Zhisheng Zheng
SLAM-LLM: A Modular, Open-Source Multimodal Large Language Model Framework and Best Practice for Speech, Language, Audio and Music Processing
Jan 14, 2026Abstract:The recent surge in open-source Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLM) frameworks, such as LLaVA, provides a convenient kickoff for artificial intelligence developers and researchers. However, most of the MLLM frameworks take vision as the main input modality, and provide limited in-depth support for the modality of speech, audio, and music. This situation hinders the development of audio-language models, and forces researchers to spend a lot of effort on code writing and hyperparameter tuning. We present SLAM-LLM, an open-source deep learning framework designed to train customized MLLMs, focused on speech, language, audio, and music processing. SLAM-LLM provides a modular configuration of different encoders, projectors, LLMs, and parameter-efficient fine-tuning plugins. SLAM-LLM also includes detailed training and inference recipes for mainstream tasks, along with high-performance checkpoints like LLM-based Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR), Automated Audio Captioning (AAC), and Music Captioning (MC). Some of these recipes have already reached or are nearing state-of-the-art performance, and some relevant techniques have also been accepted by academic papers. We hope SLAM-LLM will accelerate iteration, development, data engineering, and model training for researchers. We are committed to continually pushing forward audio-based MLLMs through this open-source framework, and call on the community to contribute to the LLM-based speech, audio and music processing.
VoiceCraft-X: Unifying Multilingual, Voice-Cloning Speech Synthesis and Speech Editing
Nov 15, 2025Abstract:We introduce VoiceCraft-X, an autoregressive neural codec language model which unifies multilingual speech editing and zero-shot Text-to-Speech (TTS) synthesis across 11 languages: English, Mandarin, Korean, Japanese, Spanish, French, German, Dutch, Italian, Portuguese, and Polish. VoiceCraft-X utilizes the Qwen3 large language model for phoneme-free cross-lingual text processing and a novel token reordering mechanism with time-aligned text and speech tokens to handle both tasks as a single sequence generation problem. The model generates high-quality, natural-sounding speech, seamlessly creating new audio or editing existing recordings within one framework. VoiceCraft-X shows robust performance in diverse linguistic settings, even with limited per-language data, underscoring the power of unified autoregressive approaches for advancing complex, real-world multilingual speech applications. Audio samples are available at https://zhishengzheng.com/voicecraft-x/.
MMAR: A Challenging Benchmark for Deep Reasoning in Speech, Audio, Music, and Their Mix
May 19, 2025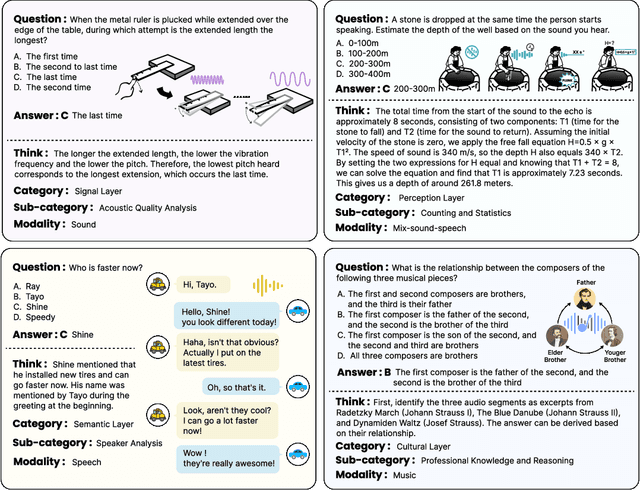
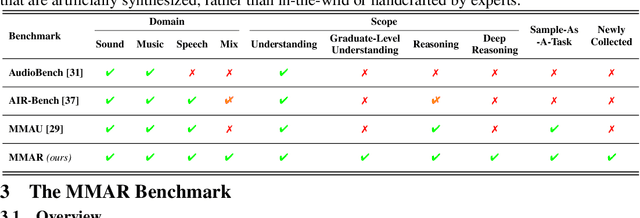
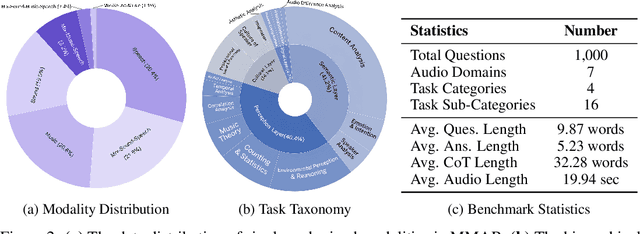
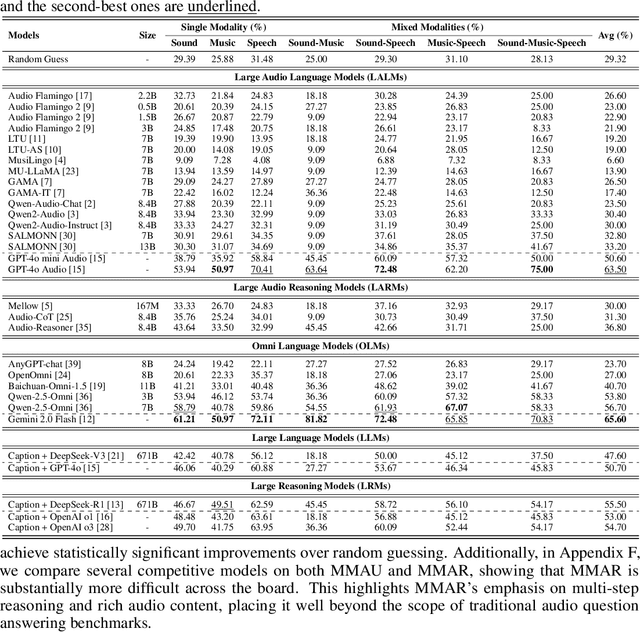
Abstract:We introduce MMAR, a new benchmark designed to evaluate the deep reasoning capabilities of Audio-Language Models (ALMs) across massive multi-disciplinary tasks. MMAR comprises 1,000 meticulously curated audio-question-answer triplets, collected from real-world internet videos and refined through iterative error corrections and quality checks to ensure high quality. Unlike existing benchmarks that are limited to specific domains of sound, music, or speech, MMAR extends them to a broad spectrum of real-world audio scenarios, including mixed-modality combinations of sound, music, and speech. Each question in MMAR is hierarchically categorized across four reasoning layers: Signal, Perception, Semantic, and Cultural, with additional sub-categories within each layer to reflect task diversity and complexity. To further foster research in this area, we annotate every question with a Chain-of-Thought (CoT) rationale to promote future advancements in audio reasoning. Each item in the benchmark demands multi-step deep reasoning beyond surface-level understanding. Moreover, a part of the questions requires graduate-level perceptual and domain-specific knowledge, elevating the benchmark's difficulty and depth. We evaluate MMAR using a broad set of models, including Large Audio-Language Models (LALMs), Large Audio Reasoning Models (LARMs), Omni Language Models (OLMs), Large Language Models (LLMs), and Large Reasoning Models (LRMs), with audio caption inputs. The performance of these models on MMAR highlights the benchmark's challenging nature, and our analysis further reveals critical limitations of understanding and reasoning capabilities among current models. We hope MMAR will serve as a catalyst for future advances in this important but little-explored area.
Scaling Rich Style-Prompted Text-to-Speech Datasets
Mar 06, 2025Abstract:We introduce Paralinguistic Speech Captions (ParaSpeechCaps), a large-scale dataset that annotates speech utterances with rich style captions. While rich abstract tags (e.g. guttural, nasal, pained) have been explored in small-scale human-annotated datasets, existing large-scale datasets only cover basic tags (e.g. low-pitched, slow, loud). We combine off-the-shelf text and speech embedders, classifiers and an audio language model to automatically scale rich tag annotations for the first time. ParaSpeechCaps covers a total of 59 style tags, including both speaker-level intrinsic tags and utterance-level situational tags. It consists of 342 hours of human-labelled data (PSC-Base) and 2427 hours of automatically annotated data (PSC-Scaled). We finetune Parler-TTS, an open-source style-prompted TTS model, on ParaSpeechCaps, and achieve improved style consistency (+7.9% Consistency MOS) and speech quality (+15.5% Naturalness MOS) over the best performing baseline that combines existing rich style tag datasets. We ablate several of our dataset design choices to lay the foundation for future work in this space. Our dataset, models and code are released at https://github.com/ajd12342/paraspeechcaps .
SLAM-AAC: Enhancing Audio Captioning with Paraphrasing Augmentation and CLAP-Refine through LLMs
Oct 12, 2024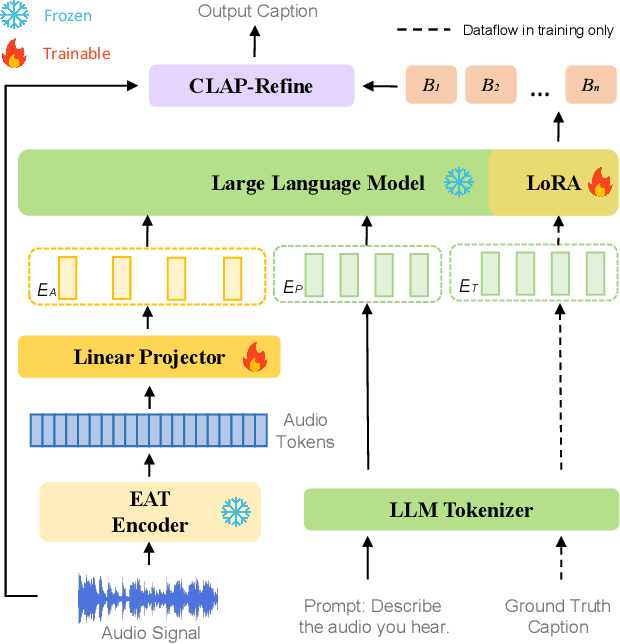

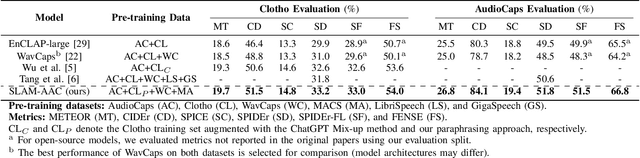
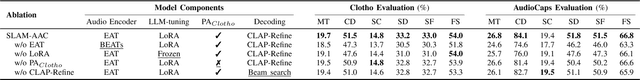
Abstract:Automated Audio Captioning (AAC) aims to generate natural textual descriptions for input audio signals. Recent progress in audio pre-trained models and large language models (LLMs) has significantly enhanced audio understanding and textual reasoning capabilities, making improvements in AAC possible. In this paper, we propose SLAM-AAC to further enhance AAC with paraphrasing augmentation and CLAP-Refine through LLMs. Our approach uses the self-supervised EAT model to extract fine-grained audio representations, which are then aligned with textual embeddings via lightweight linear layers. The caption generation LLM is efficiently fine-tuned using the LoRA adapter. Drawing inspiration from the back-translation method in machine translation, we implement paraphrasing augmentation to expand the Clotho dataset during pre-training. This strategy helps alleviate the limitation of scarce audio-text pairs and generates more diverse captions from a small set of audio clips. During inference, we introduce the plug-and-play CLAP-Refine strategy to fully exploit multiple decoding outputs, akin to the n-best rescoring strategy in speech recognition. Using the CLAP model for audio-text similarity calculation, we could select the textual descriptions generated by multiple searching beams that best match the input audio. Experimental results show that SLAM-AAC achieves state-of-the-art performance on Clotho V2 and AudioCaps, surpassing previous mainstream models.
DRCap: Decoding CLAP Latents with Retrieval-augmented Generation for Zero-shot Audio Captioning
Oct 12, 2024



Abstract:While automated audio captioning (AAC) has made notable progress, traditional fully supervised AAC models still face two critical challenges: the need for expensive audio-text pair data for training and performance degradation when transferring across domains. To overcome these limitations, we present DRCap, a data-efficient and flexible zero-shot audio captioning system that requires text-only data for training and can quickly adapt to new domains without additional fine-tuning. DRCap integrates a contrastive language-audio pre-training (CLAP) model and a large-language model (LLM) as its backbone. During training, the model predicts the ground-truth caption with a fixed text encoder from CLAP, whereas, during inference, the text encoder is replaced with the audio encoder to generate captions for audio clips in a zero-shot manner. To mitigate the modality gap of the CLAP model, we use both the projection strategy from the encoder side and the retrieval-augmented generation strategy from the decoder side. Specifically, audio embeddings are first projected onto a text embedding support to absorb extensive semantic information within the joint multi-modal space of CLAP. At the same time, similar captions retrieved from a datastore are fed as prompts to instruct the LLM, incorporating external knowledge to take full advantage of its strong generative capability. Conditioned on both the projected CLAP embedding and the retrieved similar captions, the model is able to produce a more accurate and semantically rich textual description. By tailoring the text embedding support and the caption datastore to the target domain, DRCap acquires a robust ability to adapt to new domains in a training-free manner. Experimental results demonstrate that DRCap outperforms all other zero-shot models in in-domain scenarios and achieves state-of-the-art performance in cross-domain scenarios.
EmoBox: Multilingual Multi-corpus Speech Emotion Recognition Toolkit and Benchmark
Jun 11, 2024Abstract:Speech emotion recognition (SER) is an important part of human-computer interaction, receiving extensive attention from both industry and academia. However, the current research field of SER has long suffered from the following problems: 1) There are few reasonable and universal splits of the datasets, making comparing different models and methods difficult. 2) No commonly used benchmark covers numerous corpus and languages for researchers to refer to, making reproduction a burden. In this paper, we propose EmoBox, an out-of-the-box multilingual multi-corpus speech emotion recognition toolkit, along with a benchmark for both intra-corpus and cross-corpus settings. For intra-corpus settings, we carefully designed the data partitioning for different datasets. For cross-corpus settings, we employ a foundation SER model, emotion2vec, to mitigate annotation errors and obtain a test set that is fully balanced in speakers and emotions distributions. Based on EmoBox, we present the intra-corpus SER results of 10 pre-trained speech models on 32 emotion datasets with 14 languages, and the cross-corpus SER results on 4 datasets with the fully balanced test sets. To the best of our knowledge, this is the largest SER benchmark, across language scopes and quantity scales. We hope that our toolkit and benchmark can facilitate the research of SER in the community.
BAT: Learning to Reason about Spatial Sounds with Large Language Models
Feb 02, 2024Abstract:Spatial sound reasoning is a fundamental human skill, enabling us to navigate and interpret our surroundings based on sound. In this paper we present BAT, which combines the spatial sound perception ability of a binaural acoustic scene analysis model with the natural language reasoning capabilities of a large language model (LLM) to replicate this innate ability. To address the lack of existing datasets of in-the-wild spatial sounds, we synthesized a binaural audio dataset using AudioSet and SoundSpaces 2.0. Next, we developed SpatialSoundQA, a spatial sound-based question-answering dataset, offering a range of QA tasks that train BAT in various aspects of spatial sound perception and reasoning. The acoustic front end encoder of BAT is a novel spatial audio encoder named Spatial Audio Spectrogram Transformer, or Spatial-AST, which by itself achieves strong performance across sound event detection, spatial localization, and distance estimation. By integrating Spatial-AST with LLaMA-2 7B model, BAT transcends standard Sound Event Localization and Detection (SELD) tasks, enabling the model to reason about the relationships between the sounds in its environment. Our experiments demonstrate BAT's superior performance on both spatial sound perception and reasoning, showcasing the immense potential of LLMs in navigating and interpreting complex spatial audio environments.
EAT: Self-Supervised Pre-Training with Efficient Audio Transformer
Jan 07, 2024



Abstract:Audio self-supervised learning (SSL) pre-training, which aims to learn good representations from unlabeled audio, has made remarkable progress. However, the extensive computational demands during pre-training pose a significant barrier to the potential application and optimization of audio SSL models. In this paper, inspired by the success of data2vec 2.0 in image modality and Audio-MAE in audio modality, we introduce Efficient Audio Transformer (EAT) to further improve the effectiveness and efficiency in audio SSL. The proposed EAT adopts the bootstrap self-supervised training paradigm to the audio domain. A novel Utterance-Frame Objective (UFO) is designed to enhance the modeling capability of acoustic events. Furthermore, we reveal that the masking strategy is critical in audio SSL pre-training, and superior audio representations can be obtained with large inverse block masks. Experiment results demonstrate that EAT achieves state-of-the-art (SOTA) performance on a range of audio-related tasks, including AudioSet (AS-2M, AS-20K), ESC-50, and SPC-2, along with a significant pre-training speedup up to ~15x compared to existing audio SSL models.
emotion2vec: Self-Supervised Pre-Training for Speech Emotion Representation
Dec 23, 2023



Abstract:We propose emotion2vec, a universal speech emotion representation model. emotion2vec is pre-trained on open-source unlabeled emotion data through self-supervised online distillation, combining utterance-level loss and frame-level loss during pre-training. emotion2vec outperforms state-of-the-art pre-trained universal models and emotion specialist models by only training linear layers for the speech emotion recognition task on the mainstream IEMOCAP dataset. In addition, emotion2vec shows consistent improvements among 10 different languages of speech emotion recognition datasets. emotion2vec also shows excellent results on other emotion tasks, such as song emotion recognition, emotion prediction in conversation, and sentiment analysis. Comparison experiments, ablation experiments, and visualization comprehensively demonstrate the universal capability of the proposed emotion2vec. To the best of our knowledge, emotion2vec is the first universal representation model in various emotion-related tasks, filling a gap in the field.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge