Fadi Nahab
KERAP: A Knowledge-Enhanced Reasoning Approach for Accurate Zero-shot Diagnosis Prediction Using Multi-agent LLMs
Jul 03, 2025



Abstract:Medical diagnosis prediction plays a critical role in disease detection and personalized healthcare. While machine learning (ML) models have been widely adopted for this task, their reliance on supervised training limits their ability to generalize to unseen cases, particularly given the high cost of acquiring large, labeled datasets. Large language models (LLMs) have shown promise in leveraging language abilities and biomedical knowledge for diagnosis prediction. However, they often suffer from hallucinations, lack structured medical reasoning, and produce useless outputs. To address these challenges, we propose KERAP, a knowledge graph (KG)-enhanced reasoning approach that improves LLM-based diagnosis prediction through a multi-agent architecture. Our framework consists of a linkage agent for attribute mapping, a retrieval agent for structured knowledge extraction, and a prediction agent that iteratively refines diagnosis predictions. Experimental results demonstrate that KERAP enhances diagnostic reliability efficiently, offering a scalable and interpretable solution for zero-shot medical diagnosis prediction.
PromptLink: Leveraging Large Language Models for Cross-Source Biomedical Concept Linking
May 13, 2024



Abstract:Linking (aligning) biomedical concepts across diverse data sources enables various integrative analyses, but it is challenging due to the discrepancies in concept naming conventions. Various strategies have been developed to overcome this challenge, such as those based on string-matching rules, manually crafted thesauri, and machine learning models. However, these methods are constrained by limited prior biomedical knowledge and can hardly generalize beyond the limited amounts of rules, thesauri, or training samples. Recently, large language models (LLMs) have exhibited impressive results in diverse biomedical NLP tasks due to their unprecedentedly rich prior knowledge and strong zero-shot prediction abilities. However, LLMs suffer from issues including high costs, limited context length, and unreliable predictions. In this research, we propose PromptLink, a novel biomedical concept linking framework that leverages LLMs. It first employs a biomedical-specialized pre-trained language model to generate candidate concepts that can fit in the LLM context windows. Then it utilizes an LLM to link concepts through two-stage prompts, where the first-stage prompt aims to elicit the biomedical prior knowledge from the LLM for the concept linking task and the second-stage prompt enforces the LLM to reflect on its own predictions to further enhance their reliability. Empirical results on the concept linking task between two EHR datasets and an external biomedical KG demonstrate the effectiveness of PromptLink. Furthermore, PromptLink is a generic framework without reliance on additional prior knowledge, context, or training data, making it well-suited for concept linking across various types of data sources. The source code is available at https://github.com/constantjxyz/PromptLink.
SQUWA: Signal Quality Aware DNN Architecture for Enhanced Accuracy in Atrial Fibrillation Detection from Noisy PPG Signals
Apr 15, 2024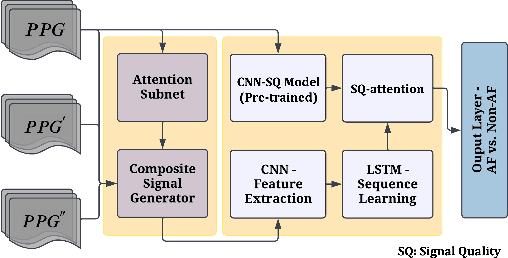
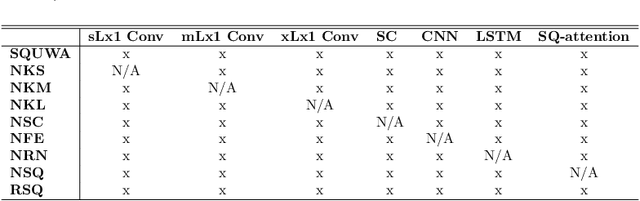
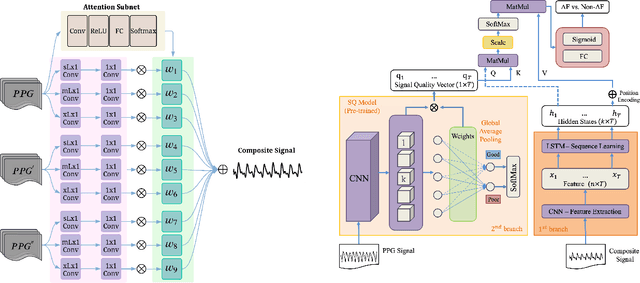
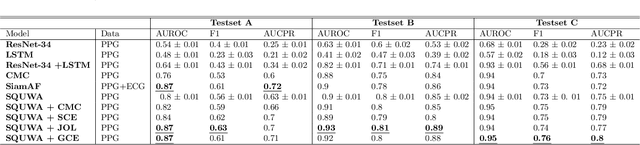
Abstract:Atrial fibrillation (AF), a common cardiac arrhythmia, significantly increases the risk of stroke, heart disease, and mortality. Photoplethysmography (PPG) offers a promising solution for continuous AF monitoring, due to its cost efficiency and integration into wearable devices. Nonetheless, PPG signals are susceptible to corruption from motion artifacts and other factors often encountered in ambulatory settings. Conventional approaches typically discard corrupted segments or attempt to reconstruct original signals, allowing for the use of standard machine learning techniques. However, this reduces dataset size and introduces biases, compromising prediction accuracy and the effectiveness of continuous monitoring. We propose a novel deep learning model, Signal Quality Weighted Fusion of Attentional Convolution and Recurrent Neural Network (SQUWA), designed to learn how to retain accurate predictions from partially corrupted PPG. Specifically, SQUWA innovatively integrates an attention mechanism that directly considers signal quality during the learning process, dynamically adjusting the weights of time series segments based on their quality. This approach enhances the influence of higher-quality segments while reducing that of lower-quality ones, effectively utilizing partially corrupted segments. This approach represents a departure from the conventional methods that exclude such segments, enabling the utilization of a broader range of data, which has great implications for less disruption when monitoring of AF risks and more accurate estimation of AF burdens. Our extensive experiments show that SQUWA outperform existing PPG-based models, achieving the highest AUCPR of 0.89 with label noise mitigation. This also exceeds the 0.86 AUCPR of models trained with using both electrocardiogram (ECG) and PPG data.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge