Menghan Hu
CompressedVQA-HDR: Generalized Full-reference and No-reference Quality Assessment Models for Compressed High Dynamic Range Videos
Jul 16, 2025Abstract:Video compression is a standard procedure applied to all videos to minimize storage and transmission demands while preserving visual quality as much as possible. Therefore, evaluating the visual quality of compressed videos is crucial for guiding the practical usage and further development of video compression algorithms. Although numerous compressed video quality assessment (VQA) methods have been proposed, they often lack the generalization capability needed to handle the increasing diversity of video types, particularly high dynamic range (HDR) content. In this paper, we introduce CompressedVQA-HDR, an effective VQA framework designed to address the challenges of HDR video quality assessment. Specifically, we adopt the Swin Transformer and SigLip 2 as the backbone networks for the proposed full-reference (FR) and no-reference (NR) VQA models, respectively. For the FR model, we compute deep structural and textural similarities between reference and distorted frames using intermediate-layer features extracted from the Swin Transformer as its quality-aware feature representation. For the NR model, we extract the global mean of the final-layer feature maps from SigLip 2 as its quality-aware representation. To mitigate the issue of limited HDR training data, we pre-train the FR model on a large-scale standard dynamic range (SDR) VQA dataset and fine-tune it on the HDRSDR-VQA dataset. For the NR model, we employ an iterative mixed-dataset training strategy across multiple compressed VQA datasets, followed by fine-tuning on the HDRSDR-VQA dataset. Experimental results show that our models achieve state-of-the-art performance compared to existing FR and NR VQA models. Moreover, CompressedVQA-HDR-FR won first place in the FR track of the Generalizable HDR & SDR Video Quality Measurement Grand Challenge at IEEE ICME 2025. The code is available at https://github.com/sunwei925/CompressedVQA-HDR.
Active Learning from Scene Embeddings for End-to-End Autonomous Driving
Mar 14, 2025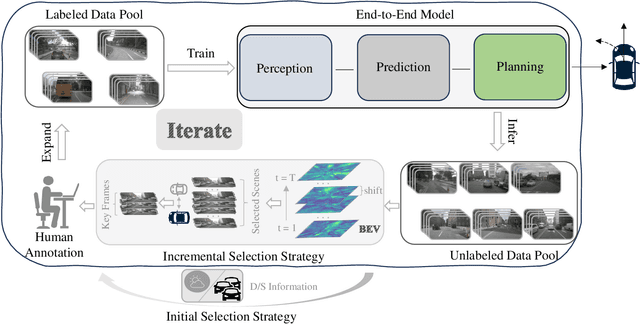
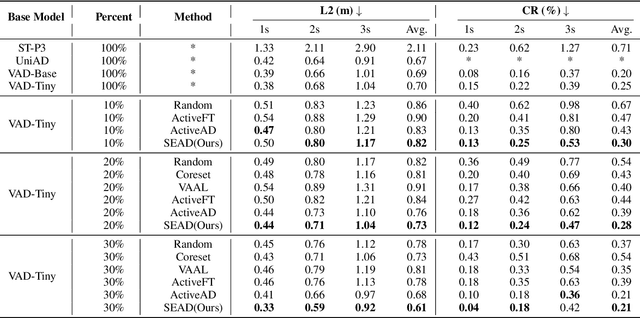
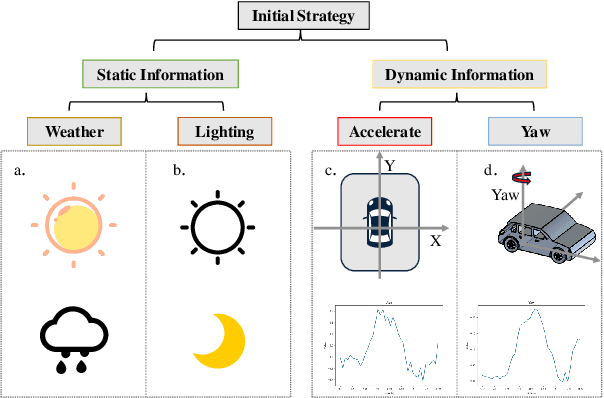
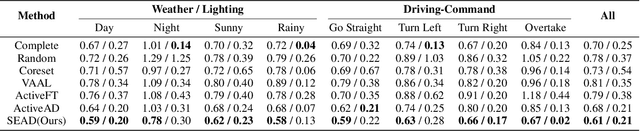
Abstract:In the field of autonomous driving, end-to-end deep learning models show great potential by learning driving decisions directly from sensor data. However, training these models requires large amounts of labeled data, which is time-consuming and expensive. Considering that the real-world driving data exhibits a long-tailed distribution where simple scenarios constitute a majority part of the data, we are thus inspired to identify the most challenging scenarios within it. Subsequently, we can efficiently improve the performance of the model by training with the selected data of the highest value. Prior research has focused on the selection of valuable data by empirically designed strategies. However, manually designed methods suffer from being less generalizable to new data distributions. Observing that the BEV (Bird's Eye View) features in end-to-end models contain all the information required to represent the scenario, we propose an active learning framework that relies on these vectorized scene-level features, called SEAD. The framework selects initial data based on driving-environmental information and incremental data based on BEV features. Experiments show that we only need 30\% of the nuScenes training data to achieve performance close to what can be achieved with the full dataset. The source code will be released.
A Semi-Supervised Approach with Error Reflection for Echocardiography Segmentation
Dec 01, 2024



Abstract:Segmenting internal structure from echocardiography is essential for the diagnosis and treatment of various heart diseases. Semi-supervised learning shows its ability in alleviating annotations scarcity. While existing semi-supervised methods have been successful in image segmentation across various medical imaging modalities, few have attempted to design methods specifically addressing the challenges posed by the poor contrast, blurred edge details and noise of echocardiography. These characteristics pose challenges to the generation of high-quality pseudo-labels in semi-supervised segmentation based on Mean Teacher. Inspired by human reflection on erroneous practices, we devise an error reflection strategy for echocardiography semi-supervised segmentation architecture. The process triggers the model to reflect on inaccuracies in unlabeled image segmentation, thereby enhancing the robustness of pseudo-label generation. Specifically, the strategy is divided into two steps. The first step is called reconstruction reflection. The network is tasked with reconstructing authentic proxy images from the semantic masks of unlabeled images and their auxiliary sketches, while maximizing the structural similarity between the original inputs and the proxies. The second step is called guidance correction. Reconstruction error maps decouple unreliable segmentation regions. Then, reliable data that are more likely to occur near high-density areas are leveraged to guide the optimization of unreliable data potentially located around decision boundaries. Additionally, we introduce an effective data augmentation strategy, termed as multi-scale mixing up strategy, to minimize the empirical distribution gap between labeled and unlabeled images and perceive diverse scales of cardiac anatomical structures. Extensive experiments demonstrate the competitiveness of the proposed method.
Deepfake Generation and Detection: A Benchmark and Survey
Apr 09, 2024



Abstract:In addition to the advancements in deepfake generation, corresponding detection technologies need to continuously evolve to regulate the potential misuse of deepfakes, such as for privacy invasion and phishing attacks. This survey comprehensively reviews the latest developments in deepfake generation and detection, summarizing and analyzing the current state of the art in this rapidly evolving field. We first unify task definitions, comprehensively introduce datasets and metrics, and discuss the development of generation and detection technology frameworks. Then, we discuss the development of several related sub-fields and focus on researching four mainstream deepfake fields: popular face swap, face reenactment, talking face generation, and facial attribute editing, as well as foreign detection. Subsequently, we comprehensively benchmark representative methods on popular datasets for each field, fully evaluating the latest and influential works published in top conferences/journals. Finally, we analyze the challenges and future research directions of the discussed fields. We closely follow the latest developments in https://github.com/flyingby/Awesome-Deepfake-Generation-and-Detection.
AIGCOIQA2024: Perceptual Quality Assessment of AI Generated Omnidirectional Images
Apr 01, 2024
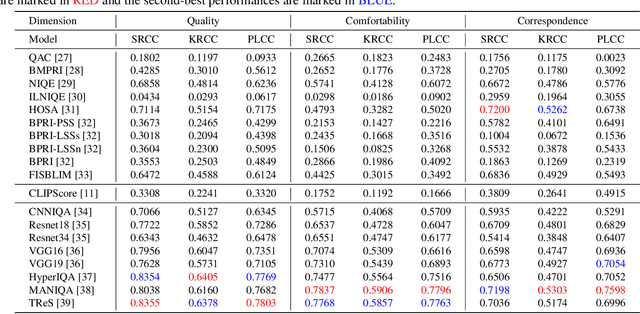

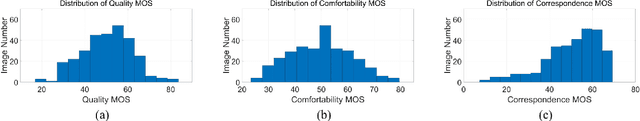
Abstract:In recent years, the rapid advancement of Artificial Intelligence Generated Content (AIGC) has attracted widespread attention. Among the AIGC, AI generated omnidirectional images hold significant potential for Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR) applications, hence omnidirectional AIGC techniques have also been widely studied. AI-generated omnidirectional images exhibit unique distortions compared to natural omnidirectional images, however, there is no dedicated Image Quality Assessment (IQA) criteria for assessing them. This study addresses this gap by establishing a large-scale AI generated omnidirectional image IQA database named AIGCOIQA2024 and constructing a comprehensive benchmark. We first generate 300 omnidirectional images based on 5 AIGC models utilizing 25 text prompts. A subjective IQA experiment is conducted subsequently to assess human visual preferences from three perspectives including quality, comfortability, and correspondence. Finally, we conduct a benchmark experiment to evaluate the performance of state-of-the-art IQA models on our database. The database will be released to facilitate future research.
Few-Shot Class-Incremental Learning with Prior Knowledge
Feb 02, 2024Abstract:To tackle the issues of catastrophic forgetting and overfitting in few-shot class-incremental learning (FSCIL), previous work has primarily concentrated on preserving the memory of old knowledge during the incremental phase. The role of pre-trained model in shaping the effectiveness of incremental learning is frequently underestimated in these studies. Therefore, to enhance the generalization ability of the pre-trained model, we propose Learning with Prior Knowledge (LwPK) by introducing nearly free prior knowledge from a few unlabeled data of subsequent incremental classes. We cluster unlabeled incremental class samples to produce pseudo-labels, then jointly train these with labeled base class samples, effectively allocating embedding space for both old and new class data. Experimental results indicate that LwPK effectively enhances the model resilience against catastrophic forgetting, with theoretical analysis based on empirical risk minimization and class distance measurement corroborating its operational principles. The source code of LwPK is publicly available at: \url{https://github.com/StevenJ308/LwPK}.
Uncertainty-aware Sampling for Long-tailed Semi-supervised Learning
Jan 09, 2024Abstract:For semi-supervised learning with imbalance classes, the long-tailed distribution of data will increase the model prediction bias toward dominant classes, undermining performance on less frequent classes. Existing methods also face challenges in ensuring the selection of sufficiently reliable pseudo-labels for model training and there is a lack of mechanisms to adjust the selection of more reliable pseudo-labels based on different training stages. To mitigate this issue, we introduce uncertainty into the modeling process for pseudo-label sampling, taking into account that the model performance on the tailed classes varies over different training stages. For example, at the early stage of model training, the limited predictive accuracy of model results in a higher rate of uncertain pseudo-labels. To counter this, we propose an Uncertainty-Aware Dynamic Threshold Selection (UDTS) approach. This approach allows the model to perceive the uncertainty of pseudo-labels at different training stages, thereby adaptively adjusting the selection thresholds for different classes. Compared to other methods such as the baseline method FixMatch, UDTS achieves an increase in accuracy of at least approximately 5.26%, 1.75%, 9.96%, and 1.28% on the natural scene image datasets CIFAR10-LT, CIFAR100-LT, STL-10-LT, and the medical image dataset TissueMNIST, respectively. The source code of UDTS is publicly available at: https://github.com/yangk/UDTS.
TransMRSR: Transformer-based Self-Distilled Generative Prior for Brain MRI Super-Resolution
Jun 11, 2023Abstract:Magnetic resonance images (MRI) acquired with low through-plane resolution compromise time and cost. The poor resolution in one orientation is insufficient to meet the requirement of high resolution for early diagnosis of brain disease and morphometric study. The common Single image super-resolution (SISR) solutions face two main challenges: (1) local detailed and global anatomical structural information combination; and (2) large-scale restoration when applied for reconstructing thick-slice MRI into high-resolution (HR) iso-tropic data. To address these problems, we propose a novel two-stage network for brain MRI SR named TransMRSR based on the convolutional blocks to extract local information and transformer blocks to capture long-range dependencies. TransMRSR consists of three modules: the shallow local feature extraction, the deep non-local feature capture, and the HR image reconstruction. We perform a generative task to encapsulate diverse priors into a generative network (GAN), which is the decoder sub-module of the deep non-local feature capture part, in the first stage. The pre-trained GAN is used for the second stage of SR task. We further eliminate the potential latent space shift caused by the two-stage training strategy through the self-distilled truncation trick. The extensive experiments show that our method achieves superior performance to other SSIR methods on both public and private datasets. Code is released at https://github.com/goddesshs/TransMRSR.git .
Energy Efficiency Optimization of Intelligent Reflective Surface-assisted Terahertz-RSMA System
Nov 21, 2022



Abstract:This paper examines the energy efficiency optimization problem of intelligent reflective surface (IRS)-assisted multi-user rate division multiple access (RSMA) downlink systems under terahertz propagation. The objective function for energy efficiency is optimized using the salp swarm algorithm (SSA) and compared with the successive convex approximation (SCA) technique. SCA technique requires multiple iterations to solve non-convex resource allocation problems, whereas SSA can consume less time to improve energy efficiency effectively. The simulation results show that SSA is better than SCA in improving system energy efficiency, and the time required is significantly reduced, thus optimizing the system's overall performance.
Cough Detection Using Selected Informative Features from Audio Signals
Aug 07, 2021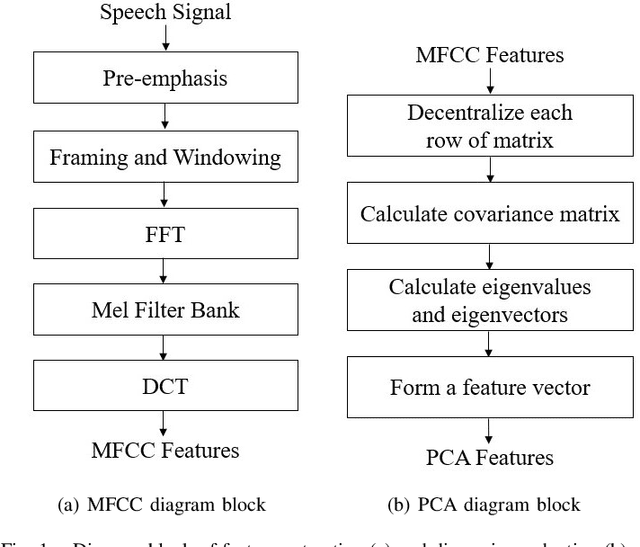


Abstract:Cough is a common symptom of respiratory and lung diseases. Cough detection is important to prevent, assess and control epidemic, such as COVID-19. This paper proposes a model to detect cough events from cough audio signals. The models are trained by the dataset combined ESC-50 dataset with self-recorded cough recordings. The test dataset contains inpatient cough recordings collected from inpatients of the respiratory disease department in Ruijin Hospital. We totally build 15 cough detection models based on different feature numbers selected by Random Frog, Uninformative Variable Elimination (UVE), and Variable influence on projection (VIP) algorithms respectively. The optimal model is based on 20 features selected from Mel Frequency Cepstral Coefficients (MFCC) features by UVE algorithm and classified with Support Vector Machine (SVM) linear two-class classifier. The best cough detection model realizes the accuracy, recall, precision and F1-score with 94.9%, 97.1%, 93.1% and 0.95 respectively. Its excellent performance with fewer dimensionality of the feature vector shows the potential of being applied to mobile devices, such as smartphones, thus making cough detection remote and non-contact.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge