Renchu Guan
Robust Misinformation Detection by Visiting Potential Commonsense Conflict
Apr 30, 2025



Abstract:The development of Internet technology has led to an increased prevalence of misinformation, causing severe negative effects across diverse domains. To mitigate this challenge, Misinformation Detection (MD), aiming to detect online misinformation automatically, emerges as a rapidly growing research topic in the community. In this paper, we propose a novel plug-and-play augmentation method for the MD task, namely Misinformation Detection with Potential Commonsense Conflict (MD-PCC). We take inspiration from the prior studies indicating that fake articles are more likely to involve commonsense conflict. Accordingly, we construct commonsense expressions for articles, serving to express potential commonsense conflicts inferred by the difference between extracted commonsense triplet and golden ones inferred by the well-established commonsense reasoning tool COMET. These expressions are then specified for each article as augmentation. Any specific MD methods can be then trained on those commonsense-augmented articles. Besides, we also collect a novel commonsense-oriented dataset named CoMis, whose all fake articles are caused by commonsense conflict. We integrate MD-PCC with various existing MD backbones and compare them across both 4 public benchmark datasets and CoMis. Empirical results demonstrate that MD-PCC can consistently outperform the existing MD baselines.
Dual-level Mixup for Graph Few-shot Learning with Fewer Tasks
Feb 19, 2025



Abstract:Graph neural networks have been demonstrated as a powerful paradigm for effectively learning graph-structured data on the web and mining content from it.Current leading graph models require a large number of labeled samples for training, which unavoidably leads to overfitting in few-shot scenarios. Recent research has sought to alleviate this issue by simultaneously leveraging graph learning and meta-learning paradigms. However, these graph meta-learning models assume the availability of numerous meta-training tasks to learn transferable meta-knowledge. Such assumption may not be feasible in the real world due to the difficulty of constructing tasks and the substantial costs involved. Therefore, we propose a SiMple yet effectIve approach for graph few-shot Learning with fEwer tasks, named SMILE. We introduce a dual-level mixup strategy, encompassing both within-task and across-task mixup, to simultaneously enrich the available nodes and tasks in meta-learning. Moreover, we explicitly leverage the prior information provided by the node degrees in the graph to encode expressive node representations. Theoretically, we demonstrate that SMILE can enhance the model generalization ability. Empirically, SMILE consistently outperforms other competitive models by a large margin across all evaluated datasets with in-domain and cross-domain settings. Our anonymous code can be found here.
Boosting Short Text Classification with Multi-Source Information Exploration and Dual-Level Contrastive Learning
Jan 16, 2025



Abstract:Short text classification, as a research subtopic in natural language processing, is more challenging due to its semantic sparsity and insufficient labeled samples in practical scenarios. We propose a novel model named MI-DELIGHT for short text classification in this work. Specifically, it first performs multi-source information (i.e., statistical information, linguistic information, and factual information) exploration to alleviate the sparsity issues. Then, the graph learning approach is adopted to learn the representation of short texts, which are presented in graph forms. Moreover, we introduce a dual-level (i.e., instance-level and cluster-level) contrastive learning auxiliary task to effectively capture different-grained contrastive information within massive unlabeled data. Meanwhile, previous models merely perform the main task and auxiliary tasks in parallel, without considering the relationship among tasks. Therefore, we introduce a hierarchical architecture to explicitly model the correlations between tasks. We conduct extensive experiments across various benchmark datasets, demonstrating that MI-DELIGHT significantly surpasses previous competitive models. It even outperforms popular large language models on several datasets.
A Simple Graph Contrastive Learning Framework for Short Text Classification
Jan 16, 2025



Abstract:Short text classification has gained significant attention in the information age due to its prevalence and real-world applications. Recent advancements in graph learning combined with contrastive learning have shown promising results in addressing the challenges of semantic sparsity and limited labeled data in short text classification. However, existing models have certain limitations. They rely on explicit data augmentation techniques to generate contrastive views, resulting in semantic corruption and noise. Additionally, these models only focus on learning the intrinsic consistency between the generated views, neglecting valuable discriminative information from other potential views. To address these issues, we propose a Simple graph contrastive learning framework for Short Text Classification (SimSTC). Our approach involves performing graph learning on multiple text-related component graphs to obtain multi-view text embeddings. Subsequently, we directly apply contrastive learning on these embeddings. Notably, our method eliminates the need for data augmentation operations to generate contrastive views while still leveraging the benefits of multi-view contrastive learning. Despite its simplicity, our model achieves outstanding performance, surpassing large language models on various datasets.
Enhancing Unsupervised Graph Few-shot Learning via Set Functions and Optimal Transport
Jan 10, 2025



Abstract:Graph few-shot learning has garnered significant attention for its ability to rapidly adapt to downstream tasks with limited labeled data, sparking considerable interest among researchers. Recent advancements in graph few-shot learning models have exhibited superior performance across diverse applications. Despite their successes, several limitations still exist. First, existing models in the meta-training phase predominantly focus on instance-level features within tasks, neglecting crucial set-level features essential for distinguishing between different categories. Second, these models often utilize query sets directly on classifiers trained with support sets containing only a few labeled examples, overlooking potential distribution shifts between these sets and leading to suboptimal performance. Finally, previous models typically require necessitate abundant labeled data from base classes to extract transferable knowledge, which is typically infeasible in real-world scenarios. To address these issues, we propose a novel model named STAR, which leverages Set funcTions and optimAl tRansport for enhancing unsupervised graph few-shot learning. Specifically, STAR utilizes expressive set functions to obtain set-level features in an unsupervised manner and employs optimal transport principles to align the distributions of support and query sets, thereby mitigating distribution shift effects. Theoretical analysis demonstrates that STAR can capture more task-relevant information and enhance generalization capabilities. Empirically, extensive experiments across multiple datasets validate the effectiveness of STAR. Our code can be found here.
Instance-adaptive Zero-shot Chain-of-Thought Prompting
Sep 30, 2024



Abstract:Zero-shot Chain-of-Thought (CoT) prompting emerges as a simple and effective strategy for enhancing the performance of large language models (LLMs) in real-world reasoning tasks. Nonetheless, the efficacy of a singular, task-level prompt uniformly applied across the whole of instances is inherently limited since one prompt cannot be a good partner for all, a more appropriate approach should consider the interaction between the prompt and each instance meticulously. This work introduces an instance-adaptive prompting algorithm as an alternative zero-shot CoT reasoning scheme by adaptively differentiating good and bad prompts. Concretely, we first employ analysis on LLMs through the lens of information flow to detect the mechanism under zero-shot CoT reasoning, in which we discover that information flows from question to prompt and question to rationale jointly influence the reasoning results most. We notice that a better zero-shot CoT reasoning needs the prompt to obtain semantic information from the question then the rationale aggregates sufficient information from the question directly and via the prompt indirectly. On the contrary, lacking any of those would probably lead to a bad one. Stem from that, we further propose an instance-adaptive prompting strategy (IAP) for zero-shot CoT reasoning. Experiments conducted with LLaMA-2, LLaMA-3, and Qwen on math, logic, and commonsense reasoning tasks (e.g., GSM8K, MMLU, Causal Judgement) obtain consistent improvement, demonstrating that the instance-adaptive zero-shot CoT prompting performs better than other task-level methods with some curated prompts or sophisticated procedures, showing the significance of our findings in the zero-shot CoT reasoning mechanism.
Harmfully Manipulated Images Matter in Multimodal Misinformation Detection
Jul 27, 2024Abstract:Nowadays, misinformation is widely spreading over various social media platforms and causes extremely negative impacts on society. To combat this issue, automatically identifying misinformation, especially those containing multimodal content, has attracted growing attention from the academic and industrial communities, and induced an active research topic named Multimodal Misinformation Detection (MMD). Typically, existing MMD methods capture the semantic correlation and inconsistency between multiple modalities, but neglect some potential clues in multimodal content. Recent studies suggest that manipulated traces of the images in articles are non-trivial clues for detecting misinformation. Meanwhile, we find that the underlying intentions behind the manipulation, e.g., harmful and harmless, also matter in MMD. Accordingly, in this work, we propose to detect misinformation by learning manipulation features that indicate whether the image has been manipulated, as well as intention features regarding the harmful and harmless intentions of the manipulation. Unfortunately, the manipulation and intention labels that make these features discriminative are unknown. To overcome the problem, we propose two weakly supervised signals as alternatives by introducing additional datasets on image manipulation detection and formulating two classification tasks as positive and unlabeled learning problems. Based on these ideas, we propose a novel MMD method, namely Harmfully Manipulated Images Matter in MMD (HAMI-M3D). Extensive experiments across three benchmark datasets can demonstrate that HAMI-M3D can consistently improve the performance of any MMD baselines.
Meta-GPS++: Enhancing Graph Meta-Learning with Contrastive Learning and Self-Training
Jul 20, 2024



Abstract:Node classification is an essential problem in graph learning. However, many models typically obtain unsatisfactory performance when applied to few-shot scenarios. Some studies have attempted to combine meta-learning with graph neural networks to solve few-shot node classification on graphs. Despite their promising performance, some limitations remain. First, they employ the node encoding mechanism of homophilic graphs to learn node embeddings, even in heterophilic graphs. Second, existing models based on meta-learning ignore the interference of randomness in the learning process. Third, they are trained using only limited labeled nodes within the specific task, without explicitly utilizing numerous unlabeled nodes. Finally, they treat almost all sampled tasks equally without customizing them for their uniqueness. To address these issues, we propose a novel framework for few-shot node classification called Meta-GPS++. Specifically, we first adopt an efficient method to learn discriminative node representations on homophilic and heterophilic graphs. Then, we leverage a prototype-based approach to initialize parameters and contrastive learning for regularizing the distribution of node embeddings. Moreover, we apply self-training to extract valuable information from unlabeled nodes. Additionally, we adopt S$^2$ (scaling & shifting) transformation to learn transferable knowledge from diverse tasks. The results on real-world datasets show the superiority of Meta-GPS++. Our code is available here.
Resolving Word Vagueness with Scenario-guided Adapter for Natural Language Inference
May 21, 2024


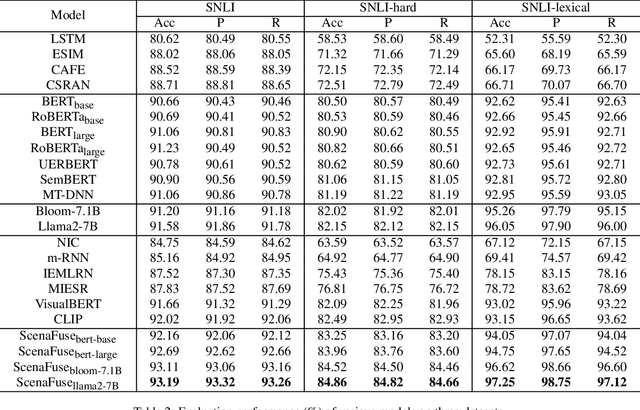
Abstract:Natural Language Inference (NLI) is a crucial task in natural language processing that involves determining the relationship between two sentences, typically referred to as the premise and the hypothesis. However, traditional NLI models solely rely on the semantic information inherent in independent sentences and lack relevant situational visual information, which can hinder a complete understanding of the intended meaning of the sentences due to the ambiguity and vagueness of language. To address this challenge, we propose an innovative ScenaFuse adapter that simultaneously integrates large-scale pre-trained linguistic knowledge and relevant visual information for NLI tasks. Specifically, we first design an image-sentence interaction module to incorporate visuals into the attention mechanism of the pre-trained model, allowing the two modalities to interact comprehensively. Furthermore, we introduce an image-sentence fusion module that can adaptively integrate visual information from images and semantic information from sentences. By incorporating relevant visual information and leveraging linguistic knowledge, our approach bridges the gap between language and vision, leading to improved understanding and inference capabilities in NLI tasks. Extensive benchmark experiments demonstrate that our proposed ScenaFuse, a scenario-guided approach, consistently boosts NLI performance.
Simple-Sampling and Hard-Mixup with Prototypes to Rebalance Contrastive Learning for Text Classification
May 19, 2024



Abstract:Text classification is a crucial and fundamental task in natural language processing. Compared with the previous learning paradigm of pre-training and fine-tuning by cross entropy loss, the recently proposed supervised contrastive learning approach has received tremendous attention due to its powerful feature learning capability and robustness. Although several studies have incorporated this technique for text classification, some limitations remain. First, many text datasets are imbalanced, and the learning mechanism of supervised contrastive learning is sensitive to data imbalance, which may harm the model performance. Moreover, these models leverage separate classification branch with cross entropy and supervised contrastive learning branch without explicit mutual guidance. To this end, we propose a novel model named SharpReCL for imbalanced text classification tasks. First, we obtain the prototype vector of each class in the balanced classification branch to act as a representation of each class. Then, by further explicitly leveraging the prototype vectors, we construct a proper and sufficient target sample set with the same size for each class to perform the supervised contrastive learning procedure. The empirical results show the effectiveness of our model, which even outperforms popular large language models across several datasets.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge