Peng Tang
FFP-300K: Scaling First-Frame Propagation for Generalizable Video Editing
Jan 06, 2026Abstract:First-Frame Propagation (FFP) offers a promising paradigm for controllable video editing, but existing methods are hampered by a reliance on cumbersome run-time guidance. We identify the root cause of this limitation as the inadequacy of current training datasets, which are often too short, low-resolution, and lack the task diversity required to teach robust temporal priors. To address this foundational data gap, we first introduce FFP-300K, a new large-scale dataset comprising 300K high-fidelity video pairs at 720p resolution and 81 frames in length, constructed via a principled two-track pipeline for diverse local and global edits. Building on this dataset, we propose a novel framework designed for true guidance-free FFP that resolves the critical tension between maintaining first-frame appearance and preserving source video motion. Architecturally, we introduce Adaptive Spatio-Temporal RoPE (AST-RoPE), which dynamically remaps positional encodings to disentangle appearance and motion references. At the objective level, we employ a self-distillation strategy where an identity propagation task acts as a powerful regularizer, ensuring long-term temporal stability and preventing semantic drift. Comprehensive experiments on the EditVerseBench benchmark demonstrate that our method significantly outperforming existing academic and commercial models by receiving about 0.2 PickScore and 0.3 VLM score improvement against these competitors.
The devil is in the details: Enhancing Video Virtual Try-On via Keyframe-Driven Details Injection
Dec 23, 2025Abstract:Although diffusion transformer (DiT)-based video virtual try-on (VVT) has made significant progress in synthesizing realistic videos, existing methods still struggle to capture fine-grained garment dynamics and preserve background integrity across video frames. They also incur high computational costs due to additional interaction modules introduced into DiTs, while the limited scale and quality of existing public datasets also restrict model generalization and effective training. To address these challenges, we propose a novel framework, KeyTailor, along with a large-scale, high-definition dataset, ViT-HD. The core idea of KeyTailor is a keyframe-driven details injection strategy, motivated by the fact that keyframes inherently contain both foreground dynamics and background consistency. Specifically, KeyTailor adopts an instruction-guided keyframe sampling strategy to filter informative frames from the input video. Subsequently,two tailored keyframe-driven modules, the garment details enhancement module and the collaborative background optimization module, are employed to distill garment dynamics into garment-related latents and to optimize the integrity of background latents, both guided by keyframes.These enriched details are then injected into standard DiT blocks together with pose, mask, and noise latents, enabling efficient and realistic try-on video synthesis. This design ensures consistency without explicitly modifying the DiT architecture, while simultaneously avoiding additional complexity. In addition, our dataset ViT-HD comprises 15, 070 high-quality video samples at a resolution of 810*1080, covering diverse garments. Extensive experiments demonstrate that KeyTailor outperforms state-of-the-art baselines in terms of garment fidelity and background integrity across both dynamic and static scenarios.
MoE-SpeQ: Speculative Quantized Decoding with Proactive Expert Prefetching and Offloading for Mixture-of-Experts
Nov 18, 2025Abstract:The immense memory requirements of state-of-the-art Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) models present a significant challenge for inference, often exceeding the capacity of a single accelerator. While offloading experts to host memory is a common solution, it introduces a severe I/O bottleneck over the PCIe bus, as the data-dependent nature of expert selection places these synchronous transfers directly on the critical path of execution, crippling performance. This paper argues that the I/O bottleneck can be overcome by trading a small amount of cheap, on-device computation to hide the immense cost of data movement. We present MoE-SpeQ, a new inference system built on a novel co-design of speculative execution and expert offloading. MoE-SpeQ employs a small, on-device draft model to predict the sequence of required experts for future tokens. This foresight enables a runtime orchestrator to prefetch these experts from host memory, effectively overlapping the expensive I/O with useful computation and hiding the latency from the critical path. To maximize performance, an adaptive governor, guided by an Amortization Roofline Model, dynamically tunes the speculation strategy to the underlying hardware. Our evaluation on memory-constrained devices shows that for the Phi-MoE model, MoE-SpeQ achieves at most 2.34x speedup over the state-of-the-art offloading framework. Our work establishes a new, principled approach for managing data-dependent memory access in resource-limited environments, making MoE inference more accessible on commodity hardware.
FedTopo: Topology-Informed Representation Alignment in Federated Learning under Non-I.I.D. Conditions
Nov 16, 2025Abstract:Current federated-learning models deteriorate under heterogeneous (non-I.I.D.) client data, as their feature representations diverge and pixel- or patch-level objectives fail to capture the global topology which is essential for high-dimensional visual tasks. We propose FedTopo, a framework that integrates Topological-Guided Block Screening (TGBS) and Topological Embedding (TE) to leverage topological information, yielding coherently aligned cross-client representations by Topological Alignment Loss (TAL). First, Topology-Guided Block Screening (TGBS) automatically selects the most topology-informative block, i.e., the one with maximal topological separability, whose persistence-based signatures best distinguish within- versus between-class pairs, ensuring that subsequent analysis focuses on topology-rich features. Next, this block yields a compact Topological Embedding, which quantifies the topological information for each client. Finally, a Topological Alignment Loss (TAL) guides clients to maintain topological consistency with the global model during optimization, reducing representation drift across rounds. Experiments on Fashion-MNIST, CIFAR-10, and CIFAR-100 under four non-I.I.D. partitions show that FedTopo accelerates convergence and improves accuracy over strong baselines.
FedDEAP: Adaptive Dual-Prompt Tuning for Multi-Domain Federated Learning
Oct 21, 2025Abstract:Federated learning (FL) enables multiple clients to collaboratively train machine learning models without exposing local data, balancing performance and privacy. However, domain shift and label heterogeneity across clients often hinder the generalization of the aggregated global model. Recently, large-scale vision-language models like CLIP have shown strong zero-shot classification capabilities, raising the question of how to effectively fine-tune CLIP across domains in a federated setting. In this work, we propose an adaptive federated prompt tuning framework, FedDEAP, to enhance CLIP's generalization in multi-domain scenarios. Our method includes the following three key components: (1) To mitigate the loss of domain-specific information caused by label-supervised tuning, we disentangle semantic and domain-specific features in images by using semantic and domain transformation networks with unbiased mappings; (2) To preserve domain-specific knowledge during global prompt aggregation, we introduce a dual-prompt design with a global semantic prompt and a local domain prompt to balance shared and personalized information; (3) To maximize the inclusion of semantic and domain information from images in the generated text features, we align textual and visual representations under the two learned transformations to preserve semantic and domain consistency. Theoretical analysis and extensive experiments on four datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of our method in enhancing the generalization of CLIP for federated image recognition across multiple domains.
Neural Canonical Polyadic Factorization for Traffic Analysis
Jun 18, 2025Abstract:Modern intelligent transportation systems rely on accurate spatiotemporal traffic analysis to optimize urban mobility and infrastructure resilience. However, pervasive missing data caused by sensor failures and heterogeneous sensing gaps fundamentally hinders reliable traffic modeling. This paper proposes a Neural Canonical Polyadic Factorization (NCPF) model that synergizes low-rank tensor algebra with deep representation learning for robust traffic data imputation. The model innovatively embeds CP decomposition into neural architecture through learnable embedding projections, where sparse traffic tensors are encoded into dense latent factors across road segments, time intervals, and mobility metrics. A hierarchical feature fusion mechanism employs Hadamard products to explicitly model multilinear interactions, while stacked multilayer perceptron layers nonlinearly refine these representations to capture complex spatiotemporal couplings. Extensive evaluations on six urban traffic datasets demonstrate NCPF's superiority over six state-of-the-art baselines. By unifying CP decomposition's interpretable factor analysis with neural network's nonlinear expressive power, NCPF provides a principled yet flexible approaches for high-dimensional traffic data imputation, offering critical support for next-generation transportation digital twins and adaptive traffic control systems.
Devil's Hand: Data Poisoning Attacks to Locally Private Graph Learning Protocols
Jun 11, 2025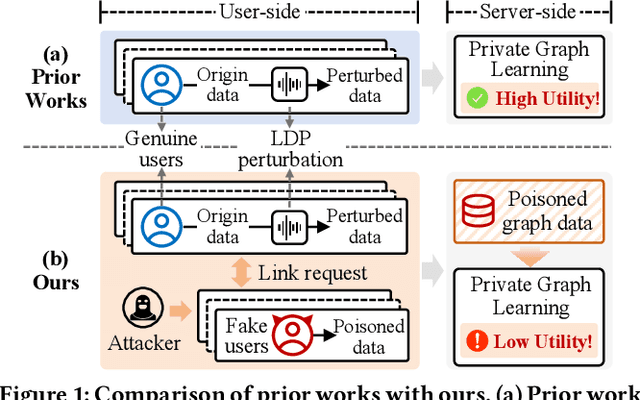
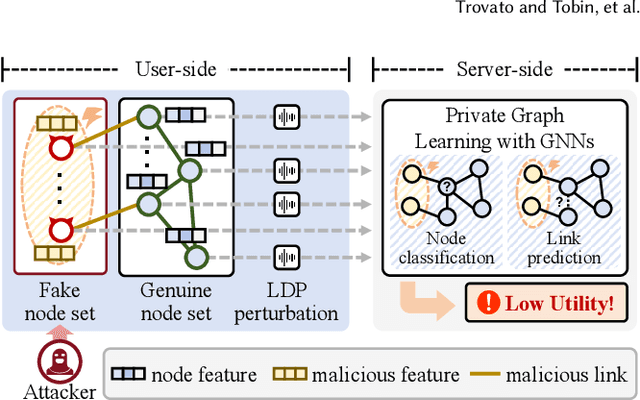
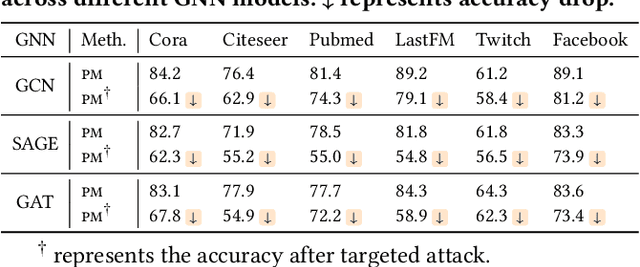
Abstract:Graph neural networks (GNNs) have achieved significant success in graph representation learning and have been applied to various domains. However, many real-world graphs contain sensitive personal information, such as user profiles in social networks, raising serious privacy concerns when graph learning is performed using GNNs. To address this issue, locally private graph learning protocols have gained considerable attention. These protocols leverage the privacy advantages of local differential privacy (LDP) and the effectiveness of GNN's message-passing in calibrating noisy data, offering strict privacy guarantees for users' local data while maintaining high utility (e.g., node classification accuracy) for graph learning. Despite these advantages, such protocols may be vulnerable to data poisoning attacks, a threat that has not been considered in previous research. Identifying and addressing these threats is crucial for ensuring the robustness and security of privacy-preserving graph learning frameworks. This work introduces the first data poisoning attack targeting locally private graph learning protocols. The attacker injects fake users into the protocol, manipulates these fake users to establish links with genuine users, and sends carefully crafted data to the server, ultimately compromising the utility of private graph learning. The effectiveness of the attack is demonstrated both theoretically and empirically. In addition, several defense strategies have also been explored, but their limited effectiveness highlights the need for more robust defenses.
Using LLMs for Automated Privacy Policy Analysis: Prompt Engineering, Fine-Tuning and Explainability
Mar 16, 2025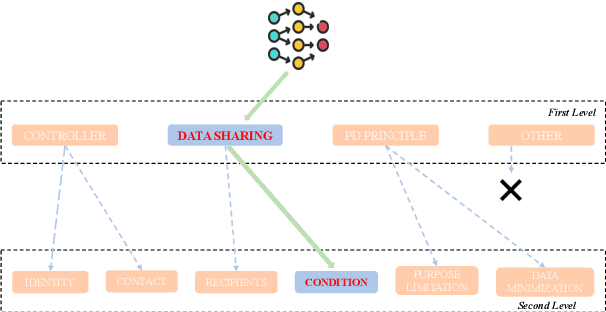
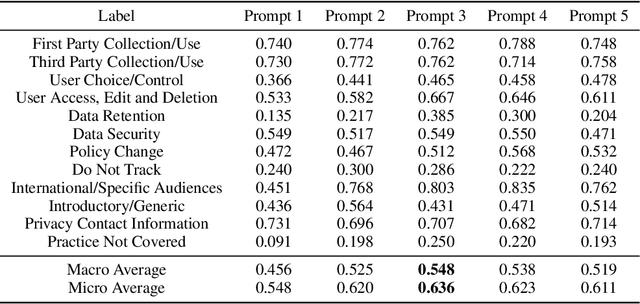
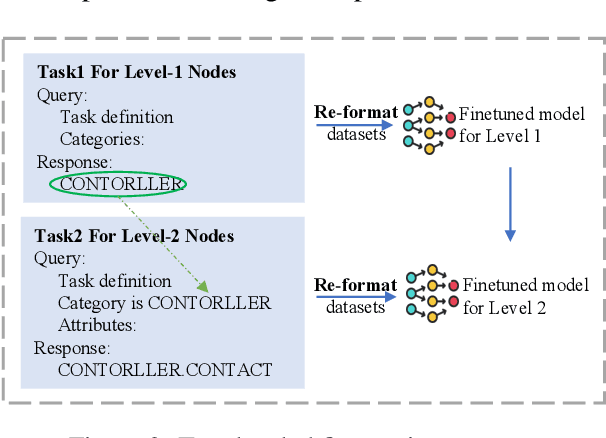
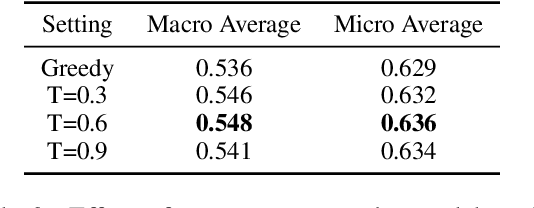
Abstract:Privacy policies are widely used by digital services and often required for legal purposes. Many machine learning based classifiers have been developed to automate detection of different concepts in a given privacy policy, which can help facilitate other automated tasks such as producing a more reader-friendly summary and detecting legal compliance issues. Despite the successful applications of large language models (LLMs) to many NLP tasks in various domains, there is very little work studying the use of LLMs for automated privacy policy analysis, therefore, if and how LLMs can help automate privacy policy analysis remains under-explored. To fill this research gap, we conducted a comprehensive evaluation of LLM-based privacy policy concept classifiers, employing both prompt engineering and LoRA (low-rank adaptation) fine-tuning, on four state-of-the-art (SOTA) privacy policy corpora and taxonomies. Our experimental results demonstrated that combining prompt engineering and fine-tuning can make LLM-based classifiers outperform other SOTA methods, \emph{significantly} and \emph{consistently} across privacy policy corpora/taxonomies and concepts. Furthermore, we evaluated the explainability of the LLM-based classifiers using three metrics: completeness, logicality, and comprehensibility. For all three metrics, a score exceeding 91.1\% was observed in our evaluation, indicating that LLMs are not only useful to improve the classification performance, but also to enhance the explainability of detection results.
Multi-Head Self-Attending Neural Tucker Factorization
Jan 16, 2025

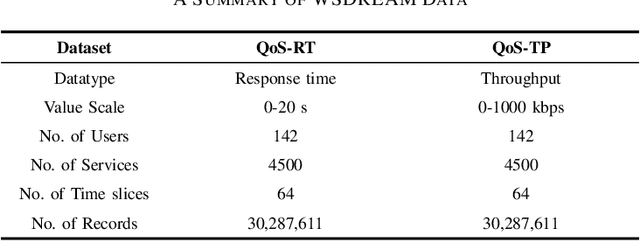
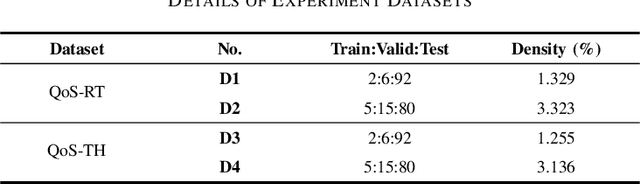
Abstract:Quality-of-service (QoS) data exhibit dynamic temporal patterns that are crucial for accurately predicting missing values. These patterns arise from the evolving interactions between users and services, making it essential to capture the temporal dynamics inherent in such data for improved prediction performance. As the size and complexity of QoS datasets increase, existing models struggle to provide accurate predictions, highlighting the need for more flexible and dynamic methods to better capture the underlying patterns in large-scale QoS data. To address this issue, we introduce a neural network-based tensor factorization approach tailored for learning spatiotemporal representations of high-dimensional and incomplete (HDI) tensors, namely the Multi-head Self-attending Neural Tucker Factorization (MSNTucF). The model is elaborately designed for modeling intricate nonlinear spatiotemporal feature interaction patterns hidden in real world data with a two-fold idea. It first employs a neural network structure to generalize the traditional framework of Tucker factorization and then proposes to leverage a multi-head self-attending module to enforce nonlinear latent interaction learning. In empirical studies on two dynamic QoS datasets from real applications, the proposed MSNTucF model demonstrates superior performance compared to state-of-the-art benchmark models in estimating missing observations. This highlights its ability to learn non-linear spatiotemporal representations of HDI tensors.
A Survey on Inference Optimization Techniques for Mixture of Experts Models
Dec 18, 2024



Abstract:The emergence of large-scale Mixture of Experts (MoE) models has marked a significant advancement in artificial intelligence, offering enhanced model capacity and computational efficiency through conditional computation. However, the deployment and inference of these models present substantial challenges in terms of computational resources, latency, and energy efficiency. This comprehensive survey systematically analyzes the current landscape of inference optimization techniques for MoE models across the entire system stack. We first establish a taxonomical framework that categorizes optimization approaches into model-level, system-level, and hardware-level optimizations. At the model level, we examine architectural innovations including efficient expert design, attention mechanisms, various compression techniques such as pruning, quantization, and knowledge distillation, as well as algorithm improvement including dynamic routing strategies and expert merging methods. At the system level, we investigate distributed computing approaches, load balancing mechanisms, and efficient scheduling algorithms that enable scalable deployment. Furthermore, we delve into hardware-specific optimizations and co-design strategies that maximize throughput and energy efficiency. This survey not only provides a structured overview of existing solutions but also identifies key challenges and promising research directions in MoE inference optimization. Our comprehensive analysis serves as a valuable resource for researchers and practitioners working on large-scale deployment of MoE models in resource-constrained environments. To facilitate ongoing updates and the sharing of cutting-edge advances in MoE inference optimization research, we have established a repository accessible at \url{https://github.com/MoE-Inf/awesome-moe-inference/}.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge