquisition. This paper proposes MIRepNet, the first EEG foundation model tailored for the MI paradigm. MIRepNet comprises a high-quality EEG preprocessing pipeline incorporating a neurophysiologically-informed channel template, adaptable to EEG headsets with arbitrary electrode configurations. Furthermore, we introduce a hybrid pretraining strategy that combines self-supervised masked token reconstruction and supervised MI classification, facilitating rapid adaptation and accurate decoding on novel downstream MI tasks with fewer than 30 trials per class. Extensive evaluations across five public MI datasets demonstrated that MIRepNet consistently achieved state-of-the-art performance, significantly outperforming both specialized and generalized EEG models. Our code will be available on GitHub\footnote{https://github.com/staraink/MIRepNet}.
AFPM: Alignment-based Frame Patch Modeling for Cross-Dataset EEG Decoding
Jul 16, 2025Abstract:Electroencephalogram (EEG) decoding models for brain-computer interfaces (BCIs) struggle with cross-dataset learning and generalization due to channel layout inconsistencies, non-stationary signal distributions, and limited neurophysiological prior integration. To address these issues, we propose a plug-and-play Alignment-Based Frame-Patch Modeling (AFPM) framework, which has two main components: 1) Spatial Alignment, which selects task-relevant channels based on brain-region priors, aligns EEG distributions across domains, and remaps the selected channels to a unified layout; and, 2) Frame-Patch Encoding, which models multi-dataset signals into unified spatiotemporal patches for EEG decoding. Compared to 17 state-of-the-art approaches that need dataset-specific tuning, the proposed calibration-free AFPM achieves performance gains of up to 4.40% on motor imagery and 3.58% on event-related potential tasks. To our knowledge, this is the first calibration-free cross-dataset EEG decoding framework, substantially enhancing the practicalness of BCIs in real-world applications.
Magnetoencephalography (MEG) Based Non-Invasive Chinese Speech Decoding
Jun 15, 2025Abstract:As an emerging paradigm of brain-computer interfaces (BCIs), speech BCI has the potential to directly reflect auditory perception and thoughts, offering a promising communication alternative for patients with aphasia. Chinese is one of the most widely spoken languages in the world, whereas there is very limited research on speech BCIs for Chinese language. This paper reports a text-magnetoencephalography (MEG) dataset for non-invasive Chinese speech BCIs. It also proposes a multi-modality assisted speech decoding (MASD) algorithm to capture both text and acoustic information embedded in brain signals during speech activities. Experiment results demonstrated the effectiveness of both our text-MEG dataset and our proposed MASD algorithm. To our knowledge, this is the first study on modality-assisted decoding for non-invasive speech BCIs.
CLEAN-MI: A Scalable and Efficient Pipeline for Constructing High-Quality Neurodata in Motor Imagery Paradigm
Jun 13, 2025Abstract:The construction of large-scale, high-quality datasets is a fundamental prerequisite for developing robust and generalizable foundation models in motor imagery (MI)-based brain-computer interfaces (BCIs). However, EEG signals collected from different subjects and devices are often plagued by low signal-to-noise ratio, heterogeneity in electrode configurations, and substantial inter-subject variability, posing significant challenges for effective model training. In this paper, we propose CLEAN-MI, a scalable and systematic data construction pipeline for constructing large-scale, efficient, and accurate neurodata in the MI paradigm. CLEAN-MI integrates frequency band filtering, channel template selection, subject screening, and marginal distribution alignment to systematically filter out irrelevant or low-quality data and standardize multi-source EEG datasets. We demonstrate the effectiveness of CLEAN-MI on multiple public MI datasets, achieving consistent improvements in data quality and classification performance.
SACM: SEEG-Audio Contrastive Matching for Chinese Speech Decoding
May 26, 2025Abstract:Speech disorders such as dysarthria and anarthria can severely impair the patient's ability to communicate verbally. Speech decoding brain-computer interfaces (BCIs) offer a potential alternative by directly translating speech intentions into spoken words, serving as speech neuroprostheses. This paper reports an experimental protocol for Mandarin Chinese speech decoding BCIs, along with the corresponding decoding algorithms. Stereo-electroencephalography (SEEG) and synchronized audio data were collected from eight drug-resistant epilepsy patients as they conducted a word-level reading task. The proposed SEEG and Audio Contrastive Matching (SACM), a contrastive learning-based framework, achieved decoding accuracies significantly exceeding chance levels in both speech detection and speech decoding tasks. Electrode-wise analysis revealed that a single sensorimotor cortex electrode achieved performance comparable to that of the full electrode array. These findings provide valuable insights for developing more accurate online speech decoding BCIs.
CMCRD: Cross-Modal Contrastive Representation Distillation for Emotion Recognition
Apr 12, 2025



Abstract:Emotion recognition is an important component of affective computing, and also human-machine interaction. Unimodal emotion recognition is convenient, but the accuracy may not be high enough; on the contrary, multi-modal emotion recognition may be more accurate, but it also increases the complexity and cost of the data collection system. This paper considers cross-modal emotion recognition, i.e., using both electroencephalography (EEG) and eye movement in training, but only EEG or eye movement in test. We propose cross-modal contrastive representation distillation (CMCRD), which uses a pre-trained eye movement classification model to assist the training of an EEG classification model, improving feature extraction from EEG signals, or vice versa. During test, only EEG signals (or eye movement signals) are acquired, eliminating the need for multi-modal data. CMCRD not only improves the emotion recognition accuracy, but also makes the system more simplified and practical. Experiments using three different neural network architectures on three multi-modal emotion recognition datasets demonstrated the effectiveness of CMCRD. Compared with the EEG-only model, it improved the average classification accuracy by about 6.2%.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge