Lixin Fan
WeBank, China
Order-Level Attention Similarity Across Language Models: A Latent Commonality
Nov 07, 2025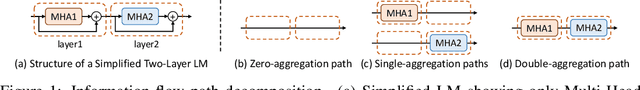
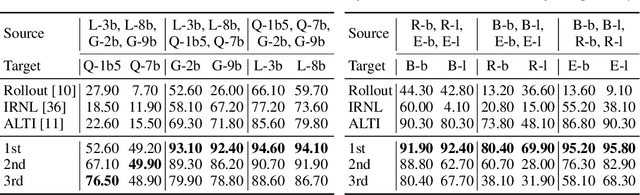
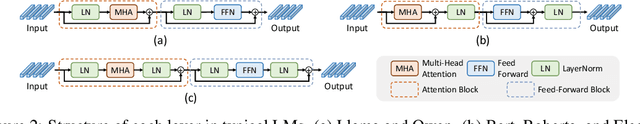
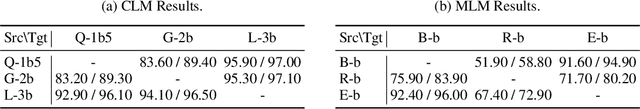
Abstract:In this paper, we explore an important yet previously neglected question: Do context aggregation patterns across Language Models (LMs) share commonalities? While some works have investigated context aggregation or attention weights in LMs, they typically focus on individual models or attention heads, lacking a systematic analysis across multiple LMs to explore their commonalities. In contrast, we focus on the commonalities among LMs, which can deepen our understanding of LMs and even facilitate cross-model knowledge transfer. In this work, we introduce the Order-Level Attention (OLA) derived from the order-wise decomposition of Attention Rollout and reveal that the OLA at the same order across LMs exhibits significant similarities. Furthermore, we discover an implicit mapping between OLA and syntactic knowledge. Based on these two findings, we propose the Transferable OLA Adapter (TOA), a training-free cross-LM adapter transfer method. Specifically, we treat the OLA as a unified syntactic feature representation and train an adapter that takes OLA as input. Due to the similarities in OLA across LMs, the adapter generalizes to unseen LMs without requiring any parameter updates. Extensive experiments demonstrate that TOA's cross-LM generalization effectively enhances the performance of unseen LMs. Code is available at https://github.com/jinglin-liang/OLAS.
PPC-GPT: Federated Task-Specific Compression of Large Language Models via Pruning and Chain-of-Thought Distillation
Feb 21, 2025



Abstract:Compressing Large Language Models (LLMs) into task-specific Small Language Models (SLMs) encounters two significant challenges: safeguarding domain-specific knowledge privacy and managing limited resources. To tackle these challenges, we propose PPC-GPT, a innovative privacy-preserving federated framework specifically designed for compressing LLMs into task-specific SLMs via pruning and Chain-of-Thought (COT) distillation. PPC-GPT works on a server-client federated architecture, where the client sends differentially private (DP) perturbed task-specific data to the server's LLM. The LLM then generates synthetic data along with their corresponding rationales. This synthetic data is subsequently used for both LLM pruning and retraining processes. Additionally, we harness COT knowledge distillation, leveraging the synthetic data to further improve the retraining of structurally-pruned SLMs. Our experimental results demonstrate the effectiveness of PPC-GPT across various text generation tasks. By compressing LLMs into task-specific SLMs, PPC-GPT not only achieves competitive performance but also prioritizes data privacy protection.
Vertical Federated Learning in Practice: The Good, the Bad, and the Ugly
Feb 12, 2025Abstract:Vertical Federated Learning (VFL) is a privacy-preserving collaborative learning paradigm that enables multiple parties with distinct feature sets to jointly train machine learning models without sharing their raw data. Despite its potential to facilitate cross-organizational collaborations, the deployment of VFL systems in real-world applications remains limited. To investigate the gap between existing VFL research and practical deployment, this survey analyzes the real-world data distributions in potential VFL applications and identifies four key findings that highlight this gap. We propose a novel data-oriented taxonomy of VFL algorithms based on real VFL data distributions. Our comprehensive review of existing VFL algorithms reveals that some common practical VFL scenarios have few or no viable solutions. Based on these observations, we outline key research directions aimed at bridging the gap between current VFL research and real-world applications.
Top Ten Challenges Towards Agentic Neural Graph Databases
Jan 24, 2025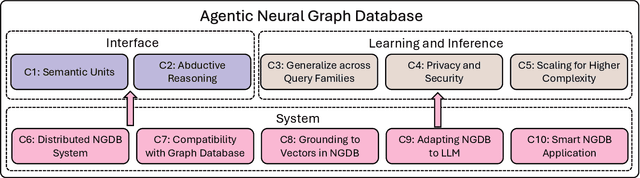
Abstract:Graph databases (GDBs) like Neo4j and TigerGraph excel at handling interconnected data but lack advanced inference capabilities. Neural Graph Databases (NGDBs) address this by integrating Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) for predictive analysis and reasoning over incomplete or noisy data. However, NGDBs rely on predefined queries and lack autonomy and adaptability. This paper introduces Agentic Neural Graph Databases (Agentic NGDBs), which extend NGDBs with three core functionalities: autonomous query construction, neural query execution, and continuous learning. We identify ten key challenges in realizing Agentic NGDBs: semantic unit representation, abductive reasoning, scalable query execution, and integration with foundation models like large language models (LLMs). By addressing these challenges, Agentic NGDBs can enable intelligent, self-improving systems for modern data-driven applications, paving the way for adaptable and autonomous data management solutions.
Addressing Spatial-Temporal Data Heterogeneity in Federated Continual Learning via Tail Anchor
Dec 24, 2024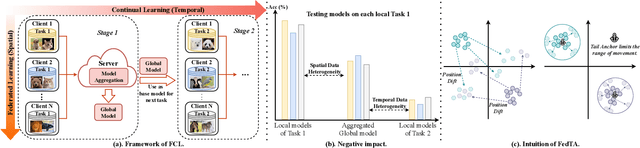
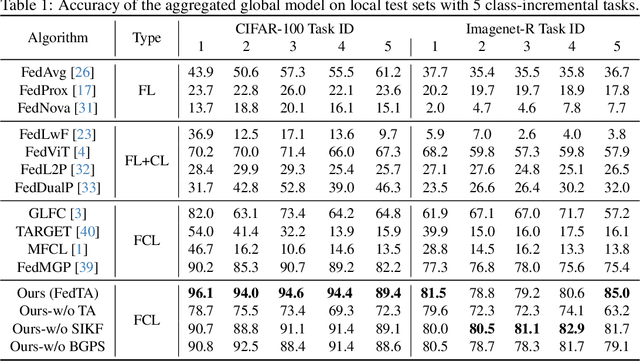
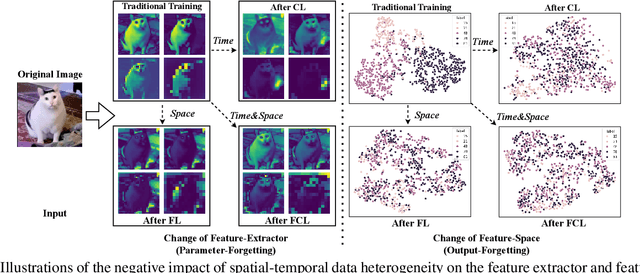
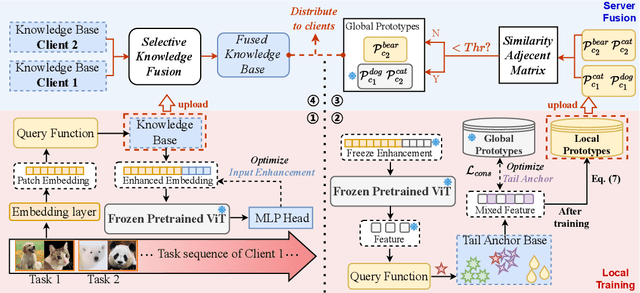
Abstract:Federated continual learning (FCL) allows each client to continually update its knowledge from task streams, enhancing the applicability of federated learning in real-world scenarios. However, FCL needs to address not only spatial data heterogeneity between clients but also temporal data heterogeneity between tasks. In this paper, empirical experiments demonstrate that such input-level heterogeneity significantly affects the model's internal parameters and outputs, leading to severe spatial-temporal catastrophic forgetting of local and previous knowledge. To this end, we propose Federated Tail Anchor (FedTA) to mix trainable Tail Anchor with the frozen output features to adjust their position in the feature space, thereby overcoming parameter-forgetting and output-forgetting. Moreover, three novel components are also included in FedTA: Input Enhancement for improving the performance of pre-trained models on downstream tasks; Selective Input Knowledge Fusion for fusion of heterogeneous local knowledge on the server side; and Best Global Prototype Selection for finding the best anchor point for each class in the feature space. Extensive experiments demonstrate that FedTA not only outperforms existing FCL methods but also effectively preserves the relative positions of features, remaining unaffected by spatial and temporal changes.
FedCoLLM: A Parameter-Efficient Federated Co-tuning Framework for Large and Small Language Models
Nov 18, 2024


Abstract:By adapting Large Language Models (LLMs) to domain-specific tasks or enriching them with domain-specific knowledge, we can fully harness the capabilities of LLMs. Nonetheless, a gap persists in achieving simultaneous mutual enhancement between the server's LLM and the downstream clients' Small Language Models (SLMs). To address this, we propose FedCoLLM, a novel and parameter-efficient federated framework designed for co-tuning LLMs and SLMs. This approach is aimed at adaptively transferring server-side LLMs knowledge to clients' SLMs while simultaneously enriching the LLMs with domain insights from the clients. To accomplish this, FedCoLLM utilizes lightweight adapters in conjunction with SLMs, facilitating knowledge exchange between server and clients in a manner that respects data privacy while also minimizing computational and communication overhead. Our evaluation of FedCoLLM, utilizing various public LLMs and SLMs across a range of NLP text generation tasks, reveals that the performance of clients' SLMs experiences notable improvements with the assistance of the LLMs. Simultaneously, the LLMs enhanced via FedCoLLM achieves comparable performance to that obtained through direct fine-tuning on clients' data.
Disentangling data distribution for Federated Learning
Oct 16, 2024Abstract:Federated Learning (FL) facilitates collaborative training of a global model whose performance is boosted by private data owned by distributed clients, without compromising data privacy. Yet the wide applicability of FL is hindered by entanglement of data distributions across different clients. This paper demonstrates for the first time that by disentangling data distributions FL can in principle achieve efficiencies comparable to those of distributed systems, requiring only one round of communication. To this end, we propose a novel FedDistr algorithm, which employs stable diffusion models to decouple and recover data distributions. Empirical results on the CIFAR100 and DomainNet datasets show that FedDistr significantly enhances model utility and efficiency in both disentangled and near-disentangled scenarios while ensuring privacy, outperforming traditional federated learning methods.
Model-Based Differentially Private Knowledge Transfer for Large Language Models
Oct 14, 2024



Abstract:As large language models (LLMs) become increasingly prevalent in web services, effectively leveraging domain-specific knowledge while ensuring privacy has become critical. Existing methods, such as retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) and differentially private data synthesis, often compromise either the utility of domain knowledge or the privacy of sensitive data, limiting their applicability in specialized domains. To address these challenges, we propose \textit{Llamdex}, a novel framework that integrates privacy-preserving, domain-specific models into LLMs. Our approach significantly enhances the accuracy of domain-specific tasks, achieving up to a 26\% improvement compared to existing methods under the same differential privacy constraints. Experimental results show that Llamdex not only improves the accuracy of LLM responses but also maintains comparable inference efficiency to the original LLM, highlighting its potential for real-world applications.
A few-shot Label Unlearning in Vertical Federated Learning
Oct 14, 2024



Abstract:This paper addresses the critical challenge of unlearning in Vertical Federated Learning (VFL), an area that has received limited attention compared to horizontal federated learning. We introduce the first approach specifically designed to tackle label unlearning in VFL, focusing on scenarios where the active party aims to mitigate the risk of label leakage. Our method leverages a limited amount of labeled data, utilizing manifold mixup to augment the forward embedding of insufficient data, followed by gradient ascent on the augmented embeddings to erase label information from the models. This combination of augmentation and gradient ascent enables high unlearning effectiveness while maintaining efficiency, completing the unlearning procedure within seconds. Extensive experiments conducted on diverse datasets, including MNIST, CIFAR10, CIFAR100, and ModelNet, validate the efficacy and scalability of our approach. This work represents a significant advancement in federated learning, addressing the unique challenges of unlearning in VFL while preserving both privacy and computational efficiency.
Diffusion-Driven Data Replay: A Novel Approach to Combat Forgetting in Federated Class Continual Learning
Sep 04, 2024Abstract:Federated Class Continual Learning (FCCL) merges the challenges of distributed client learning with the need for seamless adaptation to new classes without forgetting old ones. The key challenge in FCCL is catastrophic forgetting, an issue that has been explored to some extent in Continual Learning (CL). However, due to privacy preservation requirements, some conventional methods, such as experience replay, are not directly applicable to FCCL. Existing FCCL methods mitigate forgetting by generating historical data through federated training of GANs or data-free knowledge distillation. However, these approaches often suffer from unstable training of generators or low-quality generated data, limiting their guidance for the model. To address this challenge, we propose a novel method of data replay based on diffusion models. Instead of training a diffusion model, we employ a pre-trained conditional diffusion model to reverse-engineer each class, searching the corresponding input conditions for each class within the model's input space, significantly reducing computational resources and time consumption while ensuring effective generation. Furthermore, we enhance the classifier's domain generalization ability on generated and real data through contrastive learning, indirectly improving the representational capability of generated data for real data. Comprehensive experiments demonstrate that our method significantly outperforms existing baselines. Code is available at https://github.com/jinglin-liang/DDDR.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge