Xiaodan Zhu
On the Robustness of Verbal Confidence of LLMs in Adversarial Attacks
Jul 09, 2025Abstract:Robust verbal confidence generated by large language models (LLMs) is crucial for the deployment of LLMs to ensure transparency, trust, and safety in human-AI interactions across many high-stakes applications. In this paper, we present the first comprehensive study on the robustness of verbal confidence under adversarial attacks. We introduce a novel framework for attacking verbal confidence scores through both perturbation and jailbreak-based methods, and show that these attacks can significantly jeopardize verbal confidence estimates and lead to frequent answer changes. We examine a variety of prompting strategies, model sizes, and application domains, revealing that current confidence elicitation methods are vulnerable and that commonly used defence techniques are largely ineffective or counterproductive. Our findings underscore the urgent need to design more robust mechanisms for confidence expression in LLMs, as even subtle semantic-preserving modifications can lead to misleading confidence in responses.
SPARE: Single-Pass Annotation with Reference-Guided Evaluation for Automatic Process Supervision and Reward Modelling
Jun 18, 2025Abstract:Process or step-wise supervision has played a crucial role in advancing complex multi-step reasoning capabilities of Large Language Models (LLMs). However, efficient, high-quality automated process annotation remains a significant challenge. To address this, we introduce Single-Pass Annotation with Reference-Guided Evaluation (SPARE), a novel structured framework that enables single-pass, per-step annotation by aligning each solution step to one or multiple steps in a reference solution, accompanied by explicit reasoning for evaluation. We show that reference-guided step-level evaluation effectively facilitates process supervision on four datasets spanning three domains: mathematical reasoning, multi-hop compositional question answering, and spatial reasoning. We demonstrate that SPARE, when compared to baselines, improves reasoning performance when used for: (1) fine-tuning models in an offline RL setup for inference-time greedy-decoding, and (2) training reward models for ranking/aggregating multiple LLM-generated outputs. Additionally, SPARE achieves competitive performance on challenging mathematical datasets while offering 2.6 times greater efficiency, requiring only 38% of the runtime, compared to tree search-based automatic annotation. The codebase, along with a trained SPARE-PRM model, is publicly released to facilitate further research and reproducibility.
Towards Robust Dialogue Breakdown Detection: Addressing Disruptors in Large Language Models with Self-Guided Reasoning
Apr 26, 2025


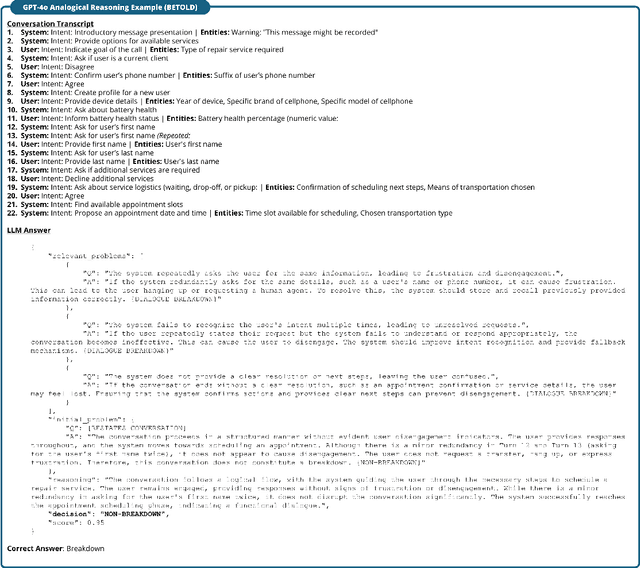
Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) are rapidly changing various domains. However, their capabilities in handling conversational breakdowns still require an in-depth exploration. This paper addresses the challenge of detecting and mitigating dialogue breakdowns within LLM-driven conversational systems. While powerful models from OpenAI and Anthropic excel in many dialogue tasks, they can still produce incoherent or contradictory responses, commonly referred to as breakdowns, which undermine user trust. To tackle this, we propose an approach that combines specialized fine-tuning with advanced prompting strategies, including few-shot learning, chain-of-thought reasoning, and analogical prompting. In particular, we fine-tune a small 8B model and demonstrate its robust classification and calibration capabilities in English and Japanese dialogue. We also validate its generalization on the BETOLD dataset, achieving a 7\% accuracy improvement over its base model. Furthermore, we introduce a real-time deployment architecture that selectively escalates suspicious responses to more resource-intensive frontier models only when breakdowns are detected, significantly cutting operational expenses and energy consumption. Experimental results show our method surpasses prior state-of-the-art specialized classifiers while also narrowing performance gaps between smaller open-source models and large proprietary ones. Our approach offers a scalable solution for robust conversational AI in high-impact domains by combining efficiency, interpretability, and reliability.
Entropy-Aware Branching for Improved Mathematical Reasoning
Mar 27, 2025Abstract:While Large Language Models (LLMs) are effectively aligned through extensive pre-training and fine-tuning, they still struggle with varying levels of uncertainty during token generation. In our investigation of mathematical reasoning, we observe that errors are more likely to arise at tokens exhibiting high entropy and variance of entropy in the model's output distribution. Based on the observation, we propose a novel approach that dynamically branches the generation process on demand instead of defaulting to the single most probable token. By exploring in parallel multiple branches stemming from high probability tokens of critical decision points, the model can discover diverse reasoning paths that might otherwise be missed. We further harness external feedback from larger models to rank and select the most coherent and accurate reasoning branch. Our experimental results on mathematical word problems and calculation questions show that this branching strategy boosts the reasoning capabilities of small LLMs up to 4.6% compared to conventional argmax decoding.
Chat-TS: Enhancing Multi-Modal Reasoning Over Time-Series and Natural Language Data
Mar 13, 2025



Abstract:Time-series analysis is critical for a wide range of fields such as healthcare, finance, transportation, and energy, among many others. The practical applications often involve analyzing time-series data alongside contextual information in the form of natural language to support informed decisions. However, current time-series models are limited in their ability to perform reasoning that involves both time-series and their textual content. In this work, we address this gap by introducing \textit{Chat-TS}, a large language model (LLM) based framework, designed to support reasoning over time series and textual data. Unlike traditional models, Chat-TS integrates time-series tokens into LLMs' vocabulary, enhancing its reasoning ability over both modalities without compromising the core natural language capabilities, enabling practical analysis and reasoning across modalities. To support learning and evaluation in this setup, we contribute new datasets: the \textit{TS Instruct Training Dataset} which pairs diverse time-series data with relevant text instructions and responses for instruction tuning, the \textit{TS Instruct Question and Answer (QA) Gold Dataset} which provides multiple-choice questions designed to evaluate multimodal reasoning, and a \textit{TS Instruct Quantitative Probing Set} which contains a small subset of the TS Instruct QA tasks alongside math and decision-making questions for LLM evaluation. We designed a training strategy to preserve the inherent reasoning capabilities of LLMs while augmenting them for time-series reasoning. Experiments show that Chat-TS achieves state-of-the-art performance in multi-modal reasoning tasks by maintaining strong natural language proficiency while improving time-series reasoning. ~\footnote{To ensure replicability and facilitate future research, all models, datasets, and code will be available at [\texttt{Github-URL}].}
Error Diversity Matters: An Error-Resistant Ensemble Method for Unsupervised Dependency Parsing
Dec 16, 2024Abstract:We address unsupervised dependency parsing by building an ensemble of diverse existing models through post hoc aggregation of their output dependency parse structures. We observe that these ensembles often suffer from low robustness against weak ensemble components due to error accumulation. To tackle this problem, we propose an efficient ensemble-selection approach that avoids error accumulation. Results demonstrate that our approach outperforms each individual model as well as previous ensemble techniques. Additionally, our experiments show that the proposed ensemble-selection method significantly enhances the performance and robustness of our ensemble, surpassing previously proposed strategies, which have not accounted for error diversity.
SMARTCAL: An Approach to Self-Aware Tool-Use Evaluation and Calibration
Dec 11, 2024



Abstract:The tool-use ability of Large Language Models (LLMs) has a profound impact on a wide range of industrial applications. However, LLMs' self-control and calibration capability in appropriately using tools remains understudied. The problem is consequential as it raises potential risks of degraded performance and poses a threat to the trustworthiness of the models. In this paper, we conduct a study on a family of state-of-the-art LLMs on three datasets with two mainstream tool-use frameworks. Our study reveals the tool-abuse behavior of LLMs, a tendency for models to misuse tools with overconfidence. We also find that this is a common issue regardless of model capability. Accordingly, we propose a novel approach, \textit{SMARTCAL}, to mitigate the observed issues, and our results show an average of 8.6 percent increase in the QA performance and a 21.6 percent decrease in Expected Calibration Error (ECE) compared to baseline models.
Exploring the Role of Reasoning Structures for Constructing Proofs in Multi-Step Natural Language Reasoning with Large Language Models
Oct 11, 2024



Abstract:When performing complex multi-step reasoning tasks, the ability of Large Language Models (LLMs) to derive structured intermediate proof steps is important for ensuring that the models truly perform the desired reasoning and for improving models' explainability. This paper is centred around a focused study: whether the current state-of-the-art generalist LLMs can leverage the structures in a few examples to better construct the proof structures with \textit{in-context learning}. Our study specifically focuses on structure-aware demonstration and structure-aware pruning. We demonstrate that they both help improve performance. A detailed analysis is provided to help understand the results.
Misinformation with Legal Consequences (MisLC): A New Task Towards Harnessing Societal Harm of Misinformation
Oct 04, 2024Abstract:Misinformation, defined as false or inaccurate information, can result in significant societal harm when it is spread with malicious or even innocuous intent. The rapid online information exchange necessitates advanced detection mechanisms to mitigate misinformation-induced harm. Existing research, however, has predominantly focused on assessing veracity, overlooking the legal implications and social consequences of misinformation. In this work, we take a novel angle to consolidate the definition of misinformation detection using legal issues as a measurement of societal ramifications, aiming to bring interdisciplinary efforts to tackle misinformation and its consequence. We introduce a new task: Misinformation with Legal Consequence (MisLC), which leverages definitions from a wide range of legal domains covering 4 broader legal topics and 11 fine-grained legal issues, including hate speech, election laws, and privacy regulations. For this task, we advocate a two-step dataset curation approach that utilizes crowd-sourced checkworthiness and expert evaluations of misinformation. We provide insights about the MisLC task through empirical evidence, from the problem definition to experiments and expert involvement. While the latest large language models and retrieval-augmented generation are effective baselines for the task, we find they are still far from replicating expert performance.
Fine-Tuning Language Models with Differential Privacy through Adaptive Noise Allocation
Oct 03, 2024
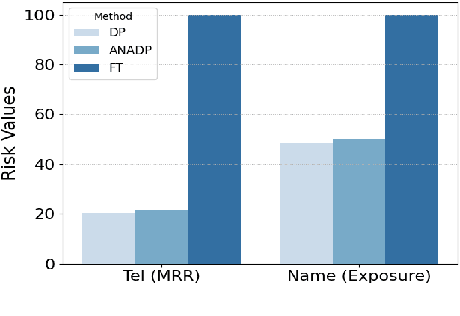
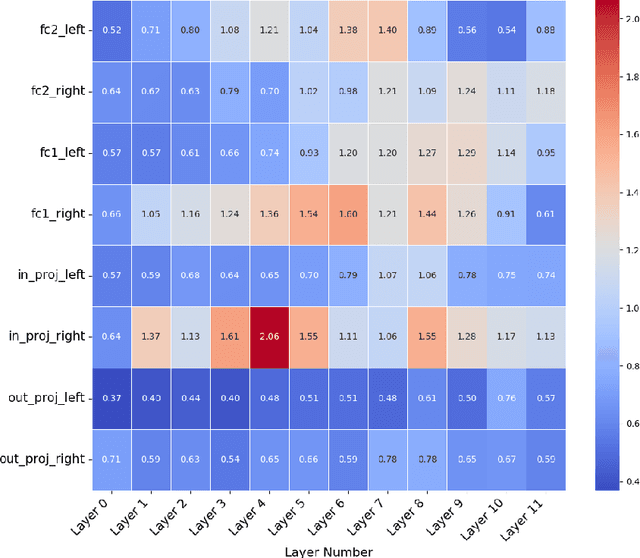

Abstract:Language models are capable of memorizing detailed patterns and information, leading to a double-edged effect: they achieve impressive modeling performance on downstream tasks with the stored knowledge but also raise significant privacy concerns. Traditional differential privacy based training approaches offer robust safeguards by employing a uniform noise distribution across all parameters. However, this overlooks the distinct sensitivities and contributions of individual parameters in privacy protection and often results in suboptimal models. To address these limitations, we propose ANADP, a novel algorithm that adaptively allocates additive noise based on the importance of model parameters. We demonstrate that ANADP narrows the performance gap between regular fine-tuning and traditional DP fine-tuning on a series of datasets while maintaining the required privacy constraints.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge