Jingyi Li
PEAR: Pixel-aligned Expressive humAn mesh Recovery
Jan 30, 2026Abstract:Reconstructing detailed 3D human meshes from a single in-the-wild image remains a fundamental challenge in computer vision. Existing SMPLX-based methods often suffer from slow inference, produce only coarse body poses, and exhibit misalignments or unnatural artifacts in fine-grained regions such as the face and hands. These issues make current approaches difficult to apply to downstream tasks. To address these challenges, we propose PEAR-a fast and robust framework for pixel-aligned expressive human mesh recovery. PEAR explicitly tackles three major limitations of existing methods: slow inference, inaccurate localization of fine-grained human pose details, and insufficient facial expression capture. Specifically, to enable real-time SMPLX parameter inference, we depart from prior designs that rely on high resolution inputs or multi-branch architectures. Instead, we adopt a clean and unified ViT-based model capable of recovering coarse 3D human geometry. To compensate for the loss of fine-grained details caused by this simplified architecture, we introduce pixel-level supervision to optimize the geometry, significantly improving the reconstruction accuracy of fine-grained human details. To make this approach practical, we further propose a modular data annotation strategy that enriches the training data and enhances the robustness of the model. Overall, PEAR is a preprocessing-free framework that can simultaneously infer EHM-s (SMPLX and scaled-FLAME) parameters at over 100 FPS. Extensive experiments on multiple benchmark datasets demonstrate that our method achieves substantial improvements in pose estimation accuracy compared to previous SMPLX-based approaches. Project page: https://wujh2001.github.io/PEAR
MelCap: A Unified Single-Codebook Neural Codec for High-Fidelity Audio Compression
Oct 02, 2025Abstract:Neural audio codecs have recently emerged as powerful tools for high-quality and low-bitrate audio compression, leveraging deep generative models to learn latent representations of audio signals. However, existing approaches either rely on a single quantizer that only processes speech domain, or on multiple quantizers that are not well suited for downstream tasks. To address this issue, we propose MelCap, a unified "one-codebook-for-all" neural codec that effectively handles speech, music, and general sound. By decomposing audio reconstruction into two stages, our method preserves more acoustic details than previous single-codebook approaches, while achieving performance comparable to mainstream multi-codebook methods. In the first stage, audio is transformed into mel-spectrograms, which are compressed and quantized into compact single tokens using a 2D tokenizer. A perceptual loss is further applied to mitigate the over-smoothing artifacts observed in spectrogram reconstruction. In the second stage, a Vocoder recovers waveforms from the mel discrete tokens in a single forward pass, enabling real-time decoding. Both objective and subjective evaluations demonstrate that MelCap achieves quality on comparable to state-of-the-art multi-codebook codecs, while retaining the computational simplicity of a single-codebook design, thereby providing an effective representation for downstream tasks.
Facilitating Longitudinal Interaction Studies of AI Systems
Aug 14, 2025Abstract:UIST researchers develop tools to address user challenges. However, user interactions with AI evolve over time through learning, adaptation, and repurposing, making one time evaluations insufficient. Capturing these dynamics requires longer-term studies, but challenges in deployment, evaluation design, and data collection have made such longitudinal research difficult to implement. Our workshop aims to tackle these challenges and prepare researchers with practical strategies for longitudinal studies. The workshop includes a keynote, panel discussions, and interactive breakout groups for discussion and hands-on protocol design and tool prototyping sessions. We seek to foster a community around longitudinal system research and promote it as a more embraced method for designing, building, and evaluating UIST tools.
Robust Super-Resolution Compressive Sensing: A Two-timescale Alternating MAP Approach
Aug 09, 2025Abstract:The problem of super-resolution compressive sensing (SR-CS) is crucial for various wireless sensing and communication applications. Existing methods often suffer from limited resolution capabilities and sensitivity to hyper-parameters, hindering their ability to accurately recover sparse signals when the grid parameters do not lie precisely on a fixed grid and are close to each other. To overcome these limitations, this paper introduces a novel robust super-resolution compressive sensing algorithmic framework using a two-timescale alternating maximum a posteriori (MAP) approach. At the slow timescale, the proposed framework iterates between a sparse signal estimation module and a grid update module. In the sparse signal estimation module, a hyperbolic-tangent prior distribution based variational Bayesian inference (tanh-VBI) algorithm with a strong sparsity promotion capability is adopted to estimate the posterior probability of the sparse vector and accurately identify active grid components carrying primary energy under a dense grid. Subsequently, the grid update module utilizes the BFGS algorithm to refine these low-dimensional active grid components at a faster timescale to achieve super-resolution estimation of the grid parameters with a low computational cost. The proposed scheme is applied to the channel extrapolation problem, and simulation results demonstrate the superiority of the proposed scheme compared to baseline schemes.
Training-Free Multi-Step Audio Source Separation
May 26, 2025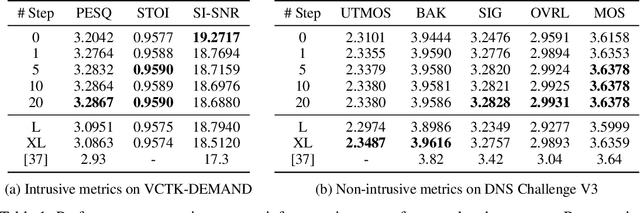
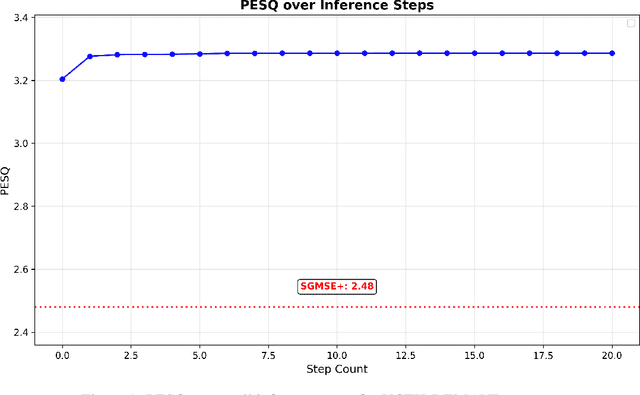
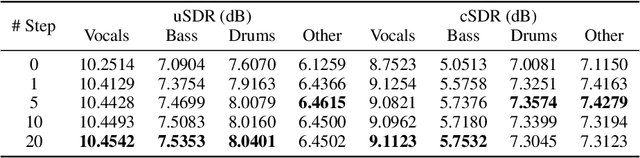
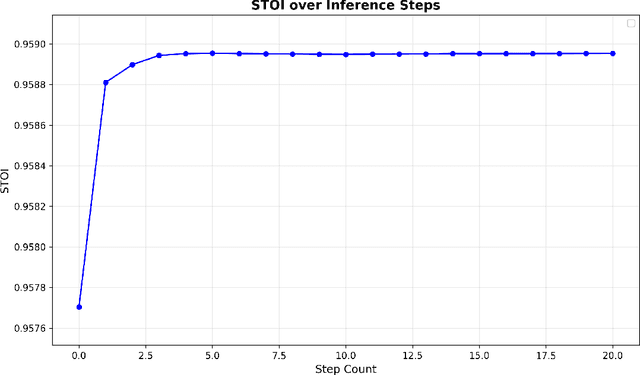
Abstract:Audio source separation aims to separate a mixture into target sources. Previous audio source separation systems usually conduct one-step inference, which does not fully explore the separation ability of models. In this work, we reveal that pretrained one-step audio source separation models can be leveraged for multi-step separation without additional training. We propose a simple yet effective inference method that iteratively applies separation by optimally blending the input mixture with the previous step's separation result. At each step, we determine the optimal blending ratio by maximizing a metric. We prove that our method always yield improvement over one-step inference, provide error bounds based on model smoothness and metric robustness, and provide theoretical analysis connecting our method to denoising along linear interpolation paths between noise and clean distributions, a property we link to denoising diffusion bridge models. Our approach effectively delivers improved separation performance as a "free lunch" from existing models. Our empirical results demonstrate that our multi-step separation approach consistently outperforms one-step inference across both speech enhancement and music source separation tasks, and can achieve scaling performance similar to training a larger model, using more data, or in some cases employing a multi-step training objective. These improvements appear not only on the optimization metric during multi-step inference, but also extend to nearly all non-optimized metrics (with one exception). We also discuss limitations of our approach and directions for future research.
Towards Harnessing the Collaborative Power of Large and Small Models for Domain Tasks
Apr 24, 2025Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have demonstrated remarkable capabilities, but they require vast amounts of data and computational resources. In contrast, smaller models (SMs), while less powerful, can be more efficient and tailored to specific domains. In this position paper, we argue that taking a collaborative approach, where large and small models work synergistically, can accelerate the adaptation of LLMs to private domains and unlock new potential in AI. We explore various strategies for model collaboration and identify potential challenges and opportunities. Building upon this, we advocate for industry-driven research that prioritizes multi-objective benchmarks on real-world private datasets and applications.
Multi-agent Application System in Office Collaboration Scenarios
Mar 26, 2025Abstract:This paper introduces a multi-agent application system designed to enhance office collaboration efficiency and work quality. The system integrates artificial intelligence, machine learning, and natural language processing technologies, achieving functionalities such as task allocation, progress monitoring, and information sharing. The agents within the system are capable of providing personalized collaboration support based on team members' needs and incorporate data analysis tools to improve decision-making quality. The paper also proposes an intelligent agent architecture that separates Plan and Solver, and through techniques such as multi-turn query rewriting and business tool retrieval, it enhances the agent's multi-intent and multi-turn dialogue capabilities. Furthermore, the paper details the design of tools and multi-turn dialogue in the context of office collaboration scenarios, and validates the system's effectiveness through experiments and evaluations. Ultimately, the system has demonstrated outstanding performance in real business applications, particularly in query understanding, task planning, and tool calling. Looking forward, the system is expected to play a more significant role in addressing complex interaction issues within dynamic environments and large-scale multi-agent systems.
Constructing a Norm for Children's Scientific Drawing: Distribution Features Based on Semantic Similarity of Large Language Models
Feb 21, 2025Abstract:The use of children's drawings to examining their conceptual understanding has been proven to be an effective method, but there are two major problems with previous research: 1. The content of the drawings heavily relies on the task, and the ecological validity of the conclusions is low; 2. The interpretation of drawings relies too much on the subjective feelings of the researchers. To address this issue, this study uses the Large Language Model (LLM) to identify 1420 children's scientific drawings (covering 9 scientific themes/concepts), and uses the word2vec algorithm to calculate their semantic similarity. The study explores whether there are consistent drawing representations for children on the same theme, and attempts to establish a norm for children's scientific drawings, providing a baseline reference for follow-up children's drawing research. The results show that the representation of most drawings has consistency, manifested as most semantic similarity greater than 0.8. At the same time, it was found that the consistency of the representation is independent of the accuracy (of LLM's recognition), indicating the existence of consistency bias. In the subsequent exploration of influencing factors, we used Kendall rank correlation coefficient to investigate the effects of Sample Size, Abstract Degree, and Focus Points on drawings, and used word frequency statistics to explore whether children represented abstract themes/concepts by reproducing what was taught in class.
Pluto and Charon: A Time and Memory Efficient Collaborative Edge AI Framework for Personal LLMs Fine-Tuning
Aug 20, 2024Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have unlocked a plethora of powerful applications at the network edge, such as intelligent personal assistants. Data privacy and security concerns have prompted a shift towards edge-based fine-tuning of personal LLMs, away from cloud reliance. However, this raises issues of computational intensity and resource scarcity, hindering training efficiency and feasibility. While current studies investigate parameter-efficient fine-tuning (PEFT) techniques to mitigate resource constraints, our analysis indicates that these techniques are not sufficiently resource-efficient for edge devices. To tackle these challenges, we propose Pluto and Charon (PAC), a time and memory efficient collaborative edge AI framework for personal LLMs fine-tuning. PAC breaks the resource wall of personal LLMs fine-tuning with a sophisticated algorithm-system co-design. (1) Algorithmically, PAC implements a personal LLMs fine-tuning technique that is efficient in terms of parameters, time, and memory. It utilizes Parallel Adapters to circumvent the need for a full backward pass through the LLM backbone. Additionally, an activation cache mechanism further streamlining the process by negating the necessity for repeated forward passes across multiple epochs. (2) Systematically, PAC leverages edge devices in close proximity, pooling them as a collective resource for in-situ personal LLMs fine-tuning, utilizing a hybrid data and pipeline parallelism to orchestrate distributed training. The use of the activation cache eliminates the need for forward pass through the LLM backbone,enabling exclusive fine-tuning of the Parallel Adapters using data parallelism. Extensive evaluation based on prototype implementation demonstrates that PAC remarkably outperforms state-of-the-art approaches, achieving up to 8.64x end-to-end speedup and up to 88.16% reduction in memory footprint.
Design and Optimization of Hierarchical Gradient Coding for Distributed Learning at Edge Devices
Jun 16, 2024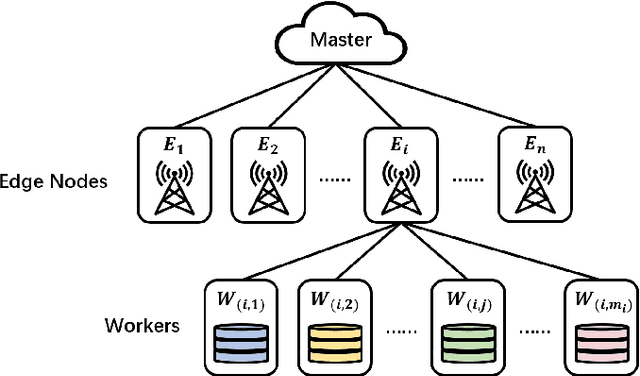
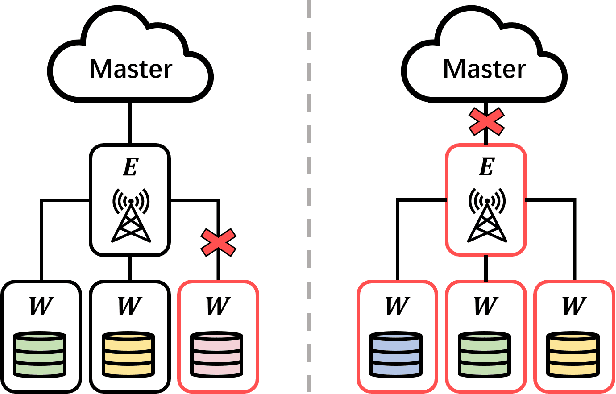
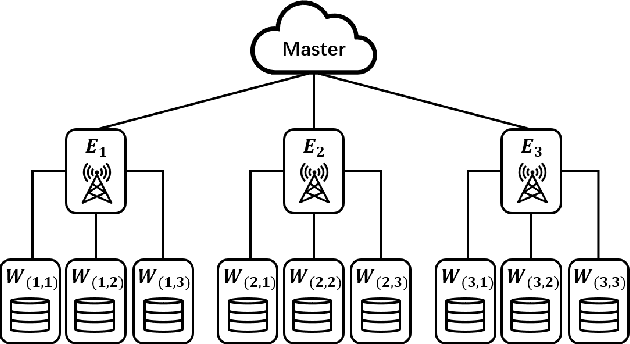

Abstract:Edge computing has recently emerged as a promising paradigm to boost the performance of distributed learning by leveraging the distributed resources at edge nodes. Architecturally, the introduction of edge nodes adds an additional intermediate layer between the master and workers in the original distributed learning systems, potentially leading to more severe straggler effect. Recently, coding theory-based approaches have been proposed for stragglers mitigation in distributed learning, but the majority focus on the conventional workers-master architecture. In this paper, along a different line, we investigate the problem of mitigating the straggler effect in hierarchical distributed learning systems with an additional layer composed of edge nodes. Technically, we first derive the fundamental trade-off between the computational loads of workers and the stragglers tolerance. Then, we propose a hierarchical gradient coding framework, which provides better stragglers mitigation, to achieve the derived computational trade-off. To further improve the performance of our framework in heterogeneous scenarios, we formulate an optimization problem with the objective of minimizing the expected execution time for each iteration in the learning process. We develop an efficient algorithm to mathematically solve the problem by outputting the optimum strategy. Extensive simulation results demonstrate the superiority of our schemes compared with conventional solutions.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge