Jiayu An
EEG Foundation Models: Progresses, Benchmarking, and Open Problems
Jan 25, 2026Abstract:Electroencephalography (EEG) foundation models have recently emerged as a promising paradigm for brain-computer interfaces (BCIs), aiming to learn transferable neural representations from large-scale heterogeneous recordings. Despite rapid progresses, there lacks fair and comprehensive comparisons of existing EEG foundation models, due to inconsistent pre-training objectives, preprocessing choices, and downstream evaluation protocols. This paper fills this gap. We first review 50 representative models and organize their design choices into a unified taxonomic framework including data standardization, model architectures, and self-supervised pre-training strategies. We then evaluate 12 open-source foundation models and competitive specialist baselines across 13 EEG datasets spanning nine BCI paradigms. Emphasizing real-world deployments, we consider both cross-subject generalization under a leave-one-subject-out protocol and rapid calibration under a within-subject few-shot setting. We further compare full-parameter fine-tuning with linear probing to assess the transferability of pre-trained representations, and examine the relationship between model scale and downstream performance. Our results indicate that: 1) linear probing is frequently insufficient; 2) specialist models trained from scratch remain competitive across many tasks; and, 3) larger foundation models do not necessarily yield better generalization performance under current data regimes and training practices.
Magnetoencephalography (MEG) Based Non-Invasive Chinese Speech Decoding
Jun 15, 2025Abstract:As an emerging paradigm of brain-computer interfaces (BCIs), speech BCI has the potential to directly reflect auditory perception and thoughts, offering a promising communication alternative for patients with aphasia. Chinese is one of the most widely spoken languages in the world, whereas there is very limited research on speech BCIs for Chinese language. This paper reports a text-magnetoencephalography (MEG) dataset for non-invasive Chinese speech BCIs. It also proposes a multi-modality assisted speech decoding (MASD) algorithm to capture both text and acoustic information embedded in brain signals during speech activities. Experiment results demonstrated the effectiveness of both our text-MEG dataset and our proposed MASD algorithm. To our knowledge, this is the first study on modality-assisted decoding for non-invasive speech BCIs.
Knowledge-Data Fusion Based Source-Free Semi-Supervised Domain Adaptation for Seizure Subtype Classification
Nov 29, 2024Abstract:Electroencephalogram (EEG)-based seizure subtype classification enhances clinical diagnosis efficiency. Source-free semi-supervised domain adaptation (SF-SSDA), which transfers a pre-trained model to a new dataset with no source data and limited labeled target data, can be used for privacy-preserving seizure subtype classification. This paper considers two challenges in SF-SSDA for EEG-based seizure subtype classification: 1) How to effectively fuse both raw EEG data and expert knowledge in classifier design? 2) How to align the source and target domain distributions for SF-SSDA? We propose a Knowledge-Data Fusion based SF-SSDA approach, KDF-MutualSHOT, for EEG-based seizure subtype classification. In source model training, KDF uses Jensen-Shannon Divergence to facilitate mutual learning between a feature-driven Decision Tree-based model and a data-driven Transformer-based model. To adapt KDF to a new target dataset, an SF-SSDA algorithm, MutualSHOT, is developed, which features a consistency-based pseudo-label selection strategy. Experiments on the public TUSZ and CHSZ datasets demonstrated that KDF-MutualSHOT outperformed other supervised and source-free domain adaptation approaches in cross-subject seizure subtype classification.
Mixture-of-Experts for Open Set Domain Adaptation: A Dual-Space Detection Approach
Nov 01, 2023

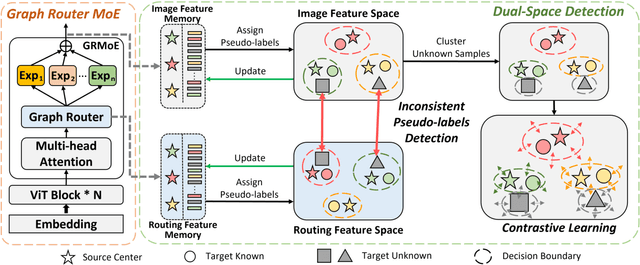

Abstract:Open Set Domain Adaptation (OSDA) aims to cope with the distribution and label shifts between the source and target domains simultaneously, performing accurate classification for known classes while identifying unknown class samples in the target domain. Most existing OSDA approaches, depending on the final image feature space of deep models, require manually-tuned thresholds, and may easily misclassify unknown samples as known classes. Mixture-of-Expert (MoE) could be a remedy. Within an MoE, different experts address different input features, producing unique expert routing patterns for different classes in a routing feature space. As a result, unknown class samples may also display different expert routing patterns to known classes. This paper proposes Dual-Space Detection, which exploits the inconsistencies between the image feature space and the routing feature space to detect unknown class samples without any threshold. Graph Router is further introduced to better make use of the spatial information among image patches. Experiments on three different datasets validated the effectiveness and superiority of our approach. The code will come soon.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge