Evi M. C. Huijben
PathoPainter: Augmenting Histopathology Segmentation via Tumor-aware Inpainting
Mar 06, 2025Abstract:Tumor segmentation plays a critical role in histopathology, but it requires costly, fine-grained image-mask pairs annotated by pathologists. Thus, synthesizing histopathology data to expand the dataset is highly desirable. Previous works suffer from inaccuracies and limited diversity in image-mask pairs, both of which affect training segmentation, particularly in small-scale datasets and the inherently complex nature of histopathology images. To address this challenge, we propose PathoPainter, which reformulates image-mask pair generation as a tumor inpainting task. Specifically, our approach preserves the background while inpainting the tumor region, ensuring precise alignment between the generated image and its corresponding mask. To enhance dataset diversity while maintaining biological plausibility, we incorporate a sampling mechanism that conditions tumor inpainting on regional embeddings from a different image. Additionally, we introduce a filtering strategy to exclude uncertain synthetic regions, further improving the quality of the generated data. Our comprehensive evaluation spans multiple datasets featuring diverse tumor types and various training data scales. As a result, segmentation improved significantly with our synthetic data, surpassing existing segmentation data synthesis approaches, e.g., 75.69% -> 77.69% on CAMELYON16. The code is available at https://github.com/HongLiuuuuu/PathoPainter.
Enhancing Reconstruction-Based Out-of-Distribution Detection in Brain MRI with Model and Metric Ensembles
Dec 23, 2024Abstract:Out-of-distribution (OOD) detection is crucial for safely deploying automated medical image analysis systems, as abnormal patterns in images could hamper their performance. However, OOD detection in medical imaging remains an open challenge, and we address three gaps: the underexplored potential of a simple OOD detection model, the lack of optimization of deep learning strategies specifically for OOD detection, and the selection of appropriate reconstruction metrics. In this study, we investigated the effectiveness of a reconstruction-based autoencoder for unsupervised detection of synthetic artifacts in brain MRI. We evaluated the general reconstruction capability of the model, analyzed the impact of the selected training epoch and reconstruction metrics, assessed the potential of model and/or metric ensembles, and tested the model on a dataset containing a diverse range of artifacts. Among the metrics assessed, the contrast component of SSIM and LPIPS consistently outperformed others in detecting homogeneous circular anomalies. By combining two well-converged models and using LPIPS and contrast as reconstruction metrics, we achieved a pixel-level area under the Precision-Recall curve of 0.66. Furthermore, with the more realistic OOD dataset, we observed that the detection performance varied between artifact types; local artifacts were more difficult to detect, while global artifacts showed better detection results. These findings underscore the importance of carefully selecting metrics and model configurations, and highlight the need for tailored approaches, as standard deep learning approaches do not always align with the unique needs of OOD detection.
Histogram- and Diffusion-Based Medical Out-of-Distribution Detection
Oct 12, 2023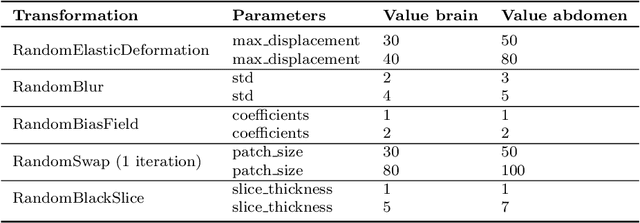
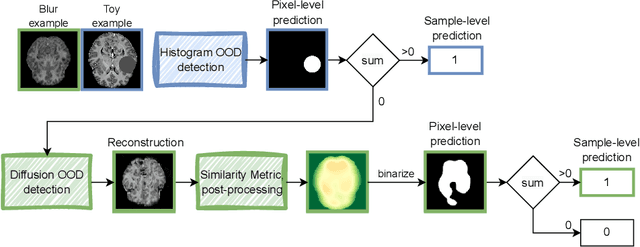
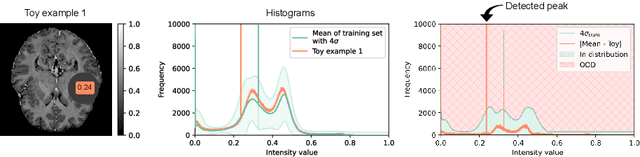
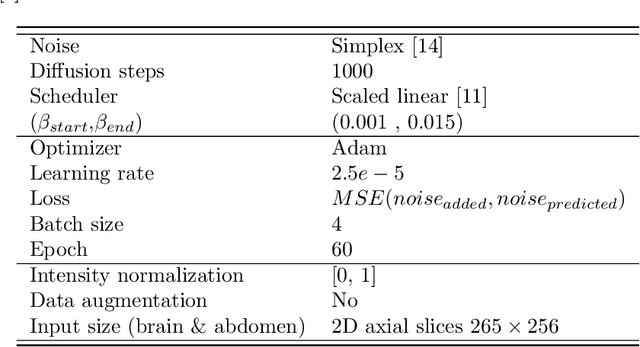
Abstract:Out-of-distribution (OOD) detection is crucial for the safety and reliability of artificial intelligence algorithms, especially in the medical domain. In the context of the Medical OOD (MOOD) detection challenge 2023, we propose a pipeline that combines a histogram-based method and a diffusion-based method. The histogram-based method is designed to accurately detect homogeneous anomalies in the toy examples of the challenge, such as blobs with constant intensity values. The diffusion-based method is based on one of the latest methods for unsupervised anomaly detection, called DDPM-OOD. We explore this method and propose extensive post-processing steps for pixel-level and sample-level anomaly detection on brain MRI and abdominal CT data provided by the challenge. Our results show that the proposed DDPM method is sensitive to blur and bias field samples, but faces challenges with anatomical deformation, black slice, and swapped patches. These findings suggest that further research is needed to improve the performance of DDPM for OOD detection in medical images.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge