Xing Wei
FARTrack: Fast Autoregressive Visual Tracking with High Performance
Feb 03, 2026Abstract:Inference speed and tracking performance are two critical evaluation metrics in the field of visual tracking. However, high-performance trackers often suffer from slow processing speeds, making them impractical for deployment on resource-constrained devices. To alleviate this issue, we propose FARTrack, a Fast Auto-Regressive Tracking framework. Since autoregression emphasizes the temporal nature of the trajectory sequence, it can maintain high performance while achieving efficient execution across various devices. FARTrack introduces Task-Specific Self-Distillation and Inter-frame Autoregressive Sparsification, designed from the perspectives of shallow-yet-accurate distillation and redundant-to-essential token optimization, respectively. Task-Specific Self-Distillation achieves model compression by distilling task-specific tokens layer by layer, enhancing the model's inference speed while avoiding suboptimal manual teacher-student layer pairs assignments. Meanwhile, Inter-frame Autoregressive Sparsification sequentially condenses multiple templates, avoiding additional runtime overhead while learning a temporally-global optimal sparsification strategy. FARTrack demonstrates outstanding speed and competitive performance. It delivers an AO of 70.6% on GOT-10k in real-time. Beyond, our fastest model achieves a speed of 343 FPS on the GPU and 121 FPS on the CPU.
JanusVLN: Decoupling Semantics and Spatiality with Dual Implicit Memory for Vision-Language Navigation
Sep 26, 2025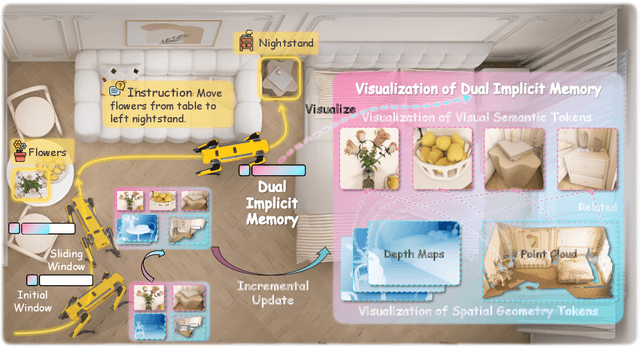
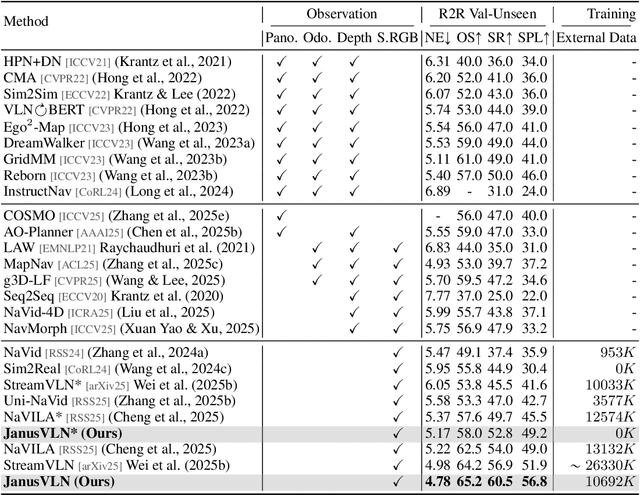
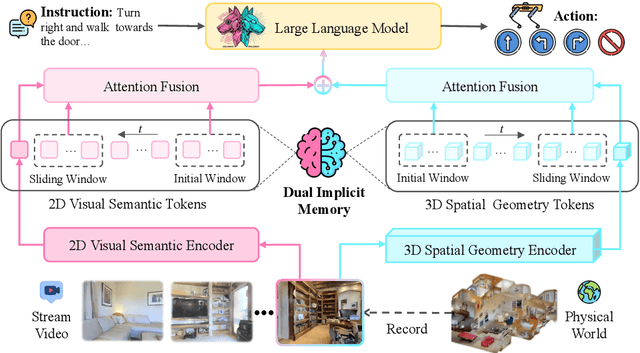
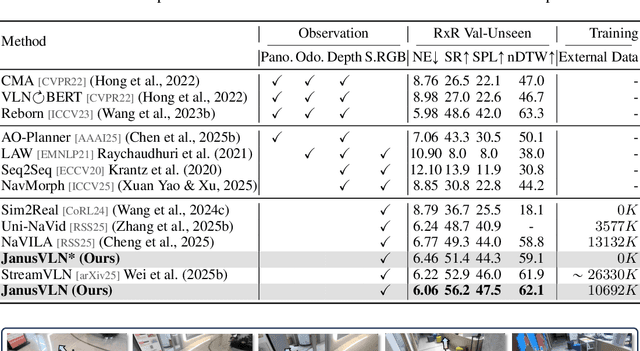
Abstract:Vision-and-Language Navigation requires an embodied agent to navigate through unseen environments, guided by natural language instructions and a continuous video stream. Recent advances in VLN have been driven by the powerful semantic understanding of Multimodal Large Language Models. However, these methods typically rely on explicit semantic memory, such as building textual cognitive maps or storing historical visual frames. This type of method suffers from spatial information loss, computational redundancy, and memory bloat, which impede efficient navigation. Inspired by the implicit scene representation in human navigation, analogous to the left brain's semantic understanding and the right brain's spatial cognition, we propose JanusVLN, a novel VLN framework featuring a dual implicit neural memory that models spatial-geometric and visual-semantic memory as separate, compact, and fixed-size neural representations. This framework first extends the MLLM to incorporate 3D prior knowledge from the spatial-geometric encoder, thereby enhancing the spatial reasoning capabilities of models based solely on RGB input. Then, the historical key-value caches from the spatial-geometric and visual-semantic encoders are constructed into a dual implicit memory. By retaining only the KVs of tokens in the initial and sliding window, redundant computation is avoided, enabling efficient incremental updates. Extensive experiments demonstrate that JanusVLN outperforms over 20 recent methods to achieve SOTA performance. For example, the success rate improves by 10.5-35.5 compared to methods using multiple data types as input and by 3.6-10.8 compared to methods using more RGB training data. This indicates that the proposed dual implicit neural memory, as a novel paradigm, explores promising new directions for future VLN research. Ours project page: https://miv-xjtu.github.io/JanusVLN.github.io/.
GPG-HT: Generalized Policy Gradient with History-Aware Decision Transformer for Probabilistic Path Planning
Aug 24, 2025Abstract:With the rapidly increased number of vehicles in urban areas, existing road infrastructure struggles to accommodate modern traffic demands, resulting in the issue of congestion. This highlights the importance of efficient path planning strategies. However, most recent navigation models focus solely on deterministic or time-dependent networks, while overlooking the correlations and the stochastic nature of traffic flows. In this work, we address the reliable shortest path problem within stochastic transportation networks under certain dependencies. We propose a path planning solution that integrates the decision Transformer with the Generalized Policy Gradient (GPG) framework. Based on the decision Transformer's capability to model long-term dependencies, our proposed solution improves the accuracy and stability of path decisions. Experimental results on the Sioux Falls Network (SFN) demonstrate that our approach outperforms previous baselines in terms of on-time arrival probability, providing more accurate path planning solutions.
FutureSightDrive: Thinking Visually with Spatio-Temporal CoT for Autonomous Driving
May 23, 2025Abstract:Visual language models (VLMs) have attracted increasing interest in autonomous driving due to their powerful reasoning capabilities. However, existing VLMs typically utilize discrete text Chain-of-Thought (CoT) tailored to the current scenario, which essentially represents highly abstract and symbolic compression of visual information, potentially leading to spatio-temporal relationship ambiguity and fine-grained information loss. Is autonomous driving better modeled on real-world simulation and imagination than on pure symbolic logic? In this paper, we propose a spatio-temporal CoT reasoning method that enables models to think visually. First, VLM serves as a world model to generate unified image frame for predicting future world states: where perception results (e.g., lane divider and 3D detection) represent the future spatial relationships, and ordinary future frame represent the temporal evolution relationships. This spatio-temporal CoT then serves as intermediate reasoning steps, enabling the VLM to function as an inverse dynamics model for trajectory planning based on current observations and future predictions. To implement visual generation in VLMs, we propose a unified pretraining paradigm integrating visual generation and understanding, along with a progressive visual CoT enhancing autoregressive image generation. Extensive experimental results demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed method, advancing autonomous driving towards visual reasoning.
TACOcc:Target-Adaptive Cross-Modal Fusion with Volume Rendering for 3D Semantic Occupancy
May 19, 2025Abstract:The performance of multi-modal 3D occupancy prediction is limited by ineffective fusion, mainly due to geometry-semantics mismatch from fixed fusion strategies and surface detail loss caused by sparse, noisy annotations. The mismatch stems from the heterogeneous scale and distribution of point cloud and image features, leading to biased matching under fixed neighborhood fusion. To address this, we propose a target-scale adaptive, bidirectional symmetric retrieval mechanism. It expands the neighborhood for large targets to enhance context awareness and shrinks it for small ones to improve efficiency and suppress noise, enabling accurate cross-modal feature alignment. This mechanism explicitly establishes spatial correspondences and improves fusion accuracy. For surface detail loss, sparse labels provide limited supervision, resulting in poor predictions for small objects. We introduce an improved volume rendering pipeline based on 3D Gaussian Splatting, which takes fused features as input to render images, applies photometric consistency supervision, and jointly optimizes 2D-3D consistency. This enhances surface detail reconstruction while suppressing noise propagation. In summary, we propose TACOcc, an adaptive multi-modal fusion framework for 3D semantic occupancy prediction, enhanced by volume rendering supervision. Experiments on the nuScenes and SemanticKITTI benchmarks validate its effectiveness.
VGAT: A Cancer Survival Analysis Framework Transitioning from Generative Visual Question Answering to Genomic Reconstruction
Mar 25, 2025Abstract:Multimodal learning combining pathology images and genomic sequences enhances cancer survival analysis but faces clinical implementation barriers due to limited access to genomic sequencing in under-resourced regions. To enable survival prediction using only whole-slide images (WSI), we propose the Visual-Genomic Answering-Guided Transformer (VGAT), a framework integrating Visual Question Answering (VQA) techniques for genomic modality reconstruction. By adapting VQA's text feature extraction approach, we derive stable genomic representations that circumvent dimensionality challenges in raw genomic data. Simultaneously, a cluster-based visual prompt module selectively enhances discriminative WSI patches, addressing noise from unfiltered image regions. Evaluated across five TCGA datasets, VGAT outperforms existing WSI-only methods, demonstrating the viability of genomic-informed inference without sequencing. This approach bridges multimodal research and clinical feasibility in resource-constrained settings. The code link is https://github.com/CZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZ/VGAT.
Semantic Segmentation Prior for Diffusion-Based Real-World Super-Resolution
Dec 04, 2024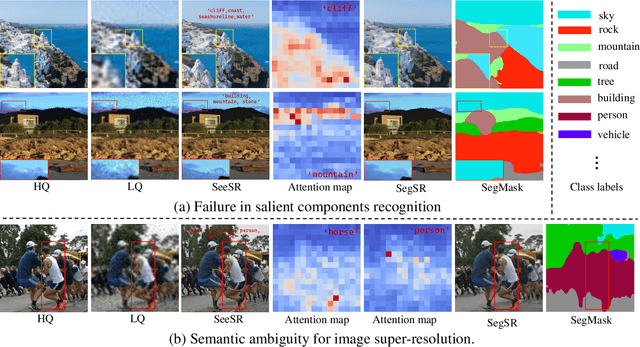
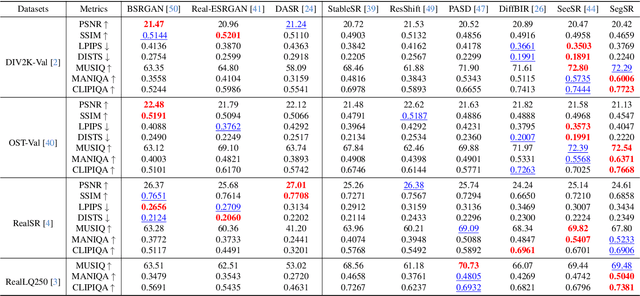
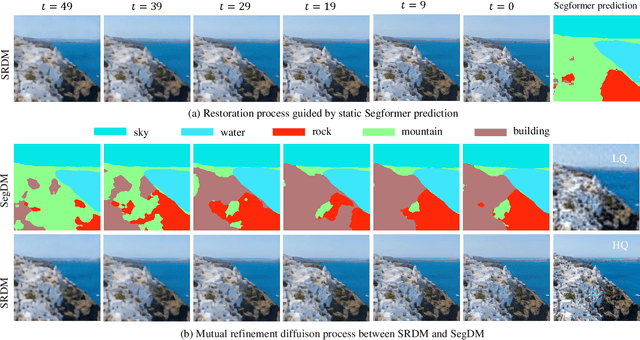
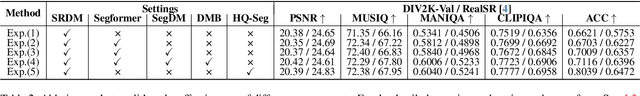
Abstract:Real-world image super-resolution (Real-ISR) has achieved a remarkable leap by leveraging large-scale text-to-image models, enabling realistic image restoration from given recognition textual prompts. However, these methods sometimes fail to recognize some salient objects, resulting in inaccurate semantic restoration in these regions. Additionally, the same region may have a strong response to more than one prompt and it will lead to semantic ambiguity for image super-resolution. To alleviate the above two issues, in this paper, we propose to consider semantic segmentation as an additional control condition into diffusion-based image super-resolution. Compared to textual prompt conditions, semantic segmentation enables a more comprehensive perception of salient objects within an image by assigning class labels to each pixel. It also mitigates the risks of semantic ambiguities by explicitly allocating objects to their respective spatial regions. In practice, inspired by the fact that image super-resolution and segmentation can benefit each other, we propose SegSR which introduces a dual-diffusion framework to facilitate interaction between the image super-resolution and segmentation diffusion models. Specifically, we develop a Dual-Modality Bridge module to enable updated information flow between these two diffusion models, achieving mutual benefit during the reverse diffusion process. Extensive experiments show that SegSR can generate realistic images while preserving semantic structures more effectively.
FLAME: Frozen Large Language Models Enable Data-Efficient Language-Image Pre-training
Nov 18, 2024Abstract:Language-image pre-training faces significant challenges due to limited data in specific formats and the constrained capacities of text encoders. While prevailing methods attempt to address these issues through data augmentation and architecture modifications, they continue to struggle with processing long-form text inputs, and the inherent limitations of traditional CLIP text encoders lead to suboptimal downstream generalization. In this paper, we propose FLAME (Frozen Large lAnguage Models Enable data-efficient language-image pre-training) that leverages frozen large language models as text encoders, naturally processing long text inputs and demonstrating impressive multilingual generalization. FLAME comprises two key components: 1) a multifaceted prompt distillation technique for extracting diverse semantic representations from long captions, which better aligns with the multifaceted nature of images, and 2) a facet-decoupled attention mechanism, complemented by an offline embedding strategy, to ensure efficient computation. Extensive empirical evaluations demonstrate FLAME's superior performance. When trained on CC3M, FLAME surpasses the previous state-of-the-art by 4.9\% in ImageNet top-1 accuracy. On YFCC15M, FLAME surpasses the WIT-400M-trained CLIP by 44.4\% in average image-to-text recall@1 across 36 languages, and by 34.6\% in text-to-image recall@1 for long-context retrieval on Urban-1k. Code is available at \url{https://github.com/MIV-XJTU/FLAME}.
Driving by the Rules: A Benchmark for Integrating Traffic Sign Regulations into Vectorized HD Map
Oct 31, 2024



Abstract:Ensuring adherence to traffic sign regulations is essential for both human and autonomous vehicle navigation. While current benchmark datasets concentrate on lane perception or basic traffic sign recognition, they often overlook the intricate task of integrating these regulations into lane operations. Addressing this gap, we introduce MapDR, a novel dataset designed for the extraction of Driving Rules from traffic signs and their association with vectorized, locally perceived HD Maps. MapDR features over 10,000 annotated video clips that capture the intricate correlation between traffic sign regulations and lanes. We define two pivotal sub-tasks: 1) Rule Extraction from Traffic Sign, which accurately deciphers regulatory instructions, and 2) Rule-Lane Correspondence Reasoning, which aligns these rules with their respective lanes. Built upon this benchmark, we provide a multimodal solution that offers a strong baseline for advancing autonomous driving technologies. It fills a critical gap in the integration of traffic sign rules, contributing to the development of reliable autonomous navigation systems.
Driving with Prior Maps: Unified Vector Prior Encoding for Autonomous Vehicle Mapping
Sep 11, 2024



Abstract:High-Definition Maps (HD maps) are essential for the precise navigation and decision-making of autonomous vehicles, yet their creation and upkeep present significant cost and timeliness challenges. The online construction of HD maps using on-board sensors has emerged as a promising solution; however, these methods can be impeded by incomplete data due to occlusions and inclement weather. This paper proposes the PriorDrive framework to addresses these limitations by harnessing the power of prior maps, significantly enhancing the robustness and accuracy of online HD map construction. Our approach integrates a variety of prior maps, such as OpenStreetMap's Standard Definition Maps (SD maps), outdated HD maps from vendors, and locally constructed maps from historical vehicle data. To effectively encode this prior information into online mapping models, we introduce a Hybrid Prior Representation (HPQuery) that standardizes the representation of diverse map elements. At the core of PriorDrive is the Unified Vector Encoder (UVE), which employs a dual encoding mechanism to process vector data. The intra-vector encoder captures fine-grained local features, while the inter-vector encoder integrates global context. Furthermore, we propose a segment-level and point-level pre-training strategy that enables the UVE to learn the prior distribution of vector data, thereby improving the encoder's generalizability and performance. Through extensive testing on the nuScenes dataset, we demonstrate that PriorDrive is highly compatible with various online mapping models and substantially improves map prediction capabilities. The integration of prior maps through the PriorDrive framework offers a robust solution to the challenges of single-perception data, paving the way for more reliable autonomous vehicle navigation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge