Youngeun Kim
MC-GRPO: Median-Centered Group Relative Policy Optimization for Small-Rollout Reinforcement Learning
Jan 30, 2026Abstract:Group-relative policy optimization methods train language models by generating multiple rollouts per prompt and normalizing rewards with a shared mean reward baseline. In resource-constrained settings where the rollout budget is small, accuracy often degrades. We find that noise in the shared baseline induces advantage sign flips, where some rollouts receive an incorrect advantage sign, and the update direction is reversed. To address this, we propose Median-Centered Group Relative Policy Optimization (MC-GRPO), a simple and effective solution for small-rollout training. Our main idea is to replace the mean baseline with a median baseline: the median is far less sensitive to outlier rewards than the mean, mitigating the sign flips under small rollout size (G). We generate one additional rollout for median reference (G+1), and compute advantages by using the group median. With an odd-sized group, exactly one completion is the median and receives zero advantage, we exclude this pivot rollout from backpropagation so the number of gradient-contributing samples per prompt remains G, preserving the core update cost of standard G-rollout training. Across various GRPO-family methods and a wide range of models and scales, this median-centered training consistently improves stability and final accuracy in the low-rollout regime, reducing the gap between G=2 and G=8 to within 1%. Code is available at https://github.com/lotusroot-kim/MC-GRPO
Task Vector Quantization for Memory-Efficient Model Merging
Mar 10, 2025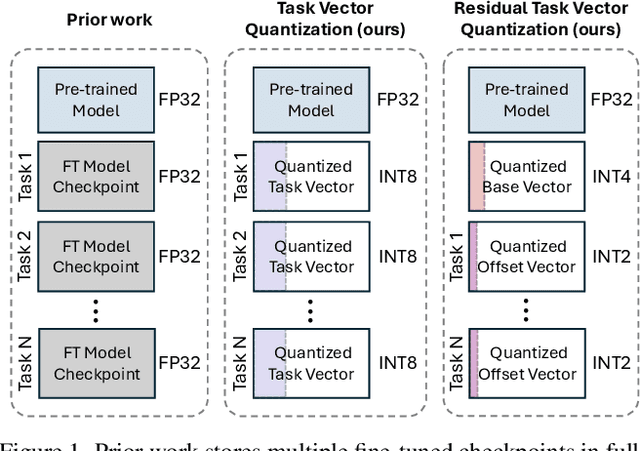
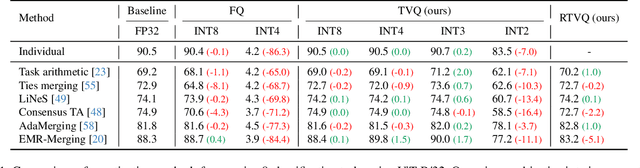
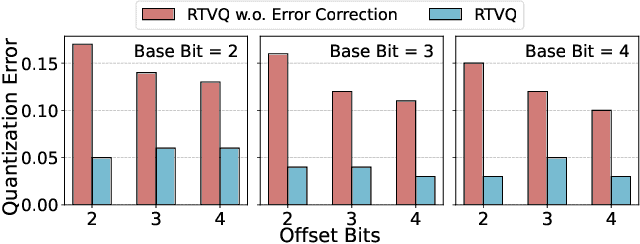
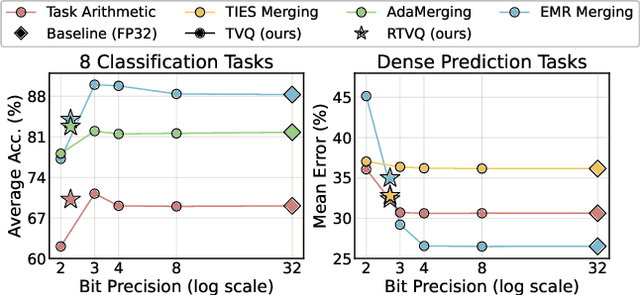
Abstract:Model merging enables efficient multi-task models by combining task-specific fine-tuned checkpoints. However, storing multiple task-specific checkpoints requires significant memory, limiting scalability and restricting model merging to larger models and diverse tasks. In this paper, we propose quantizing task vectors (i.e., the difference between pre-trained and fine-tuned checkpoints) instead of quantizing fine-tuned checkpoints. We observe that task vectors exhibit a narrow weight range, enabling low precision quantization (up to 4 bit) within existing task vector merging frameworks. To further mitigate quantization errors within ultra-low bit precision (e.g., 2 bit), we introduce Residual Task Vector Quantization, which decomposes the task vector into a base vector and offset component. We allocate bits based on quantization sensitivity, ensuring precision while minimizing error within a memory budget. Experiments on image classification and dense prediction show our method maintains or improves model merging performance while using only 8% of the memory required for full-precision checkpoints.
Spiking Transformer with Spatial-Temporal Attention
Sep 29, 2024



Abstract:Spiking Neural Networks (SNNs) present a compelling and energy-efficient alternative to traditional Artificial Neural Networks (ANNs) due to their sparse binary activation. Leveraging the success of the transformer architecture, the spiking transformer architecture is explored to scale up dataset size and performance. However, existing works only consider the spatial self-attention in spiking transformer, neglecting the inherent temporal context across the timesteps. In this work, we introduce Spiking Transformer with Spatial-Temporal Attention (STAtten), a simple and straightforward architecture designed to integrate spatial and temporal information in self-attention with negligible additional computational load. The STAtten divides the temporal or token index and calculates the self-attention in a cross-manner to effectively incorporate spatial-temporal information. We first verify our spatial-temporal attention mechanism's ability to capture long-term temporal dependencies using sequential datasets. Moreover, we validate our approach through extensive experiments on varied datasets, including CIFAR10/100, ImageNet, CIFAR10-DVS, and N-Caltech101. Notably, our cross-attention mechanism achieves an accuracy of 78.39 % on the ImageNet dataset.
Open-World Dynamic Prompt and Continual Visual Representation Learning
Sep 09, 2024

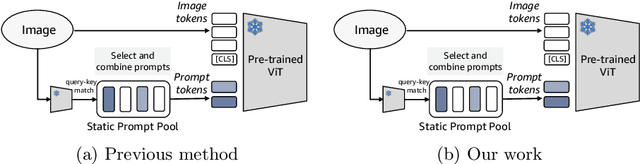

Abstract:The open world is inherently dynamic, characterized by ever-evolving concepts and distributions. Continual learning (CL) in this dynamic open-world environment presents a significant challenge in effectively generalizing to unseen test-time classes. To address this challenge, we introduce a new practical CL setting tailored for open-world visual representation learning. In this setting, subsequent data streams systematically introduce novel classes that are disjoint from those seen in previous training phases, while also remaining distinct from the unseen test classes. In response, we present Dynamic Prompt and Representation Learner (DPaRL), a simple yet effective Prompt-based CL (PCL) method. Our DPaRL learns to generate dynamic prompts for inference, as opposed to relying on a static prompt pool in previous PCL methods. In addition, DPaRL jointly learns dynamic prompt generation and discriminative representation at each training stage whereas prior PCL methods only refine the prompt learning throughout the process. Our experimental results demonstrate the superiority of our approach, surpassing state-of-the-art methods on well-established open-world image retrieval benchmarks by an average of 4.7\% improvement in Recall@1 performance.
ReSpike: Residual Frames-based Hybrid Spiking Neural Networks for Efficient Action Recognition
Sep 03, 2024Abstract:Spiking Neural Networks (SNNs) have emerged as a compelling, energy-efficient alternative to traditional Artificial Neural Networks (ANNs) for static image tasks such as image classification and segmentation. However, in the more complex video classification domain, SNN-based methods fall considerably short of ANN-based benchmarks due to the challenges in processing dense frame sequences. To bridge this gap, we propose ReSpike, a hybrid framework that synergizes the strengths of ANNs and SNNs to tackle action recognition tasks with high accuracy and low energy cost. By decomposing film clips into spatial and temporal components, i.e., RGB image Key Frames and event-like Residual Frames, ReSpike leverages ANN for learning spatial information and SNN for learning temporal information. In addition, we propose a multi-scale cross-attention mechanism for effective feature fusion. Compared to state-of-the-art SNN baselines, our ReSpike hybrid architecture demonstrates significant performance improvements (e.g., >30% absolute accuracy improvement on HMDB-51, UCF-101, and Kinetics-400). Furthermore, ReSpike achieves comparable performance with prior ANN approaches while bringing better accuracy-energy tradeoff.
When In-memory Computing Meets Spiking Neural Networks -- A Perspective on Device-Circuit-System-and-Algorithm Co-design
Aug 22, 2024



Abstract:This review explores the intersection of bio-plausible artificial intelligence in the form of Spiking Neural Networks (SNNs) with the analog In-Memory Computing (IMC) domain, highlighting their collective potential for low-power edge computing environments. Through detailed investigation at the device, circuit, and system levels, we highlight the pivotal synergies between SNNs and IMC architectures. Additionally, we emphasize the critical need for comprehensive system-level analyses, considering the inter-dependencies between algorithms, devices, circuit & system parameters, crucial for optimal performance. An in-depth analysis leads to identification of key system-level bottlenecks arising from device limitations which can be addressed using SNN-specific algorithm-hardware co-design techniques. This review underscores the imperative for holistic device to system design space co-exploration, highlighting the critical aspects of hardware and algorithm research endeavors for low-power neuromorphic solutions.
TReX- Reusing Vision Transformer's Attention for Efficient Xbar-based Computing
Aug 22, 2024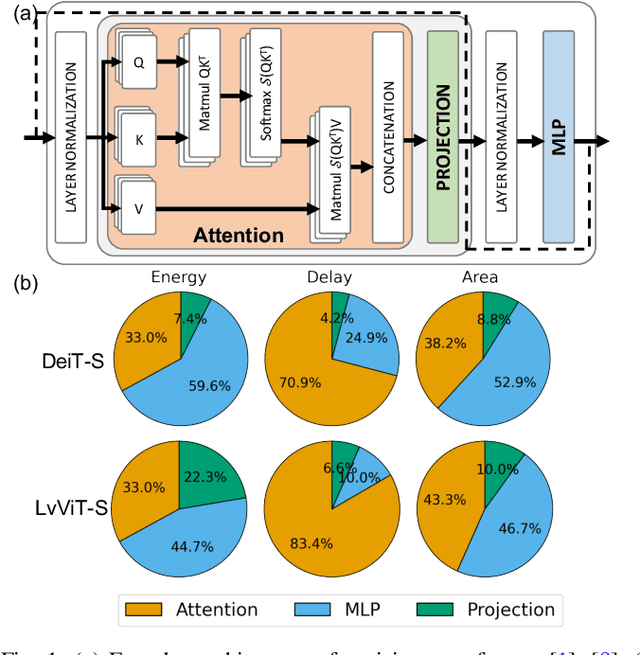
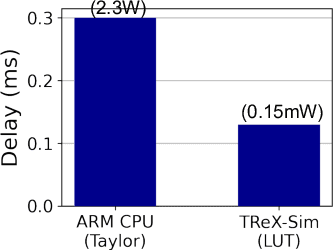
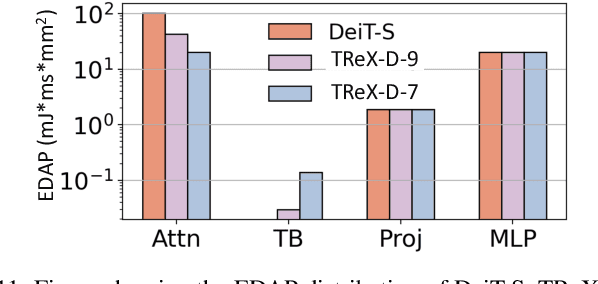
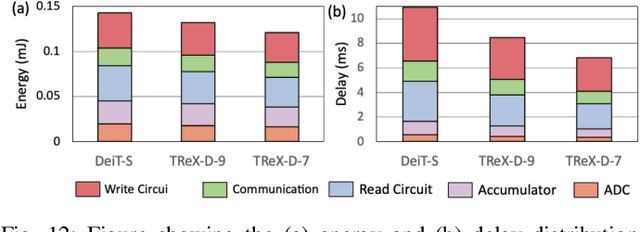
Abstract:Due to the high computation overhead of Vision Transformers (ViTs), In-memory Computing architectures are being researched towards energy-efficient deployment in edge-computing scenarios. Prior works have proposed efficient algorithm-hardware co-design and IMC-architectural improvements to improve the energy-efficiency of IMC-implemented ViTs. However, all prior works have neglected the overhead and co-depencence of attention blocks on the accuracy-energy-delay-area of IMC-implemented ViTs. To this end, we propose TReX- an attention-reuse-driven ViT optimization framework that effectively performs attention reuse in ViT models to achieve optimal accuracy-energy-delay-area tradeoffs. TReX optimally chooses the transformer encoders for attention reuse to achieve near iso-accuracy performance while meeting the user-specified delay requirement. Based on our analysis on the Imagenet-1k dataset, we find that TReX achieves 2.3x (2.19x) EDAP reduction and 1.86x (1.79x) TOPS/mm2 improvement with ~1% accuracy drop in case of DeiT-S (LV-ViT-S) ViT models. Additionally, TReX achieves high accuracy at high EDAP reduction compared to state-of-the-art token pruning and weight sharing approaches. On NLP tasks such as CoLA, TReX leads to 2% higher non-ideal accuracy compared to baseline at 1.6x lower EDAP.
LoAS: Fully Temporal-Parallel Datatflow for Dual-Sparse Spiking Neural Networks
Jul 19, 2024Abstract:Spiking Neural Networks (SNNs) have gained significant research attention in the last decade due to their potential to drive resource-constrained edge devices. Though existing SNN accelerators offer high efficiency in processing sparse spikes with dense weights, opportunities are less explored in SNNs with sparse weights, i.e., dual-sparsity. In this work, we study the acceleration of dual-sparse SNNs, focusing on their core operation, sparse-matrix-sparse-matrix multiplication (spMspM). We observe that naively running a dual-sparse SNN on existing spMspM accelerators designed for dual-sparse Artificial Neural Networks (ANNs) exhibits sub-optimal efficiency. The main challenge is that processing timesteps, a natural property of SNNs, introduces an extra loop to ANN spMspM, leading to longer latency and more memory traffic. To address the problem, we propose a fully temporal-parallel (FTP) dataflow, which minimizes both data movement across timesteps and the end-to-end latency of dual-sparse SNNs. To maximize the efficiency of FTP dataflow, we propose an FTP-friendly spike compression mechanism that efficiently compresses single-bit spikes and ensures contiguous memory access. We further propose an FTP-friendly inner-join circuit that can lower the cost of the expensive prefix-sum circuits with almost no throughput penalty. All the above techniques for FTP dataflow are encapsulated in LoAS, a Low-latency inference Accelerator for dual-sparse SNNs. With FTP dataflow, compression, and inner-join, running dual-sparse SNN workloads on LoAS demonstrates significant speedup (up to $8.51\times$) and energy reduction (up to $3.68\times$) compared to running it on prior dual-sparse accelerators.
One-stage Prompt-based Continual Learning
Feb 25, 2024



Abstract:Prompt-based Continual Learning (PCL) has gained considerable attention as a promising continual learning solution as it achieves state-of-the-art performance while preventing privacy violation and memory overhead issues. Nonetheless, existing PCL approaches face significant computational burdens because of two Vision Transformer (ViT) feed-forward stages; one is for the query ViT that generates a prompt query to select prompts inside a prompt pool; the other one is a backbone ViT that mixes information between selected prompts and image tokens. To address this, we introduce a one-stage PCL framework by directly using the intermediate layer's token embedding as a prompt query. This design removes the need for an additional feed-forward stage for query ViT, resulting in ~50% computational cost reduction for both training and inference with marginal accuracy drop < 1%. We further introduce a Query-Pool Regularization (QR) loss that regulates the relationship between the prompt query and the prompt pool to improve representation power. The QR loss is only applied during training time, so there is no computational overhead at inference from the QR loss. With the QR loss, our approach maintains ~ 50% computational cost reduction during inference as well as outperforms the prior two-stage PCL methods by ~1.4% on public class-incremental continual learning benchmarks including CIFAR-100, ImageNet-R, and DomainNet.
TT-SNN: Tensor Train Decomposition for Efficient Spiking Neural Network Training
Jan 15, 2024Abstract:Spiking Neural Networks (SNNs) have gained significant attention as a potentially energy-efficient alternative for standard neural networks with their sparse binary activation. However, SNNs suffer from memory and computation overhead due to spatio-temporal dynamics and multiple backpropagation computations across timesteps during training. To address this issue, we introduce Tensor Train Decomposition for Spiking Neural Networks (TT-SNN), a method that reduces model size through trainable weight decomposition, resulting in reduced storage, FLOPs, and latency. In addition, we propose a parallel computation pipeline as an alternative to the typical sequential tensor computation, which can be flexibly integrated into various existing SNN architectures. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first of its kind application of tensor decomposition in SNNs. We validate our method using both static and dynamic datasets, CIFAR10/100 and N-Caltech101, respectively. We also propose a TT-SNN-tailored training accelerator to fully harness the parallelism in TT-SNN. Our results demonstrate substantial reductions in parameter size (7.98X), FLOPs (9.25X), training time (17.7%), and training energy (28.3%) during training for the N-Caltech101 dataset, with negligible accuracy degradation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge