Sixue Xing
ClinicalReTrial: A Self-Evolving AI Agent for Clinical Trial Protocol Optimization
Jan 01, 2026Abstract:Clinical trial failure remains a central bottleneck in drug development, where minor protocol design flaws can irreversibly compromise outcomes despite promising therapeutics. Although cutting-edge AI methods achieve strong performance in predicting trial success, they are inherently reactive for merely diagnosing risk without offering actionable remedies once failure is anticipated. To fill this gap, this paper proposes ClinicalReTrial, a self-evolving AI agent framework that addresses this gap by casting clinical trial reasoning as an iterative protocol redesign problem. Our method integrates failure diagnosis, safety-aware modification, and candidate evaluation in a closed-loop, reward-driven optimization framework. Serving the outcome prediction model as a simulation environment, ClinicalReTrial enables low-cost evaluation of protocol modifications and provides dense reward signals for continuous self-improvement. To support efficient exploration, the framework maintains hierarchical memory that captures iteration-level feedback within trials and distills transferable redesign patterns across trials. Empirically, ClinicalReTrial improves 83.3% of trial protocols with a mean success probability gain of 5.7%, and retrospective case studies demonstrate strong alignment between the discovered redesign strategies and real-world clinical trial modifications.
PIANIST: Learning Partially Observable World Models with LLMs for Multi-Agent Decision Making
Nov 24, 2024



Abstract:Effective extraction of the world knowledge in LLMs for complex decision-making tasks remains a challenge. We propose a framework PIANIST for decomposing the world model into seven intuitive components conducive to zero-shot LLM generation. Given only the natural language description of the game and how input observations are formatted, our method can generate a working world model for fast and efficient MCTS simulation. We show that our method works well on two different games that challenge the planning and decision making skills of the agent for both language and non-language based action taking, without any training on domain-specific training data or explicitly defined world model.
BioMamba: A Pre-trained Biomedical Language Representation Model Leveraging Mamba
Aug 05, 2024
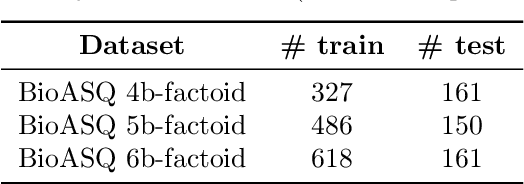
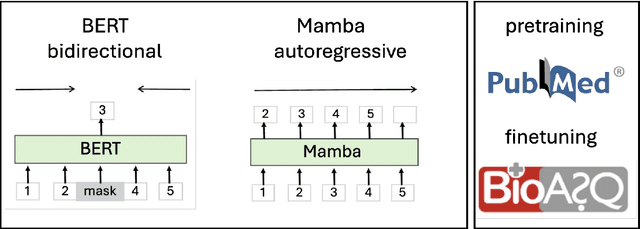
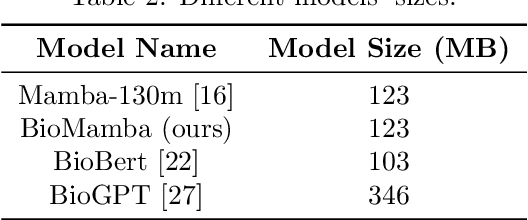
Abstract:The advancement of natural language processing (NLP) in biology hinges on models' ability to interpret intricate biomedical literature. Traditional models often struggle with the complex and domain-specific language in this field. In this paper, we present BioMamba, a pre-trained model specifically designed for biomedical text mining. BioMamba builds upon the Mamba architecture and is pre-trained on an extensive corpus of biomedical literature. Our empirical studies demonstrate that BioMamba significantly outperforms models like BioBERT and general-domain Mamba across various biomedical tasks. For instance, BioMamba achieves a 100 times reduction in perplexity and a 4 times reduction in cross-entropy loss on the BioASQ test set. We provide an overview of the model architecture, pre-training process, and fine-tuning techniques. Additionally, we release the code and trained model to facilitate further research.
TrialEnroll: Predicting Clinical Trial Enrollment Success with Deep & Cross Network and Large Language Models
Jul 18, 2024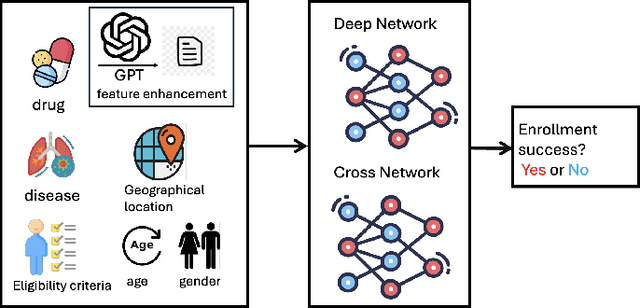

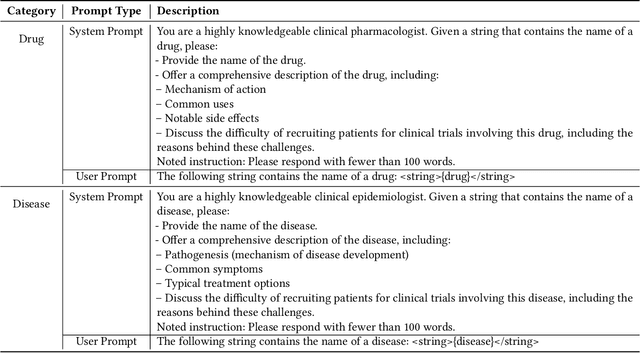
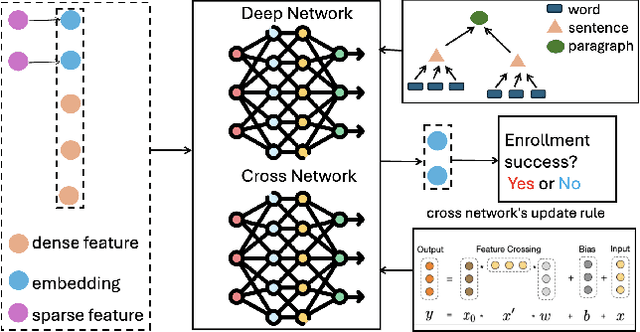
Abstract:Clinical trials need to recruit a sufficient number of volunteer patients to demonstrate the statistical power of the treatment (e.g., a new drug) in curing a certain disease. Clinical trial recruitment has a significant impact on trial success. Forecasting whether the recruitment process would be successful before we run the trial would save many resources and time. This paper develops a novel deep & cross network with large language model (LLM)-augmented text feature that learns semantic information from trial eligibility criteria and predicts enrollment success. The proposed method enables interpretability by understanding which sentence/word in eligibility criteria contributes heavily to prediction. We also demonstrate the empirical superiority of the proposed method (0.7002 PR-AUC) over a bunch of well-established machine learning methods. The code and curated dataset are publicly available at https://anonymous.4open.science/r/TrialEnroll-7E12.
On the Robustness of Language Models for Tabular Question Answering
Jun 18, 2024



Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs), originally shown to ace various text comprehension tasks have also remarkably been shown to tackle table comprehension tasks without specific training. While previous research has explored LLM capabilities with tabular dataset tasks, our study assesses the influence of $\textit{in-context learning}$,$ \textit{model scale}$, $\textit{instruction tuning}$, and $\textit{domain biases}$ on Tabular Question Answering (TQA). We evaluate the robustness of LLMs on Wikipedia-based $\textbf{WTQ}$ and financial report-based $\textbf{TAT-QA}$ TQA datasets, focusing on their ability to robustly interpret tabular data under various augmentations and perturbations. Our findings indicate that instructions significantly enhance performance, with recent models like Llama3 exhibiting greater robustness over earlier versions. However, data contamination and practical reliability issues persist, especially with WTQ. We highlight the need for improved methodologies, including structure-aware self-attention mechanisms and better handling of domain-specific tabular data, to develop more reliable LLMs for table comprehension.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge