Qiang Yang
WeBank, China, Hong Kong University of Science and Technology, China
FedGRPO: Privately Optimizing Foundation Models with Group-Relative Rewards from Domain Client
Feb 12, 2026Abstract:One important direction of Federated Foundation Models (FedFMs) is leveraging data from small client models to enhance the performance of a large server-side foundation model. Existing methods based on model level or representation level knowledge transfer either require expensive local training or incur high communication costs and introduce unavoidable privacy risks. We reformulate this problem as a reinforcement learning style evaluation process and propose FedGRPO, a privacy preserving framework comprising two modules. The first module performs competence-based expert selection by building a lightweight confidence graph from auxiliary data to identify the most suitable clients for each question. The second module leverages the "Group Relative" concept from the Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO) framework by packaging each question together with its solution rationale into candidate policies, dispatching these policies to a selected subset of expert clients, and aggregating solely the resulting scalar reward signals via a federated group-relative loss function. By exchanging reward values instead of data or model updates, FedGRPO reduces privacy risk and communication overhead while enabling parallel evaluation across heterogeneous devices. Empirical results on diverse domain tasks demonstrate that FedGRPO achieves superior downstream accuracy and communication efficiency compared to conventional FedFMs baselines.
Rethinking LoRA for Data Heterogeneous Federated Learning: Subspace and State Alignment
Feb 02, 2026Abstract:Low-Rank Adaptation (LoRA) is widely used for federated fine-tuning. Yet under non-IID settings, it can substantially underperform full-parameter fine-tuning. Through with-high-probability robustness analysis, we uncover that this gap can be attributed to two coupled mismatches: (i) update-space mismatch, where clients optimize in a low-rank subspace but aggregation occurs in the full space; and (ii) optimizer-state mismatch, where unsynchronized adaptive states amplify drift across rounds. We propose FedGaLore, which combines client-side GaLore-style gradient-subspace optimization with server-side drift-robust synchronization of projected second-moment states via spectral shared-signal extraction, to address this challenge. Across NLU, vision, and NLG benchmarks, FedGaLore improves robustness and accuracy over state-of-the-art federated LoRA baselines in non-IID settings.
MFC-RFNet: A Multi-scale Guided Rectified Flow Network for Radar Sequence Prediction
Jan 07, 2026Abstract:Accurate and high-resolution precipitation nowcasting from radar echo sequences is crucial for disaster mitigation and economic planning, yet it remains a significant challenge. Key difficulties include modeling complex multi-scale evolution, correcting inter-frame feature misalignment caused by displacement, and efficiently capturing long-range spatiotemporal context without sacrificing spatial fidelity. To address these issues, we present the Multi-scale Feature Communication Rectified Flow (RF) Network (MFC-RFNet), a generative framework that integrates multi-scale communication with guided feature fusion. To enhance multi-scale fusion while retaining fine detail, a Wavelet-Guided Skip Connection (WGSC) preserves high-frequency components, and a Feature Communication Module (FCM) promotes bidirectional cross-scale interaction. To correct inter-frame displacement, a Condition-Guided Spatial Transform Fusion (CGSTF) learns spatial transforms from conditioning echoes to align shallow features. The backbone adopts rectified flow training to learn near-linear probability-flow trajectories, enabling few-step sampling with stable fidelity. Additionally, lightweight Vision-RWKV (RWKV) blocks are placed at the encoder tail, the bottleneck, and the first decoder layer to capture long-range spatiotemporal dependencies at low spatial resolutions with moderate compute. Evaluations on four public datasets (SEVIR, MeteoNet, Shanghai, and CIKM) demonstrate consistent improvements over strong baselines, yielding clearer echo morphology at higher rain-rate thresholds and sustained skill at longer lead times. These results suggest that the proposed synergy of RF training with scale-aware communication, spatial alignment, and frequency-aware fusion presents an effective and robust approach for radar-based nowcasting.
Oblivionis: A Lightweight Learning and Unlearning Framework for Federated Large Language Models
Aug 12, 2025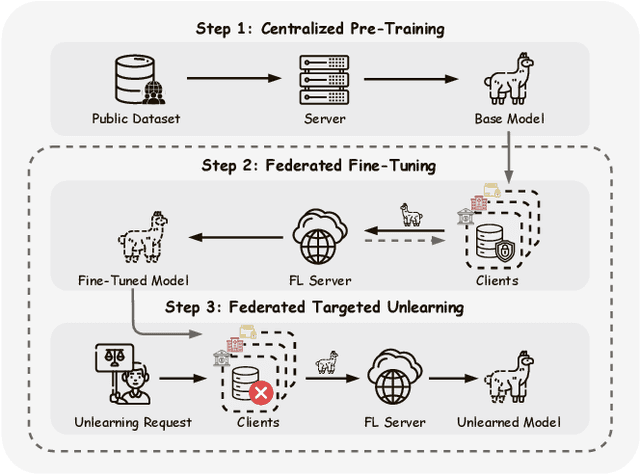
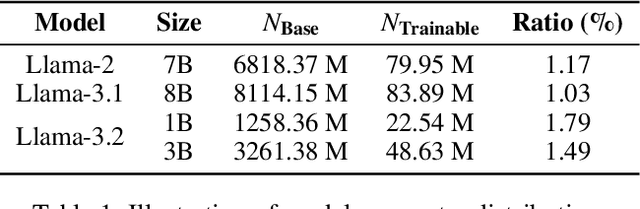
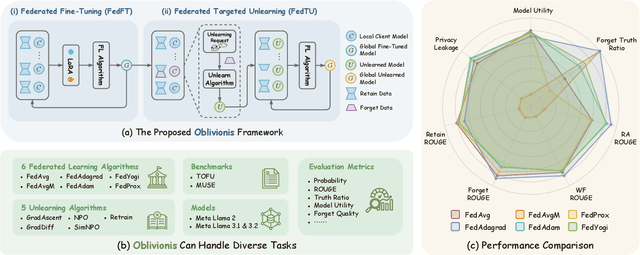
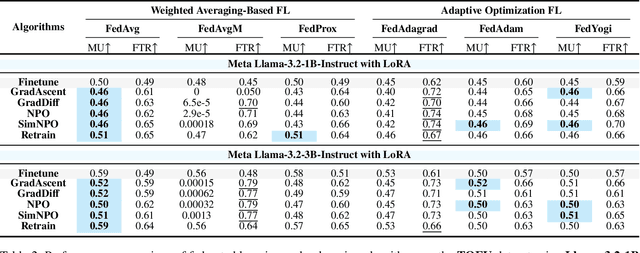
Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) increasingly leverage Federated Learning (FL) to utilize private, task-specific datasets for fine-tuning while preserving data privacy. However, while federated LLM frameworks effectively enable collaborative training without raw data sharing, they critically lack built-in mechanisms for regulatory compliance like GDPR's right to be forgotten. Integrating private data heightens concerns over data quality and long-term governance, yet existing distributed training frameworks offer no principled way to selectively remove specific client contributions post-training. Due to distributed data silos, stringent privacy constraints, and the intricacies of interdependent model aggregation, federated LLM unlearning is significantly more complex than centralized LLM unlearning. To address this gap, we introduce Oblivionis, a lightweight learning and unlearning framework that enables clients to selectively remove specific private data during federated LLM training, enhancing trustworthiness and regulatory compliance. By unifying FL and unlearning as a dual optimization objective, we incorporate 6 FL and 5 unlearning algorithms for comprehensive evaluation and comparative analysis, establishing a robust pipeline for federated LLM unlearning. Extensive experiments demonstrate that Oblivionis outperforms local training, achieving a robust balance between forgetting efficacy and model utility, with cross-algorithm comparisons providing clear directions for future LLM development.
The Starlink Robot: A Platform and Dataset for Mobile Satellite Communication
Jun 24, 2025Abstract:The integration of satellite communication into mobile devices represents a paradigm shift in connectivity, yet the performance characteristics under motion and environmental occlusion remain poorly understood. We present the Starlink Robot, the first mobile robotic platform equipped with Starlink satellite internet, comprehensive sensor suite including upward-facing camera, LiDAR, and IMU, designed to systematically study satellite communication performance during movement. Our multi-modal dataset captures synchronized communication metrics, motion dynamics, sky visibility, and 3D environmental context across diverse scenarios including steady-state motion, variable speeds, and different occlusion conditions. This platform and dataset enable researchers to develop motion-aware communication protocols, predict connectivity disruptions, and optimize satellite communication for emerging mobile applications from smartphones to autonomous vehicles. The project is available at https://github.com/StarlinkRobot.
HtFLlib: A Comprehensive Heterogeneous Federated Learning Library and Benchmark
Jun 04, 2025Abstract:As AI evolves, collaboration among heterogeneous models helps overcome data scarcity by enabling knowledge transfer across institutions and devices. Traditional Federated Learning (FL) only supports homogeneous models, limiting collaboration among clients with heterogeneous model architectures. To address this, Heterogeneous Federated Learning (HtFL) methods are developed to enable collaboration across diverse heterogeneous models while tackling the data heterogeneity issue at the same time. However, a comprehensive benchmark for standardized evaluation and analysis of the rapidly growing HtFL methods is lacking. Firstly, the highly varied datasets, model heterogeneity scenarios, and different method implementations become hurdles to making easy and fair comparisons among HtFL methods. Secondly, the effectiveness and robustness of HtFL methods are under-explored in various scenarios, such as the medical domain and sensor signal modality. To fill this gap, we introduce the first Heterogeneous Federated Learning Library (HtFLlib), an easy-to-use and extensible framework that integrates multiple datasets and model heterogeneity scenarios, offering a robust benchmark for research and practical applications. Specifically, HtFLlib integrates (1) 12 datasets spanning various domains, modalities, and data heterogeneity scenarios; (2) 40 model architectures, ranging from small to large, across three modalities; (3) a modularized and easy-to-extend HtFL codebase with implementations of 10 representative HtFL methods; and (4) systematic evaluations in terms of accuracy, convergence, computation costs, and communication costs. We emphasize the advantages and potential of state-of-the-art HtFL methods and hope that HtFLlib will catalyze advancing HtFL research and enable its broader applications. The code is released at https://github.com/TsingZ0/HtFLlib.
INFERENCEDYNAMICS: Efficient Routing Across LLMs through Structured Capability and Knowledge Profiling
May 22, 2025


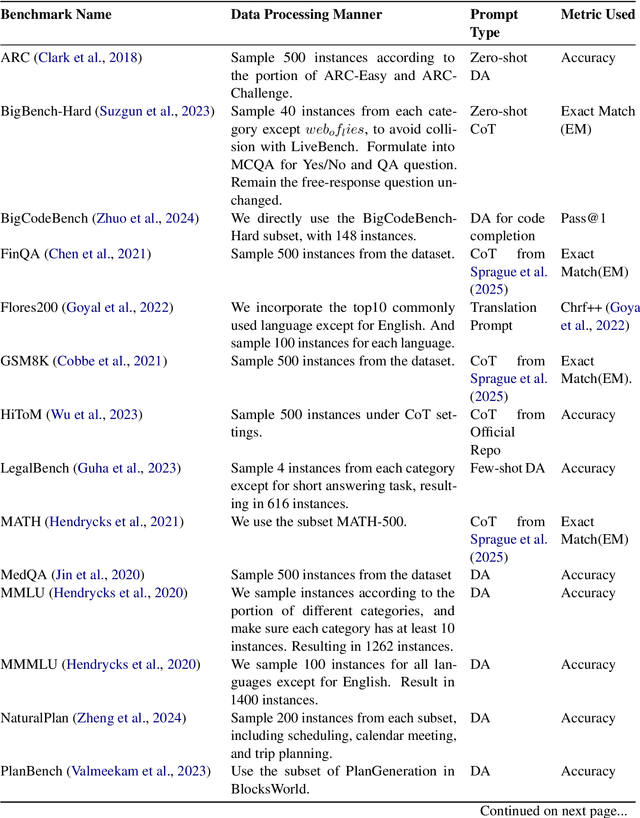
Abstract:Large Language Model (LLM) routing is a pivotal technique for navigating a diverse landscape of LLMs, aiming to select the best-performing LLMs tailored to the domains of user queries, while managing computational resources. However, current routing approaches often face limitations in scalability when dealing with a large pool of specialized LLMs, or in their adaptability to extending model scope and evolving capability domains. To overcome those challenges, we propose InferenceDynamics, a flexible and scalable multi-dimensional routing framework by modeling the capability and knowledge of models. We operate it on our comprehensive dataset RouteMix, and demonstrate its effectiveness and generalizability in group-level routing using modern benchmarks including MMLU-Pro, GPQA, BigGenBench, and LiveBench, showcasing its ability to identify and leverage top-performing models for given tasks, leading to superior outcomes with efficient resource utilization. The broader adoption of Inference Dynamics can empower users to harness the full specialized potential of the LLM ecosystem, and our code will be made publicly available to encourage further research.
Towards Multi-Agent Reasoning Systems for Collaborative Expertise Delegation: An Exploratory Design Study
May 12, 2025Abstract:Designing effective collaboration structure for multi-agent LLM systems to enhance collective reasoning is crucial yet remains under-explored. In this paper, we systematically investigate how collaborative reasoning performance is affected by three key design dimensions: (1) Expertise-Domain Alignment, (2) Collaboration Paradigm (structured workflow vs. diversity-driven integration), and (3) System Scale. Our findings reveal that expertise alignment benefits are highly domain-contingent, proving most effective for contextual reasoning tasks. Furthermore, collaboration focused on integrating diverse knowledge consistently outperforms rigid task decomposition. Finally, we empirically explore the impact of scaling the multi-agent system with expertise specialization and study the computational trade off, highlighting the need for more efficient communication protocol design. This work provides concrete guidelines for configuring specialized multi-agent system and identifies critical architectural trade-offs and bottlenecks for scalable multi-agent reasoning. The code will be made available upon acceptance.
Towards Harnessing the Collaborative Power of Large and Small Models for Domain Tasks
Apr 24, 2025Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have demonstrated remarkable capabilities, but they require vast amounts of data and computational resources. In contrast, smaller models (SMs), while less powerful, can be more efficient and tailored to specific domains. In this position paper, we argue that taking a collaborative approach, where large and small models work synergistically, can accelerate the adaptation of LLMs to private domains and unlock new potential in AI. We explore various strategies for model collaboration and identify potential challenges and opportunities. Building upon this, we advocate for industry-driven research that prioritizes multi-objective benchmarks on real-world private datasets and applications.
Advances and Challenges in Foundation Agents: From Brain-Inspired Intelligence to Evolutionary, Collaborative, and Safe Systems
Mar 31, 2025Abstract:The advent of large language models (LLMs) has catalyzed a transformative shift in artificial intelligence, paving the way for advanced intelligent agents capable of sophisticated reasoning, robust perception, and versatile action across diverse domains. As these agents increasingly drive AI research and practical applications, their design, evaluation, and continuous improvement present intricate, multifaceted challenges. This survey provides a comprehensive overview, framing intelligent agents within a modular, brain-inspired architecture that integrates principles from cognitive science, neuroscience, and computational research. We structure our exploration into four interconnected parts. First, we delve into the modular foundation of intelligent agents, systematically mapping their cognitive, perceptual, and operational modules onto analogous human brain functionalities, and elucidating core components such as memory, world modeling, reward processing, and emotion-like systems. Second, we discuss self-enhancement and adaptive evolution mechanisms, exploring how agents autonomously refine their capabilities, adapt to dynamic environments, and achieve continual learning through automated optimization paradigms, including emerging AutoML and LLM-driven optimization strategies. Third, we examine collaborative and evolutionary multi-agent systems, investigating the collective intelligence emerging from agent interactions, cooperation, and societal structures, highlighting parallels to human social dynamics. Finally, we address the critical imperative of building safe, secure, and beneficial AI systems, emphasizing intrinsic and extrinsic security threats, ethical alignment, robustness, and practical mitigation strategies necessary for trustworthy real-world deployment.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge