Wei Pang
STProtein: predicting spatial protein expression from multi-omics data
Feb 05, 2026Abstract:The integration of spatial multi-omics data from single tissues is crucial for advancing biological research. However, a significant data imbalance impedes progress: while spatial transcriptomics data is relatively abundant, spatial proteomics data remains scarce due to technical limitations and high costs. To overcome this challenge we propose STProtein, a novel framework leveraging graph neural networks with multi-task learning strategy. STProtein is designed to accurately predict unknown spatial protein expression using more accessible spatial multi-omics data, such as spatial transcriptomics. We believe that STProtein can effectively addresses the scarcity of spatial proteomics, accelerating the integration of spatial multi-omics and potentially catalyzing transformative breakthroughs in life sciences. This tool enables scientists to accelerate discovery by identifying complex and previously hidden spatial patterns of proteins within tissues, uncovering novel relationships between different marker genes, and exploring the biological "Dark Matter".
From Scalar Rewards to Potential Trends: Shaping Potential Landscapes for Model-Based Reinforcement Learning
Feb 03, 2026Abstract:Model-based reinforcement learning (MBRL) achieves high sample efficiency by simulating future trajectories with learned dynamics and reward models. However, its effectiveness is severely compromised in sparse reward settings. The core limitation lies in the standard paradigm of regressing ground-truth scalar rewards: in sparse environments, this yields a flat, gradient-free landscape that fails to provide directional guidance for planning. To address this challenge, we propose Shaping Landscapes with Optimistic Potential Estimates (SLOPE), a novel framework that shifts reward modeling from predicting scalars to constructing informative potential landscapes. SLOPE employs optimistic distributional regression to estimate high-confidence upper bounds, which amplifies rare success signals and ensures sufficient exploration gradients. Evaluations on 30+ tasks across 5 benchmarks demonstrate that SLOPE consistently outperforms leading baselines in fully sparse, semi-sparse, and dense rewards.
XR: Cross-Modal Agents for Composed Image Retrieval
Jan 20, 2026Abstract:Retrieval is being redefined by agentic AI, demanding multimodal reasoning beyond conventional similarity-based paradigms. Composed Image Retrieval (CIR) exemplifies this shift as each query combines a reference image with textual modifications, requiring compositional understanding across modalities. While embedding-based CIR methods have achieved progress, they remain narrow in perspective, capturing limited cross-modal cues and lacking semantic reasoning. To address these limitations, we introduce XR, a training-free multi-agent framework that reframes retrieval as a progressively coordinated reasoning process. It orchestrates three specialized types of agents: imagination agents synthesize target representations through cross-modal generation, similarity agents perform coarse filtering via hybrid matching, and question agents verify factual consistency through targeted reasoning for fine filtering. Through progressive multi-agent coordination, XR iteratively refines retrieval to meet both semantic and visual query constraints, achieving up to a 38% gain over strong training-free and training-based baselines on FashionIQ, CIRR, and CIRCO, while ablations show each agent is essential. Code is available: https://01yzzyu.github.io/xr.github.io/.
Intelligent Collaborative Optimization for Rubber Tyre Film Production Based on Multi-path Differentiated Clipping Proximal Policy Optimization
Nov 19, 2025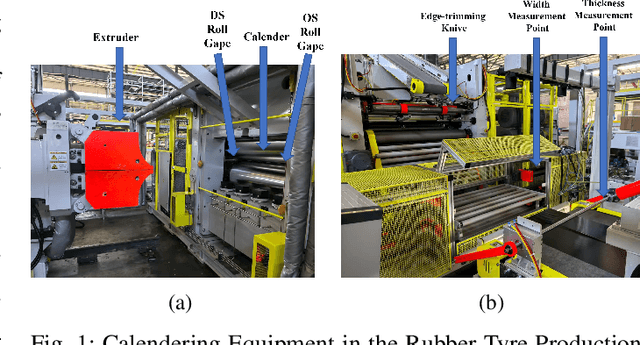
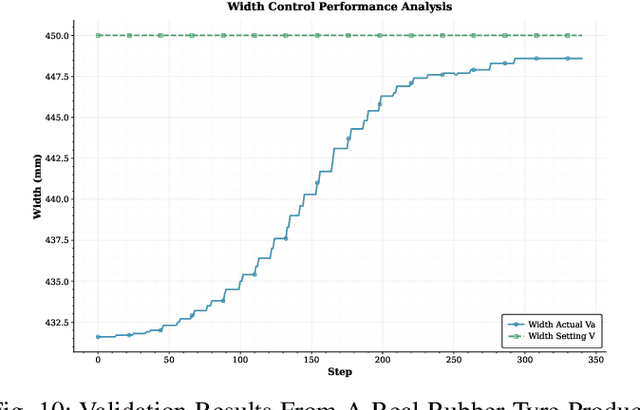
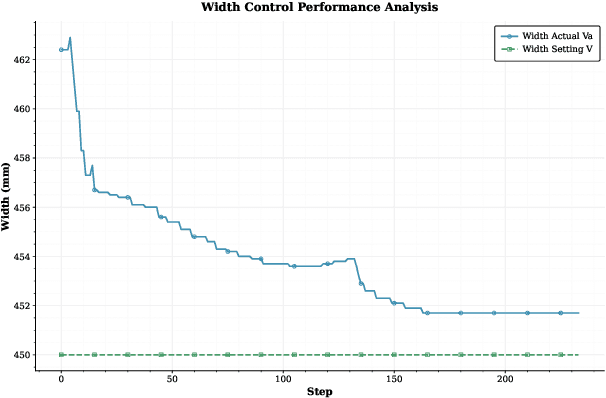
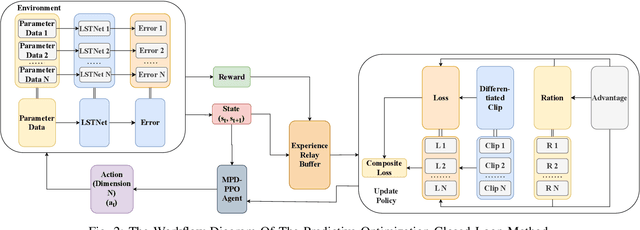
Abstract:The advent of smart manufacturing is addressing the limitations of traditional centralized scheduling and inflexible production line configurations in the rubber tyre industry, especially in terms of coping with dynamic production demands. Contemporary tyre manufacturing systems form complex networks of tightly coupled subsystems pronounced nonlinear interactions and emergent dynamics. This complexity renders the effective coordination of multiple subsystems, posing an essential yet formidable task. For high-dimensional, multi-objective optimization problems in this domain, we introduce a deep reinforcement learning algorithm: Multi-path Differentiated Clipping Proximal Policy Optimization (MPD-PPO). This algorithm employs a multi-branch policy architecture with differentiated gradient clipping constraints to ensure stable and efficient high-dimensional policy updates. Validated through experiments on width and thickness control in rubber tyre film production, MPD-PPO demonstrates substantial improvements in both tuning accuracy and operational efficiency. The framework successfully tackles key challenges, including high dimensionality, multi-objective trade-offs, and dynamic adaptation, thus delivering enhanced performance and production stability for real-time industrial deployment in tyre manufacturing.
Paper2Poster: Towards Multimodal Poster Automation from Scientific Papers
May 27, 2025Abstract:Academic poster generation is a crucial yet challenging task in scientific communication, requiring the compression of long-context interleaved documents into a single, visually coherent page. To address this challenge, we introduce the first benchmark and metric suite for poster generation, which pairs recent conference papers with author-designed posters and evaluates outputs on (i)Visual Quality-semantic alignment with human posters, (ii)Textual Coherence-language fluency, (iii)Holistic Assessment-six fine-grained aesthetic and informational criteria scored by a VLM-as-judge, and notably (iv)PaperQuiz-the poster's ability to convey core paper content as measured by VLMs answering generated quizzes. Building on this benchmark, we propose PosterAgent, a top-down, visual-in-the-loop multi-agent pipeline: the (a)Parser distills the paper into a structured asset library; the (b)Planner aligns text-visual pairs into a binary-tree layout that preserves reading order and spatial balance; and the (c)Painter-Commenter loop refines each panel by executing rendering code and using VLM feedback to eliminate overflow and ensure alignment. In our comprehensive evaluation, we find that GPT-4o outputs-though visually appealing at first glance-often exhibit noisy text and poor PaperQuiz scores, and we find that reader engagement is the primary aesthetic bottleneck, as human-designed posters rely largely on visual semantics to convey meaning. Our fully open-source variants (e.g. based on the Qwen-2.5 series) outperform existing 4o-driven multi-agent systems across nearly all metrics, while using 87% fewer tokens. It transforms a 22-page paper into a finalized yet editable .pptx poster - all for just $0.005. These findings chart clear directions for the next generation of fully automated poster-generation models. The code and datasets are available at https://github.com/Paper2Poster/Paper2Poster.
LazyVLM: Neuro-Symbolic Approach to Video Analytics
May 27, 2025Abstract:Current video analytics approaches face a fundamental trade-off between flexibility and efficiency. End-to-end Vision Language Models (VLMs) often struggle with long-context processing and incur high computational costs, while neural-symbolic methods depend heavily on manual labeling and rigid rule design. In this paper, we introduce LazyVLM, a neuro-symbolic video analytics system that provides a user-friendly query interface similar to VLMs, while addressing their scalability limitation. LazyVLM enables users to effortlessly drop in video data and specify complex multi-frame video queries using a semi-structured text interface for video analytics. To address the scalability limitations of VLMs, LazyVLM decomposes multi-frame video queries into fine-grained operations and offloads the bulk of the processing to efficient relational query execution and vector similarity search. We demonstrate that LazyVLM provides a robust, efficient, and user-friendly solution for querying open-domain video data at scale.
Survey of Video Diffusion Models: Foundations, Implementations, and Applications
Apr 22, 2025Abstract:Recent advances in diffusion models have revolutionized video generation, offering superior temporal consistency and visual quality compared to traditional generative adversarial networks-based approaches. While this emerging field shows tremendous promise in applications, it faces significant challenges in motion consistency, computational efficiency, and ethical considerations. This survey provides a comprehensive review of diffusion-based video generation, examining its evolution, technical foundations, and practical applications. We present a systematic taxonomy of current methodologies, analyze architectural innovations and optimization strategies, and investigate applications across low-level vision tasks such as denoising and super-resolution. Additionally, we explore the synergies between diffusionbased video generation and related domains, including video representation learning, question answering, and retrieval. Compared to the existing surveys (Lei et al., 2024a;b; Melnik et al., 2024; Cao et al., 2023; Xing et al., 2024c) which focus on specific aspects of video generation, such as human video synthesis (Lei et al., 2024a) or long-form content generation (Lei et al., 2024b), our work provides a broader, more updated, and more fine-grained perspective on diffusion-based approaches with a special section for evaluation metrics, industry solutions, and training engineering techniques in video generation. This survey serves as a foundational resource for researchers and practitioners working at the intersection of diffusion models and video generation, providing insights into both the theoretical frameworks and practical implementations that drive this rapidly evolving field. A structured list of related works involved in this survey is also available on https://github.com/Eyeline-Research/Survey-Video-Diffusion.
GraphOmni: A Comprehensive and Extendable Benchmark Framework for Large Language Models on Graph-theoretic Tasks
Apr 17, 2025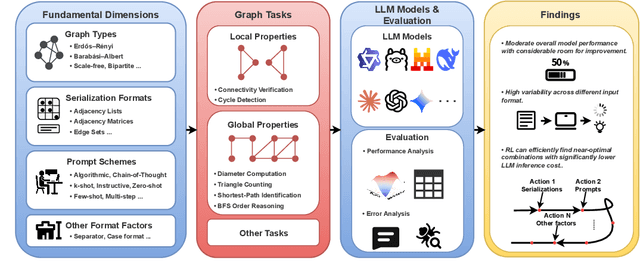
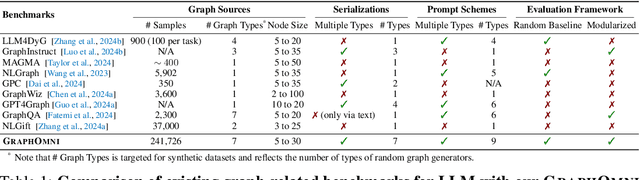
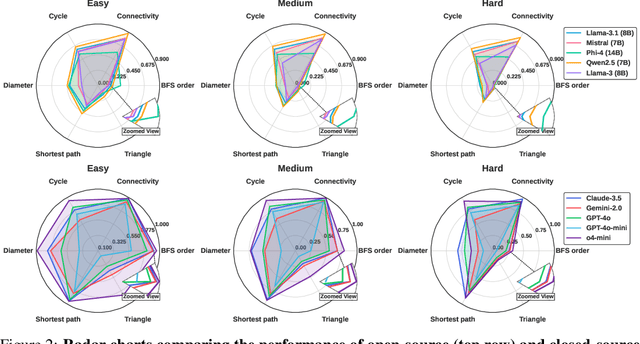
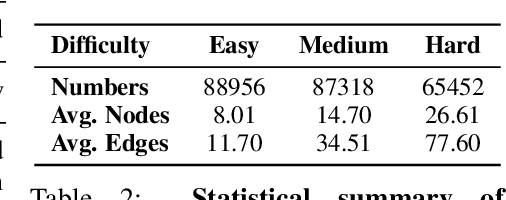
Abstract:In this paper, we presented GraphOmni, a comprehensive benchmark framework for systematically evaluating the graph reasoning capabilities of LLMs. By analyzing critical dimensions, including graph types, serialization formats, and prompt schemes, we provided extensive insights into the strengths and limitations of current LLMs. Our empirical findings emphasize that no single serialization or prompting strategy consistently outperforms others. Motivated by these insights, we propose a reinforcement learning-based approach that dynamically selects the best serialization-prompt pairings, resulting in significant accuracy improvements. GraphOmni's modular and extensible design establishes a robust foundation for future research, facilitating advancements toward general-purpose graph reasoning models.
An Efficient Diffusion-based Non-Autoregressive Solver for Traveling Salesman Problem
Jan 23, 2025



Abstract:Recent advances in neural models have shown considerable promise in solving Traveling Salesman Problems (TSPs) without relying on much hand-crafted engineering. However, while non-autoregressive (NAR) approaches benefit from faster inference through parallelism, they typically deliver solutions of inferior quality compared to autoregressive ones. To enhance the solution quality while maintaining fast inference, we propose DEITSP, a diffusion model with efficient iterations tailored for TSP that operates in a NAR manner. Firstly, we introduce a one-step diffusion model that integrates the controlled discrete noise addition process with self-consistency enhancement, enabling optimal solution prediction through simultaneous denoising of multiple solutions. Secondly, we design a dual-modality graph transformer to bolster the extraction and fusion of features from node and edge modalities, while further accelerating the inference with fewer layers. Thirdly, we develop an efficient iterative strategy that alternates between adding and removing noise to improve exploration compared to previous diffusion methods. Additionally, we devise a scheduling framework to progressively refine the solution space by adjusting noise levels, facilitating a smooth search for optimal solutions. Extensive experiments on real-world and large-scale TSP instances demonstrate that DEITSP performs favorably against existing neural approaches in terms of solution quality, inference latency, and generalization ability. Our code is available at $\href{https://github.com/DEITSP/DEITSP}{https://github.com/DEITSP/DEITSP}$.
Boosting Short Text Classification with Multi-Source Information Exploration and Dual-Level Contrastive Learning
Jan 16, 2025



Abstract:Short text classification, as a research subtopic in natural language processing, is more challenging due to its semantic sparsity and insufficient labeled samples in practical scenarios. We propose a novel model named MI-DELIGHT for short text classification in this work. Specifically, it first performs multi-source information (i.e., statistical information, linguistic information, and factual information) exploration to alleviate the sparsity issues. Then, the graph learning approach is adopted to learn the representation of short texts, which are presented in graph forms. Moreover, we introduce a dual-level (i.e., instance-level and cluster-level) contrastive learning auxiliary task to effectively capture different-grained contrastive information within massive unlabeled data. Meanwhile, previous models merely perform the main task and auxiliary tasks in parallel, without considering the relationship among tasks. Therefore, we introduce a hierarchical architecture to explicitly model the correlations between tasks. We conduct extensive experiments across various benchmark datasets, demonstrating that MI-DELIGHT significantly surpasses previous competitive models. It even outperforms popular large language models on several datasets.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge