Josien P. W. Pluim
Deep learning motion correction of quantitative stress perfusion cardiovascular magnetic resonance
Oct 01, 2025Abstract:Background: Quantitative stress perfusion cardiovascular magnetic resonance (CMR) is a powerful tool for assessing myocardial ischemia. Motion correction is essential for accurate pixel-wise mapping but traditional registration-based methods are slow and sensitive to acquisition variability, limiting robustness and scalability. Methods: We developed an unsupervised deep learning-based motion correction pipeline that replaces iterative registration with efficient one-shot estimation. The method corrects motion in three steps and uses robust principal component analysis to reduce contrast-related effects. It aligns the perfusion series and auxiliary images (arterial input function and proton density-weighted series). Models were trained and validated on multivendor data from 201 patients, with 38 held out for testing. Performance was assessed via temporal alignment and quantitative perfusion values, compared to a previously published registration-based method. Results: The deep learning approach significantly improved temporal smoothness of time-intensity curves (p<0.001). Myocardial alignment (Dice = 0.92 (0.04) and 0.91 (0.05)) was comparable to the baseline and superior to before registration (Dice = 0.80 (0.09), p<0.001). Perfusion maps showed reduced motion, with lower standard deviation in the myocardium (0.52 (0.39) ml/min/g) compared to baseline (0.55 (0.44) ml/min/g). Processing time was reduced 15-fold. Conclusion: This deep learning pipeline enables fast, robust motion correction for stress perfusion CMR, improving accuracy across dynamic and auxiliary images. Trained on multivendor data, it generalizes across sequences and may facilitate broader clinical adoption of quantitative perfusion imaging.
DeepMultiConnectome: Deep Multi-Task Prediction of Structural Connectomes Directly from Diffusion MRI Tractography
May 27, 2025



Abstract:Diffusion MRI (dMRI) tractography enables in vivo mapping of brain structural connections, but traditional connectome generation is time-consuming and requires gray matter parcellation, posing challenges for large-scale studies. We introduce DeepMultiConnectome, a deep-learning model that predicts structural connectomes directly from tractography, bypassing the need for gray matter parcellation while supporting multiple parcellation schemes. Using a point-cloud-based neural network with multi-task learning, the model classifies streamlines according to their connected regions across two parcellation schemes, sharing a learned representation. We train and validate DeepMultiConnectome on tractography from the Human Connectome Project Young Adult dataset ($n = 1000$), labeled with an 84 and 164 region gray matter parcellation scheme. DeepMultiConnectome predicts multiple structural connectomes from a whole-brain tractogram containing 3 million streamlines in approximately 40 seconds. DeepMultiConnectome is evaluated by comparing predicted connectomes with traditional connectomes generated using the conventional method of labeling streamlines using a gray matter parcellation. The predicted connectomes are highly correlated with traditionally generated connectomes ($r = 0.992$ for an 84-region scheme; $r = 0.986$ for a 164-region scheme) and largely preserve network properties. A test-retest analysis of DeepMultiConnectome demonstrates reproducibility comparable to traditionally generated connectomes. The predicted connectomes perform similarly to traditionally generated connectomes in predicting age and cognitive function. Overall, DeepMultiConnectome provides a scalable, fast model for generating subject-specific connectomes across multiple parcellation schemes.
A Spatially-Aware Multiple Instance Learning Framework for Digital Pathology
Apr 24, 2025Abstract:Multiple instance learning (MIL) is a promising approach for weakly supervised classification in pathology using whole slide images (WSIs). However, conventional MIL methods such as Attention-Based Deep Multiple Instance Learning (ABMIL) typically disregard spatial interactions among patches that are crucial to pathological diagnosis. Recent advancements, such as Transformer based MIL (TransMIL), have incorporated spatial context and inter-patch relationships. However, it remains unclear whether explicitly modeling patch relationships yields similar performance gains in ABMIL, which relies solely on Multi-Layer Perceptrons (MLPs). In contrast, TransMIL employs Transformer-based layers, introducing a fundamental architectural shift at the cost of substantially increased computational complexity. In this work, we enhance the ABMIL framework by integrating interaction-aware representations to address this question. Our proposed model, Global ABMIL (GABMIL), explicitly captures inter-instance dependencies while preserving computational efficiency. Experimental results on two publicly available datasets for tumor subtyping in breast and lung cancers demonstrate that GABMIL achieves up to a 7 percentage point improvement in AUPRC and a 5 percentage point increase in the Kappa score over ABMIL, with minimal or no additional computational overhead. These findings underscore the importance of incorporating patch interactions within MIL frameworks.
Adaptive Prototype Learning for Multimodal Cancer Survival Analysis
Mar 06, 2025Abstract:Leveraging multimodal data, particularly the integration of whole-slide histology images (WSIs) and transcriptomic profiles, holds great promise for improving cancer survival prediction. However, excessive redundancy in multimodal data can degrade model performance. In this paper, we propose Adaptive Prototype Learning (APL), a novel and effective approach for multimodal cancer survival analysis. APL adaptively learns representative prototypes in a data-driven manner, reducing redundancy while preserving critical information. Our method employs two sets of learnable query vectors that serve as a bridge between high-dimensional representations and survival prediction, capturing task-relevant features. Additionally, we introduce a multimodal mixed self-attention mechanism to enable cross-modal interactions, further enhancing information fusion. Extensive experiments on five benchmark cancer datasets demonstrate the superiority of our approach over existing methods. The code is available at https://github.com/HongLiuuuuu/APL.
PathoPainter: Augmenting Histopathology Segmentation via Tumor-aware Inpainting
Mar 06, 2025Abstract:Tumor segmentation plays a critical role in histopathology, but it requires costly, fine-grained image-mask pairs annotated by pathologists. Thus, synthesizing histopathology data to expand the dataset is highly desirable. Previous works suffer from inaccuracies and limited diversity in image-mask pairs, both of which affect training segmentation, particularly in small-scale datasets and the inherently complex nature of histopathology images. To address this challenge, we propose PathoPainter, which reformulates image-mask pair generation as a tumor inpainting task. Specifically, our approach preserves the background while inpainting the tumor region, ensuring precise alignment between the generated image and its corresponding mask. To enhance dataset diversity while maintaining biological plausibility, we incorporate a sampling mechanism that conditions tumor inpainting on regional embeddings from a different image. Additionally, we introduce a filtering strategy to exclude uncertain synthetic regions, further improving the quality of the generated data. Our comprehensive evaluation spans multiple datasets featuring diverse tumor types and various training data scales. As a result, segmentation improved significantly with our synthetic data, surpassing existing segmentation data synthesis approaches, e.g., 75.69% -> 77.69% on CAMELYON16. The code is available at https://github.com/HongLiuuuuu/PathoPainter.
Scaling up self-supervised learning for improved surgical foundation models
Jan 16, 2025Abstract:Foundation models have revolutionized computer vision by achieving vastly superior performance across diverse tasks through large-scale pretraining on extensive datasets. However, their application in surgical computer vision has been limited. This study addresses this gap by introducing SurgeNetXL, a novel surgical foundation model that sets a new benchmark in surgical computer vision. Trained on the largest reported surgical dataset to date, comprising over 4.7 million video frames, SurgeNetXL achieves consistent top-tier performance across six datasets spanning four surgical procedures and three tasks, including semantic segmentation, phase recognition, and critical view of safety (CVS) classification. Compared with the best-performing surgical foundation models, SurgeNetXL shows mean improvements of 2.4, 9.0, and 12.6 percent for semantic segmentation, phase recognition, and CVS classification, respectively. Additionally, SurgeNetXL outperforms the best-performing ImageNet-based variants by 14.4, 4.0, and 1.6 percent in the respective tasks. In addition to advancing model performance, this study provides key insights into scaling pretraining datasets, extending training durations, and optimizing model architectures specifically for surgical computer vision. These findings pave the way for improved generalizability and robustness in data-scarce scenarios, offering a comprehensive framework for future research in this domain. All models and a subset of the SurgeNetXL dataset, including over 2 million video frames, are publicly available at: https://github.com/TimJaspers0801/SurgeNet.
Enhancing Reconstruction-Based Out-of-Distribution Detection in Brain MRI with Model and Metric Ensembles
Dec 23, 2024Abstract:Out-of-distribution (OOD) detection is crucial for safely deploying automated medical image analysis systems, as abnormal patterns in images could hamper their performance. However, OOD detection in medical imaging remains an open challenge, and we address three gaps: the underexplored potential of a simple OOD detection model, the lack of optimization of deep learning strategies specifically for OOD detection, and the selection of appropriate reconstruction metrics. In this study, we investigated the effectiveness of a reconstruction-based autoencoder for unsupervised detection of synthetic artifacts in brain MRI. We evaluated the general reconstruction capability of the model, analyzed the impact of the selected training epoch and reconstruction metrics, assessed the potential of model and/or metric ensembles, and tested the model on a dataset containing a diverse range of artifacts. Among the metrics assessed, the contrast component of SSIM and LPIPS consistently outperformed others in detecting homogeneous circular anomalies. By combining two well-converged models and using LPIPS and contrast as reconstruction metrics, we achieved a pixel-level area under the Precision-Recall curve of 0.66. Furthermore, with the more realistic OOD dataset, we observed that the detection performance varied between artifact types; local artifacts were more difficult to detect, while global artifacts showed better detection results. These findings underscore the importance of carefully selecting metrics and model configurations, and highlight the need for tailored approaches, as standard deep learning approaches do not always align with the unique needs of OOD detection.
Dataset Distribution Impacts Model Fairness: Single vs. Multi-Task Learning
Jul 24, 2024Abstract:The influence of bias in datasets on the fairness of model predictions is a topic of ongoing research in various fields. We evaluate the performance of skin lesion classification using ResNet-based CNNs, focusing on patient sex variations in training data and three different learning strategies. We present a linear programming method for generating datasets with varying patient sex and class labels, taking into account the correlations between these variables. We evaluated the model performance using three different learning strategies: a single-task model, a reinforcing multi-task model, and an adversarial learning scheme. Our observations include: 1) sex-specific training data yields better results, 2) single-task models exhibit sex bias, 3) the reinforcement approach does not remove sex bias, 4) the adversarial model eliminates sex bias in cases involving only female patients, and 5) datasets that include male patients enhance model performance for the male subgroup, even when female patients are the majority. To generalise these findings, in future research, we will examine more demographic attributes, like age, and other possibly confounding factors, such as skin colour and artefacts in the skin lesions. We make all data and models available on GitHub.
WSI-SAM: Multi-resolution Segment Anything Model (SAM) for histopathology whole-slide images
Mar 17, 2024



Abstract:The Segment Anything Model (SAM) marks a significant advancement in segmentation models, offering robust zero-shot abilities and dynamic prompting. However, existing medical SAMs are not suitable for the multi-scale nature of whole-slide images (WSIs), restricting their effectiveness. To resolve this drawback, we present WSI-SAM, enhancing SAM with precise object segmentation capabilities for histopathology images using multi-resolution patches, while preserving its efficient, prompt-driven design, and zero-shot abilities. To fully exploit pretrained knowledge while minimizing training overhead, we keep SAM frozen, introducing only minimal extra parameters and computational overhead. In particular, we introduce High-Resolution (HR) token, Low-Resolution (LR) token and dual mask decoder. This decoder integrates the original SAM mask decoder with a lightweight fusion module that integrates features at multiple scales. Instead of predicting a mask independently, we integrate HR and LR token at intermediate layer to jointly learn features of the same object across multiple resolutions. Experiments show that our WSI-SAM outperforms state-of-the-art SAM and its variants. In particular, our model outperforms SAM by 4.1 and 2.5 percent points on a ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) segmentation tasks and breast cancer metastasis segmentation task (CAMELYON16 dataset). The code will be available at https://github.com/HongLiuuuuu/WSI-SAM.
Histogram- and Diffusion-Based Medical Out-of-Distribution Detection
Oct 12, 2023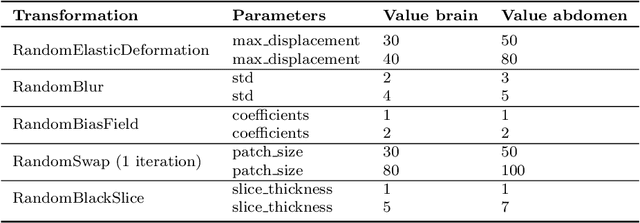
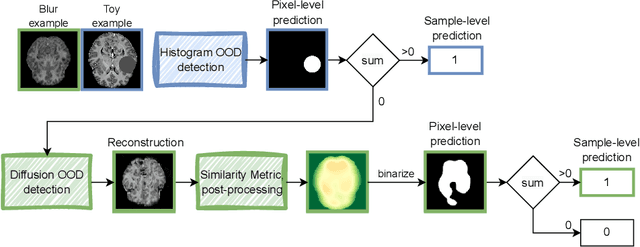
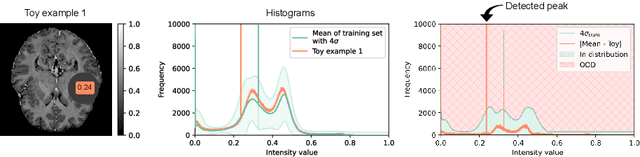
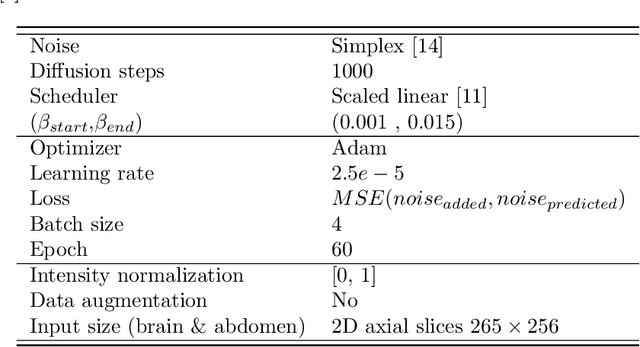
Abstract:Out-of-distribution (OOD) detection is crucial for the safety and reliability of artificial intelligence algorithms, especially in the medical domain. In the context of the Medical OOD (MOOD) detection challenge 2023, we propose a pipeline that combines a histogram-based method and a diffusion-based method. The histogram-based method is designed to accurately detect homogeneous anomalies in the toy examples of the challenge, such as blobs with constant intensity values. The diffusion-based method is based on one of the latest methods for unsupervised anomaly detection, called DDPM-OOD. We explore this method and propose extensive post-processing steps for pixel-level and sample-level anomaly detection on brain MRI and abdominal CT data provided by the challenge. Our results show that the proposed DDPM method is sensitive to blur and bias field samples, but faces challenges with anatomical deformation, black slice, and swapped patches. These findings suggest that further research is needed to improve the performance of DDPM for OOD detection in medical images.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge