Shihong Duan
Subgoal-based Hierarchical Reinforcement Learning for Multi-Agent Collaboration
Aug 21, 2024Abstract:Recent advancements in reinforcement learning have made significant impacts across various domains, yet they often struggle in complex multi-agent environments due to issues like algorithm instability, low sampling efficiency, and the challenges of exploration and dimensionality explosion. Hierarchical reinforcement learning (HRL) offers a structured approach to decompose complex tasks into simpler sub-tasks, which is promising for multi-agent settings. This paper advances the field by introducing a hierarchical architecture that autonomously generates effective subgoals without explicit constraints, enhancing both flexibility and stability in training. We propose a dynamic goal generation strategy that adapts based on environmental changes. This method significantly improves the adaptability and sample efficiency of the learning process. Furthermore, we address the critical issue of credit assignment in multi-agent systems by synergizing our hierarchical architecture with a modified QMIX network, thus improving overall strategy coordination and efficiency. Comparative experiments with mainstream reinforcement learning algorithms demonstrate the superior convergence speed and performance of our approach in both single-agent and multi-agent environments, confirming its effectiveness and flexibility in complex scenarios. Our code is open-sourced at: \url{https://github.com/SICC-Group/GMAH}.
Dynamic Deep Factor Graph for Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning
May 09, 2024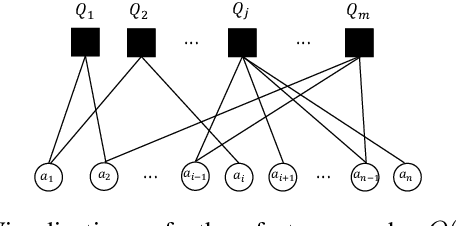
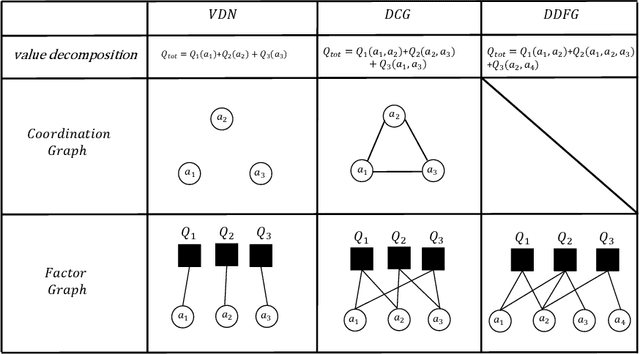
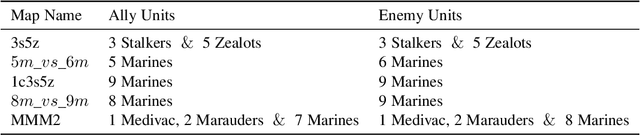
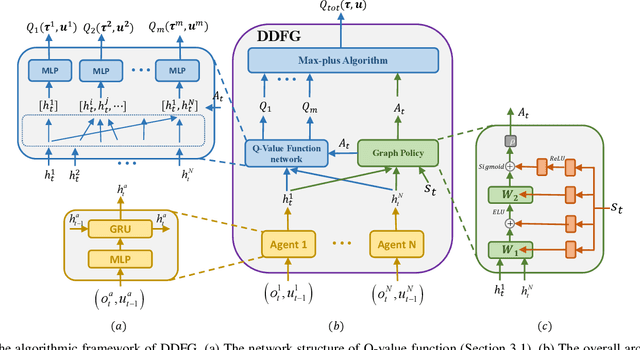
Abstract:This work introduces a novel value decomposition algorithm, termed \textit{Dynamic Deep Factor Graphs} (DDFG). Unlike traditional coordination graphs, DDFG leverages factor graphs to articulate the decomposition of value functions, offering enhanced flexibility and adaptability to complex value function structures. Central to DDFG is a graph structure generation policy that innovatively generates factor graph structures on-the-fly, effectively addressing the dynamic collaboration requirements among agents. DDFG strikes an optimal balance between the computational overhead associated with aggregating value functions and the performance degradation inherent in their complete decomposition. Through the application of the max-sum algorithm, DDFG efficiently identifies optimal policies. We empirically validate DDFG's efficacy in complex scenarios, including higher-order predator-prey tasks and the StarCraft II Multi-agent Challenge (SMAC), thus underscoring its capability to surmount the limitations faced by existing value decomposition algorithms. DDFG emerges as a robust solution for MARL challenges that demand nuanced understanding and facilitation of dynamic agent collaboration. The implementation of DDFG is made publicly accessible, with the source code available at \url{https://github.com/SICC-Group/DDFG}.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge