TReX- Reusing Vision Transformer's Attention for Efficient Xbar-based Computing
Paper and Code
Aug 22, 2024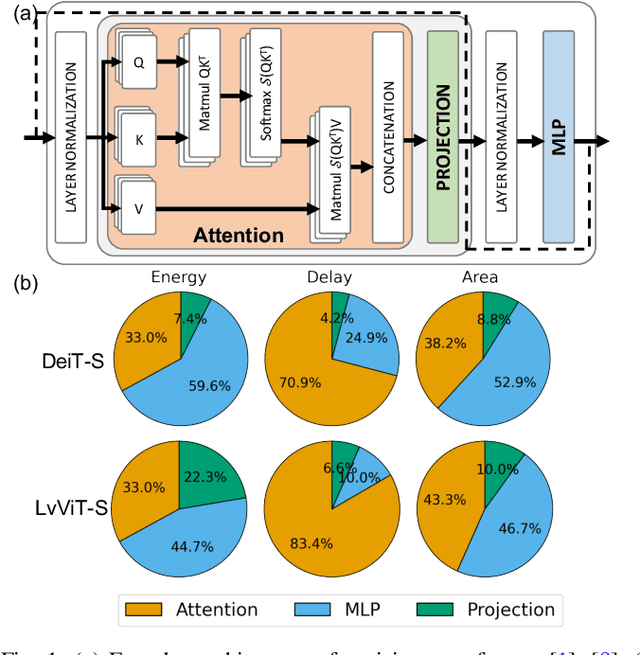
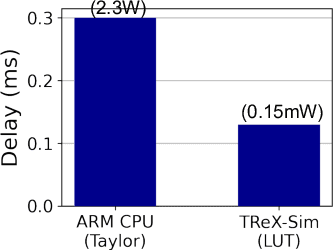
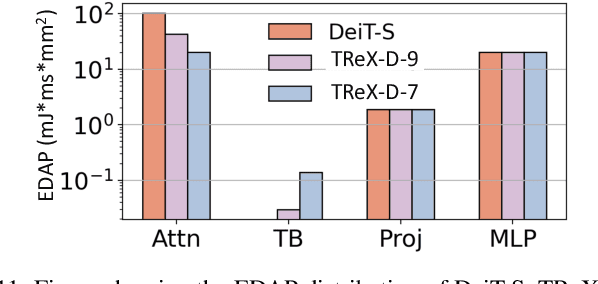
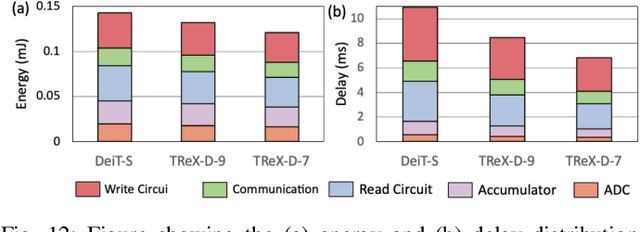
Due to the high computation overhead of Vision Transformers (ViTs), In-memory Computing architectures are being researched towards energy-efficient deployment in edge-computing scenarios. Prior works have proposed efficient algorithm-hardware co-design and IMC-architectural improvements to improve the energy-efficiency of IMC-implemented ViTs. However, all prior works have neglected the overhead and co-depencence of attention blocks on the accuracy-energy-delay-area of IMC-implemented ViTs. To this end, we propose TReX- an attention-reuse-driven ViT optimization framework that effectively performs attention reuse in ViT models to achieve optimal accuracy-energy-delay-area tradeoffs. TReX optimally chooses the transformer encoders for attention reuse to achieve near iso-accuracy performance while meeting the user-specified delay requirement. Based on our analysis on the Imagenet-1k dataset, we find that TReX achieves 2.3x (2.19x) EDAP reduction and 1.86x (1.79x) TOPS/mm2 improvement with ~1% accuracy drop in case of DeiT-S (LV-ViT-S) ViT models. Additionally, TReX achieves high accuracy at high EDAP reduction compared to state-of-the-art token pruning and weight sharing approaches. On NLP tasks such as CoLA, TReX leads to 2% higher non-ideal accuracy compared to baseline at 1.6x lower EDAP.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge