Yimu Wang
UNIFORM: Unifying Knowledge from Large-scale and Diverse Pre-trained Models
Aug 27, 2025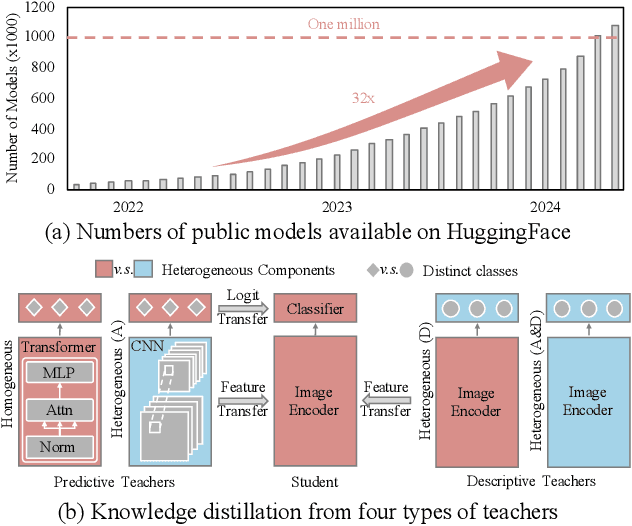
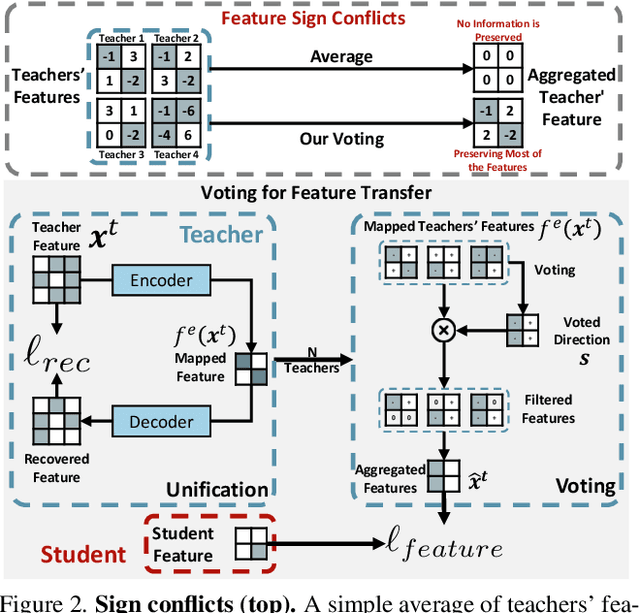
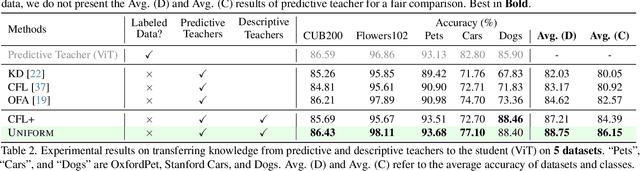
Abstract:In the era of deep learning, the increasing number of pre-trained models available online presents a wealth of knowledge. These models, developed with diverse architectures and trained on varied datasets for different tasks, provide unique interpretations of the real world. Their collective consensus is likely universal and generalizable to unseen data. However, effectively harnessing this collective knowledge poses a fundamental challenge due to the heterogeneity of pre-trained models. Existing knowledge integration solutions typically rely on strong assumptions about training data distributions and network architectures, limiting them to learning only from specific types of models and resulting in data and/or inductive biases. In this work, we introduce a novel framework, namely UNIFORM, for knowledge transfer from a diverse set of off-the-shelf models into one student model without such constraints. Specifically, we propose a dedicated voting mechanism to capture the consensus of knowledge both at the logit level -- incorporating teacher models that are capable of predicting target classes of interest -- and at the feature level, utilizing visual representations learned on arbitrary label spaces. Extensive experiments demonstrate that UNIFORM effectively enhances unsupervised object recognition performance compared to strong knowledge transfer baselines. Notably, it exhibits remarkable scalability by benefiting from over one hundred teachers, while existing methods saturate at a much smaller scale.
HAWAII: Hierarchical Visual Knowledge Transfer for Efficient Vision-Language Models
Jun 23, 2025Abstract:Improving the visual understanding ability of vision-language models (VLMs) is crucial for enhancing their performance across various tasks. While using multiple pretrained visual experts has shown great promise, it often incurs significant computational costs during training and inference. To address this challenge, we propose HAWAII, a novel framework that distills knowledge from multiple visual experts into a single vision encoder, enabling it to inherit the complementary strengths of several experts with minimal computational overhead. To mitigate conflicts among different teachers and switch between different teacher-specific knowledge, instead of using a fixed set of adapters for multiple teachers, we propose to use teacher-specific Low-Rank Adaptation (LoRA) adapters with a corresponding router. Each adapter is aligned with a specific teacher, avoiding noisy guidance during distillation. To enable efficient knowledge distillation, we propose fine-grained and coarse-grained distillation. At the fine-grained level, token importance scores are employed to emphasize the most informative tokens from each teacher adaptively. At the coarse-grained level, we summarize the knowledge from multiple teachers and transfer it to the student using a set of general-knowledge LoRA adapters with a router. Extensive experiments on various vision-language tasks demonstrate the superiority of HAWAII, compared to the popular open-source VLMs.
Survey of Video Diffusion Models: Foundations, Implementations, and Applications
Apr 22, 2025Abstract:Recent advances in diffusion models have revolutionized video generation, offering superior temporal consistency and visual quality compared to traditional generative adversarial networks-based approaches. While this emerging field shows tremendous promise in applications, it faces significant challenges in motion consistency, computational efficiency, and ethical considerations. This survey provides a comprehensive review of diffusion-based video generation, examining its evolution, technical foundations, and practical applications. We present a systematic taxonomy of current methodologies, analyze architectural innovations and optimization strategies, and investigate applications across low-level vision tasks such as denoising and super-resolution. Additionally, we explore the synergies between diffusionbased video generation and related domains, including video representation learning, question answering, and retrieval. Compared to the existing surveys (Lei et al., 2024a;b; Melnik et al., 2024; Cao et al., 2023; Xing et al., 2024c) which focus on specific aspects of video generation, such as human video synthesis (Lei et al., 2024a) or long-form content generation (Lei et al., 2024b), our work provides a broader, more updated, and more fine-grained perspective on diffusion-based approaches with a special section for evaluation metrics, industry solutions, and training engineering techniques in video generation. This survey serves as a foundational resource for researchers and practitioners working at the intersection of diffusion models and video generation, providing insights into both the theoretical frameworks and practical implementations that drive this rapidly evolving field. A structured list of related works involved in this survey is also available on https://github.com/Eyeline-Research/Survey-Video-Diffusion.
LEO-MINI: An Efficient Multimodal Large Language Model using Conditional Token Reduction and Mixture of Multi-Modal Experts
Apr 07, 2025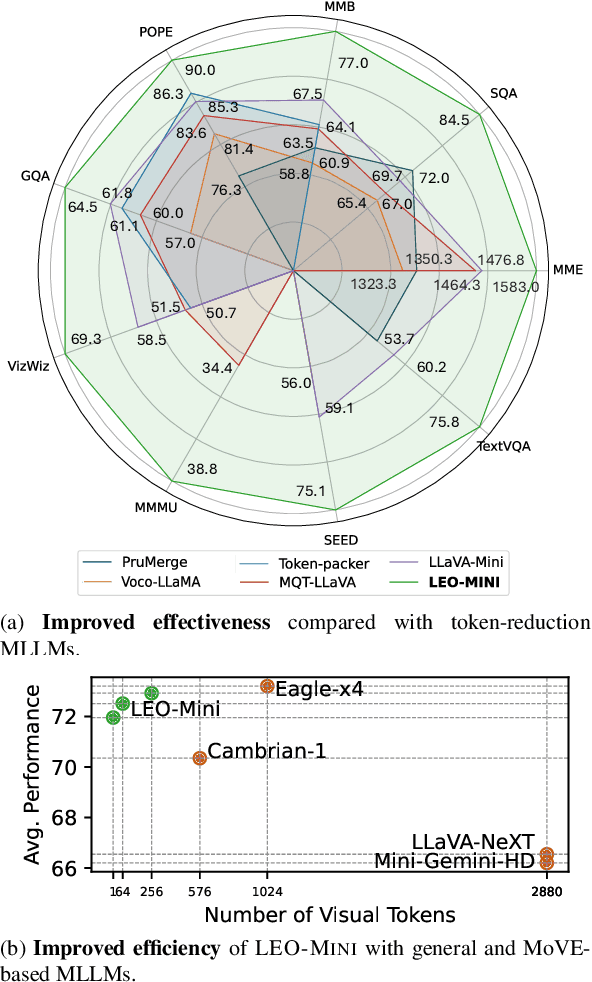
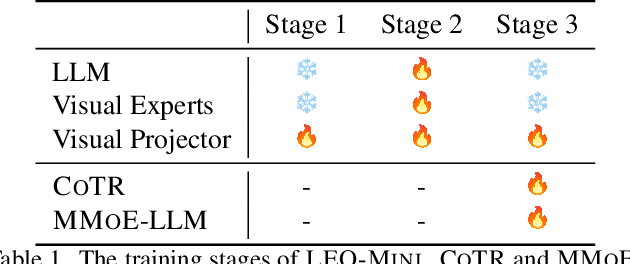
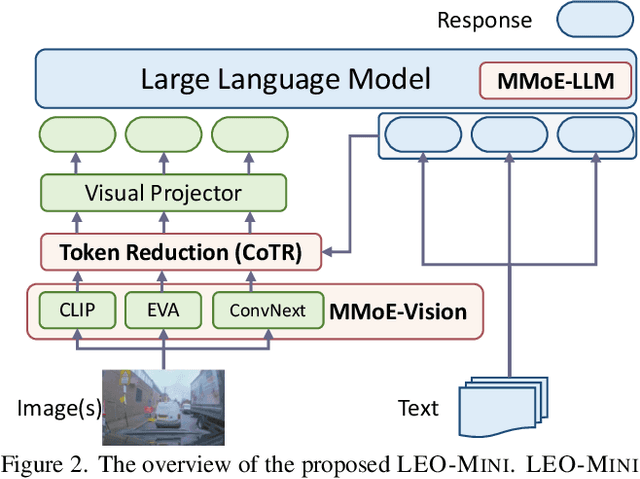
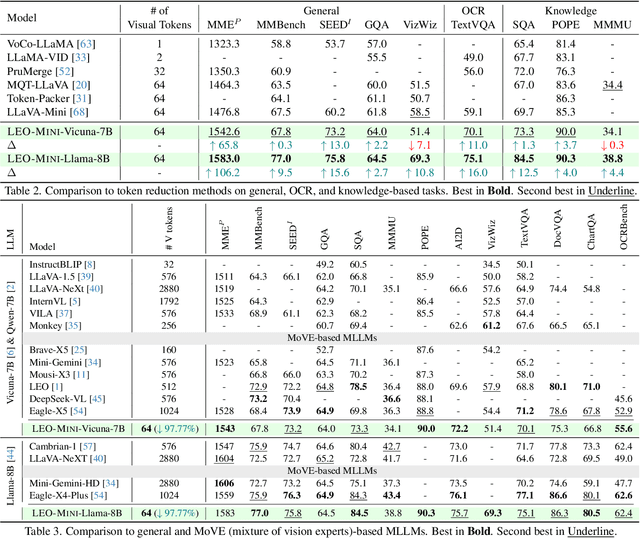
Abstract:Redundancy of visual tokens in multi-modal large language models (MLLMs) significantly reduces their computational efficiency. Recent approaches, such as resamplers and summarizers, have sought to reduce the number of visual tokens, but at the cost of visual reasoning ability. To address this, we propose LEO-MINI, a novel MLLM that significantly reduces the number of visual tokens and simultaneously boosts visual reasoning capabilities. For efficiency, LEO-MINI incorporates CoTR, a novel token reduction module to consolidate a large number of visual tokens into a smaller set of tokens, using the similarity between visual tokens, text tokens, and a compact learnable query. For effectiveness, to scale up the model's ability with minimal computational overhead, LEO-MINI employs MMoE, a novel mixture of multi-modal experts module. MMOE employs a set of LoRA experts with a novel router to switch between them based on the input text and visual tokens instead of only using the input hidden state. MMoE also includes a general LoRA expert that is always activated to learn general knowledge for LLM reasoning. For extracting richer visual features, MMOE employs a set of vision experts trained on diverse domain-specific data. To demonstrate LEO-MINI's improved efficiency and performance, we evaluate it against existing efficient MLLMs on various benchmark vision-language tasks.
OV-SCAN: Semantically Consistent Alignment for Novel Object Discovery in Open-Vocabulary 3D Object Detection
Mar 09, 2025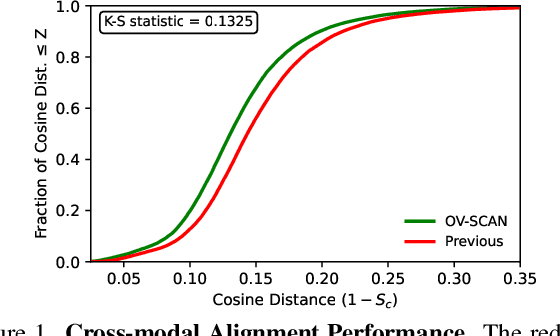
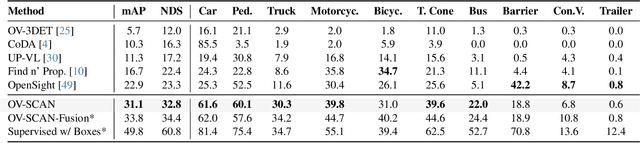
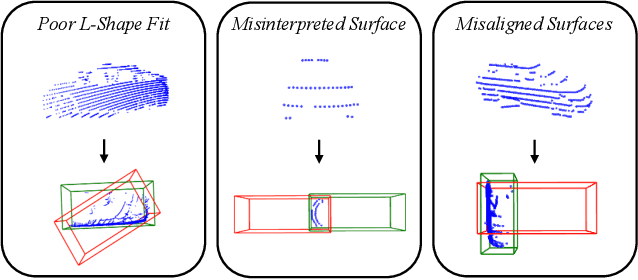
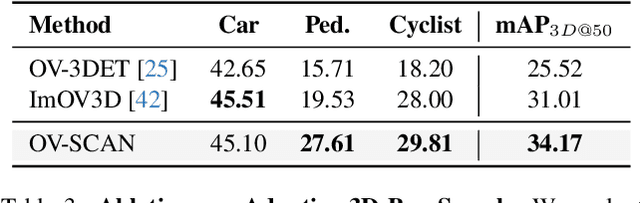
Abstract:Open-vocabulary 3D object detection for autonomous driving aims to detect novel objects beyond the predefined training label sets in point cloud scenes. Existing approaches achieve this by connecting traditional 3D object detectors with vision-language models (VLMs) to regress 3D bounding boxes for novel objects and perform open-vocabulary classification through cross-modal alignment between 3D and 2D features. However, achieving robust cross-modal alignment remains a challenge due to semantic inconsistencies when generating corresponding 3D and 2D feature pairs. To overcome this challenge, we present OV-SCAN, an Open-Vocabulary 3D framework that enforces Semantically Consistent Alignment for Novel object discovery. OV-SCAN employs two core strategies: discovering precise 3D annotations and filtering out low-quality or corrupted alignment pairs (arising from 3D annotation, occlusion-induced, or resolution-induced noise). Extensive experiments on the nuScenes dataset demonstrate that OV-SCAN achieves state-of-the-art performance.
Do spectral cues matter in contrast-based graph self-supervised learning?
May 30, 2024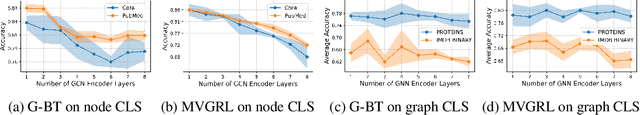
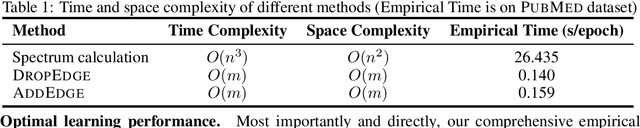
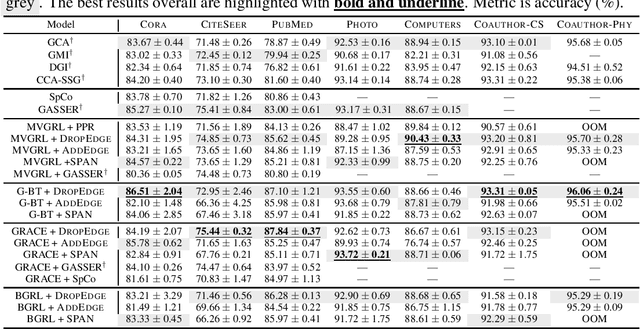
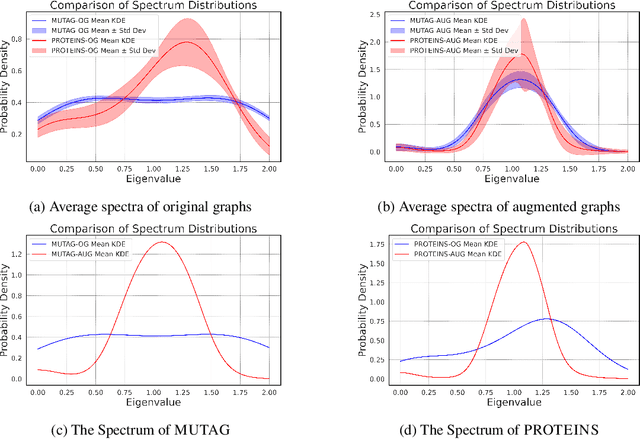
Abstract:The recent surge in contrast-based graph self-supervised learning has prominently featured an intensified exploration of spectral cues. However, an intriguing paradox emerges, as methods grounded in seemingly conflicting assumptions or heuristic approaches regarding the spectral domain demonstrate notable enhancements in learning performance. This paradox prompts a critical inquiry into the genuine contribution of spectral information to contrast-based graph self-supervised learning. This study undertakes an extensive investigation into this inquiry, conducting a thorough study of the relationship between spectral characteristics and the learning outcomes of contemporary methodologies. Based on this analysis, we claim that the effectiveness and significance of spectral information need to be questioned. Instead, we revisit simple edge perturbation: random edge dropping designed for node-level self-supervised learning and random edge adding intended for graph-level self-supervised learning. Compelling evidence is presented that these simple yet effective strategies consistently yield superior performance while demanding significantly fewer computational resources compared to all prior spectral augmentation methods. The proposed insights represent a significant leap forward in the field, potentially reshaping the understanding and implementation of graph self-supervised learning.
HaVTR: Improving Video-Text Retrieval Through Augmentation Using Large Foundation Models
Apr 07, 2024



Abstract:While recent progress in video-text retrieval has been driven by the exploration of powerful model architectures and training strategies, the representation learning ability of video-text retrieval models is still limited due to low-quality and scarce training data annotations. To address this issue, we present a novel video-text learning paradigm, HaVTR, which augments video and text data to learn more generalized features. Specifically, we first adopt a simple augmentation method, which generates self-similar data by randomly duplicating or dropping subwords and frames. In addition, inspired by the recent advancement in visual and language generative models, we propose a more powerful augmentation method through textual paraphrasing and video stylization using large language models (LLMs) and visual generative models (VGMs). Further, to bring richer information into video and text, we propose a hallucination-based augmentation method, where we use LLMs and VGMs to generate and add new relevant information to the original data. Benefiting from the enriched data, extensive experiments on several video-text retrieval benchmarks demonstrate the superiority of HaVTR over existing methods.
Pretext Training Algorithms for Event Sequence Data
Feb 16, 2024



Abstract:Pretext training followed by task-specific fine-tuning has been a successful approach in vision and language domains. This paper proposes a self-supervised pretext training framework tailored to event sequence data. We introduce a novel alignment verification task that is specialized to event sequences, building on good practices in masked reconstruction and contrastive learning. Our pretext tasks unlock foundational representations that are generalizable across different down-stream tasks, including next-event prediction for temporal point process models, event sequence classification, and missing event interpolation. Experiments on popular public benchmarks demonstrate the potential of the proposed method across different tasks and data domains.
Efficient Algorithms for Generalized Linear Bandits with Heavy-tailed Rewards
Oct 28, 2023
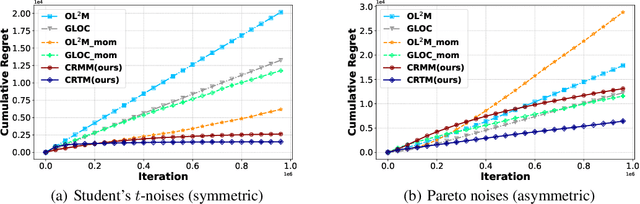
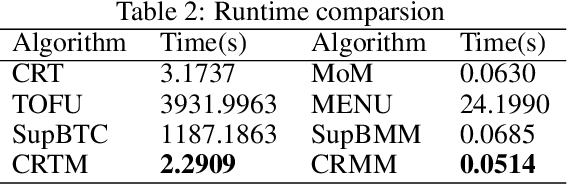
Abstract:This paper investigates the problem of generalized linear bandits with heavy-tailed rewards, whose $(1+\epsilon)$-th moment is bounded for some $\epsilon\in (0,1]$. Although there exist methods for generalized linear bandits, most of them focus on bounded or sub-Gaussian rewards and are not well-suited for many real-world scenarios, such as financial markets and web-advertising. To address this issue, we propose two novel algorithms based on truncation and mean of medians. These algorithms achieve an almost optimal regret bound of $\widetilde{O}(dT^{\frac{1}{1+\epsilon}})$, where $d$ is the dimension of contextual information and $T$ is the time horizon. Our truncation-based algorithm supports online learning, distinguishing it from existing truncation-based approaches. Additionally, our mean-of-medians-based algorithm requires only $O(\log T)$ rewards and one estimator per epoch, making it more practical. Moreover, our algorithms improve the regret bounds by a logarithmic factor compared to existing algorithms when $\epsilon=1$. Numerical experimental results confirm the merits of our algorithms.
InvGC: Robust Cross-Modal Retrieval by Inverse Graph Convolution
Oct 25, 2023Abstract:Over recent decades, significant advancements in cross-modal retrieval are mainly driven by breakthroughs in visual and linguistic modeling. However, a recent study shows that multi-modal data representations tend to cluster within a limited convex cone (as representation degeneration problem), which hinders retrieval performance due to the inseparability of these representations. In our study, we first empirically validate the presence of the representation degeneration problem across multiple cross-modal benchmarks and methods. Next, to address it, we introduce a novel method, called InvGC, a post-processing technique inspired by graph convolution and average pooling. Specifically, InvGC defines the graph topology within the datasets and then applies graph convolution in a subtractive manner. This method effectively separates representations by increasing the distances between data points. To improve the efficiency and effectiveness of InvGC, we propose an advanced graph topology, LocalAdj, which only aims to increase the distances between each data point and its nearest neighbors. To understand why InvGC works, we present a detailed theoretical analysis, proving that the lower bound of recall will be improved after deploying InvGC. Extensive empirical results show that InvGC and InvGC w/LocalAdj significantly mitigate the representation degeneration problem, thereby enhancing retrieval performance. Our code is available at https://github.com/yimuwangcs/Better_Cross_Modal_Retrieval
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge