Paul J. van Diest
WSI-SAM: Multi-resolution Segment Anything Model (SAM) for histopathology whole-slide images
Mar 17, 2024



Abstract:The Segment Anything Model (SAM) marks a significant advancement in segmentation models, offering robust zero-shot abilities and dynamic prompting. However, existing medical SAMs are not suitable for the multi-scale nature of whole-slide images (WSIs), restricting their effectiveness. To resolve this drawback, we present WSI-SAM, enhancing SAM with precise object segmentation capabilities for histopathology images using multi-resolution patches, while preserving its efficient, prompt-driven design, and zero-shot abilities. To fully exploit pretrained knowledge while minimizing training overhead, we keep SAM frozen, introducing only minimal extra parameters and computational overhead. In particular, we introduce High-Resolution (HR) token, Low-Resolution (LR) token and dual mask decoder. This decoder integrates the original SAM mask decoder with a lightweight fusion module that integrates features at multiple scales. Instead of predicting a mask independently, we integrate HR and LR token at intermediate layer to jointly learn features of the same object across multiple resolutions. Experiments show that our WSI-SAM outperforms state-of-the-art SAM and its variants. In particular, our model outperforms SAM by 4.1 and 2.5 percent points on a ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) segmentation tasks and breast cancer metastasis segmentation task (CAMELYON16 dataset). The code will be available at https://github.com/HongLiuuuuu/WSI-SAM.
Deep Learning-Based Grading of Ductal Carcinoma In Situ in Breast Histopathology Images
Oct 07, 2020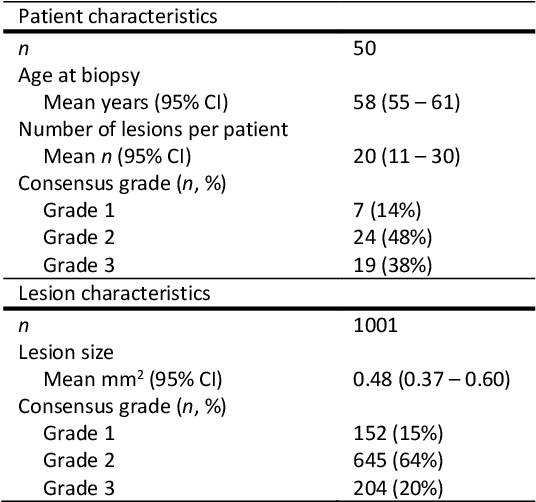
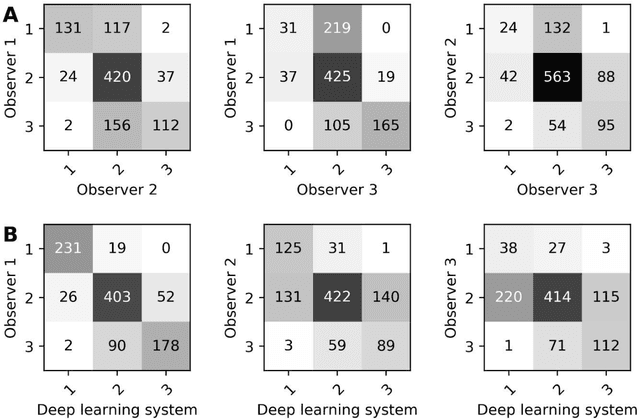
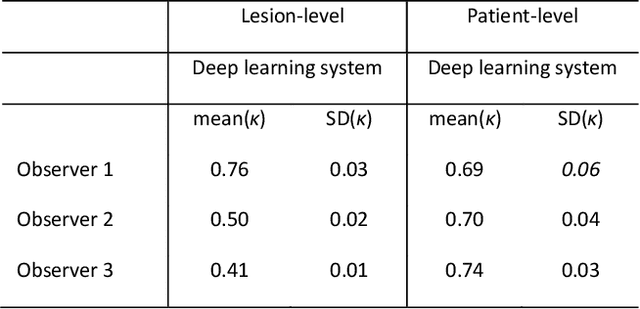
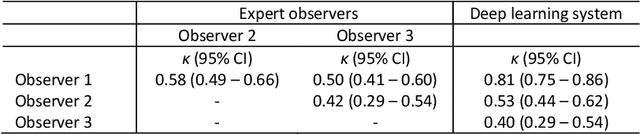
Abstract:Ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) is a non-invasive breast cancer that can progress into invasive ductal carcinoma (IDC). Studies suggest DCIS is often overtreated since a considerable part of DCIS lesions may never progress into IDC. Lower grade lesions have a lower progression speed and risk, possibly allowing treatment de-escalation. However, studies show significant inter-observer variation in DCIS grading. Automated image analysis may provide an objective solution to address high subjectivity of DCIS grading by pathologists. In this study, we developed a deep learning-based DCIS grading system. It was developed using the consensus DCIS grade of three expert observers on a dataset of 1186 DCIS lesions from 59 patients. The inter-observer agreement, measured by quadratic weighted Cohen's kappa, was used to evaluate the system and compare its performance to that of expert observers. We present an analysis of the lesion-level and patient-level inter-observer agreement on an independent test set of 1001 lesions from 50 patients. The deep learning system (dl) achieved on average slightly higher inter-observer agreement to the observers (o1, o2 and o3) ($\kappa_{o1,dl}=0.81, \kappa_{o2,dl}=0.53, \kappa_{o3,dl}=0.40$) than the observers amongst each other ($\kappa_{o1,o2}=0.58, \kappa_{o1,o3}=0.50, \kappa_{o2,o3}=0.42$) at the lesion-level. At the patient-level, the deep learning system achieved similar agreement to the observers ($\kappa_{o1,dl}=0.77, \kappa_{o2,dl}=0.75, \kappa_{o3,dl}=0.70$) as the observers amongst each other ($\kappa_{o1,o2}=0.77, \kappa_{o1,o3}=0.75, \kappa_{o2,o3}=0.72$). In conclusion, we developed a deep learning-based DCIS grading system that achieved a performance similar to expert observers. We believe this is the first automated system that could assist pathologists by providing robust and reproducible second opinions on DCIS grade.
Predicting breast tumor proliferation from whole-slide images: the TUPAC16 challenge
Jul 22, 2018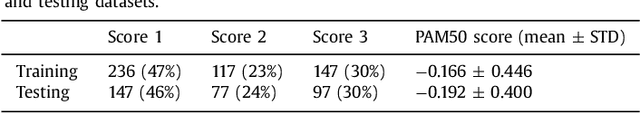
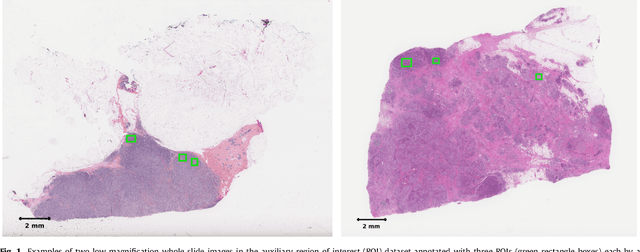
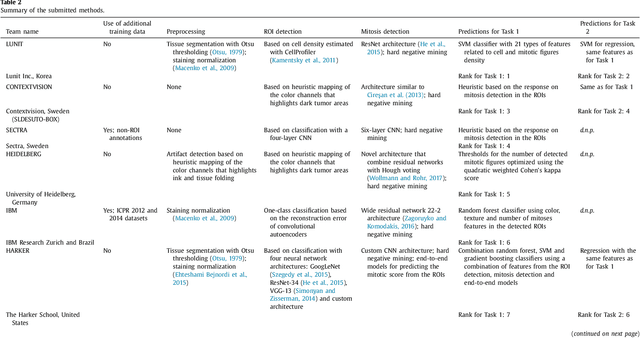
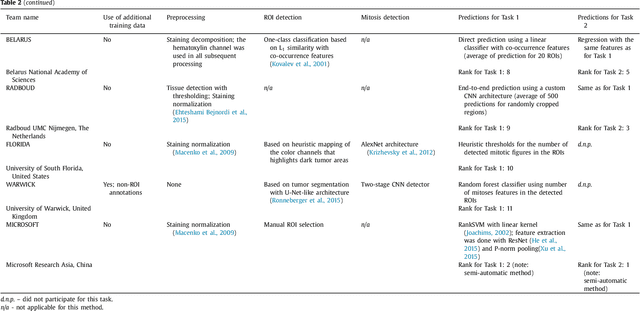
Abstract:Tumor proliferation is an important biomarker indicative of the prognosis of breast cancer patients. Assessment of tumor proliferation in a clinical setting is highly subjective and labor-intensive task. Previous efforts to automate tumor proliferation assessment by image analysis only focused on mitosis detection in predefined tumor regions. However, in a real-world scenario, automatic mitosis detection should be performed in whole-slide images (WSIs) and an automatic method should be able to produce a tumor proliferation score given a WSI as input. To address this, we organized the TUmor Proliferation Assessment Challenge 2016 (TUPAC16) on prediction of tumor proliferation scores from WSIs. The challenge dataset consisted of 500 training and 321 testing breast cancer histopathology WSIs. In order to ensure fair and independent evaluation, only the ground truth for the training dataset was provided to the challenge participants. The first task of the challenge was to predict mitotic scores, i.e., to reproduce the manual method of assessing tumor proliferation by a pathologist. The second task was to predict the gene expression based PAM50 proliferation scores from the WSI. The best performing automatic method for the first task achieved a quadratic-weighted Cohen's kappa score of $\kappa$ = 0.567, 95% CI [0.464, 0.671] between the predicted scores and the ground truth. For the second task, the predictions of the top method had a Spearman's correlation coefficient of r = 0.617, 95% CI [0.581 0.651] with the ground truth. This was the first study that investigated tumor proliferation assessment from WSIs. The achieved results are promising given the difficulty of the tasks and weakly-labelled nature of the ground truth. However, further research is needed to improve the practical utility of image analysis methods for this task.
Cutting out the middleman: measuring nuclear area in histopathology slides without segmentation
Jun 20, 2016


Abstract:The size of nuclei in histological preparations from excised breast tumors is predictive of patient outcome (large nuclei indicate poor outcome). Pathologists take into account nuclear size when performing breast cancer grading. In addition, the mean nuclear area (MNA) has been shown to have independent prognostic value. The straightforward approach to measuring nuclear size is by performing nuclei segmentation. We hypothesize that given an image of a tumor region with known nuclei locations, the area of the individual nuclei and region statistics such as the MNA can be reliably computed directly from the image data by employing a machine learning model, without the intermediate step of nuclei segmentation. Towards this goal, we train a deep convolutional neural network model that is applied locally at each nucleus location, and can reliably measure the area of the individual nuclei and the MNA. Furthermore, we show how such an approach can be extended to perform combined nuclei detection and measurement, which is reminiscent of granulometry.
Assessment of algorithms for mitosis detection in breast cancer histopathology images
Nov 21, 2014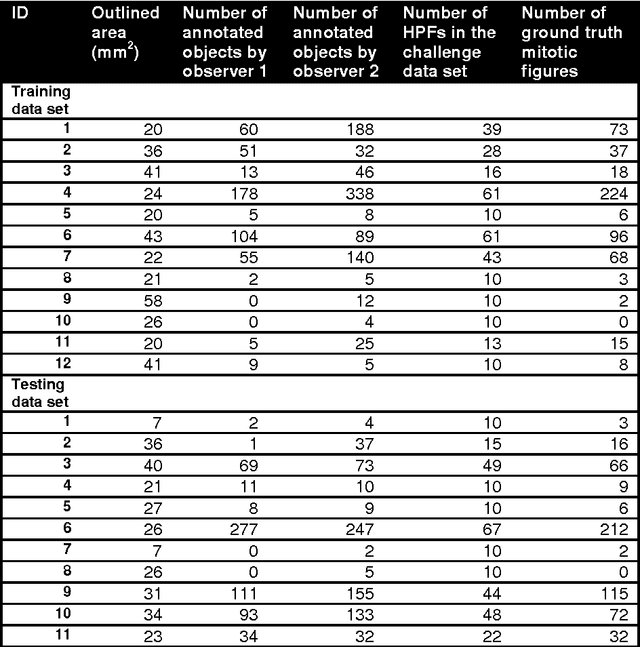
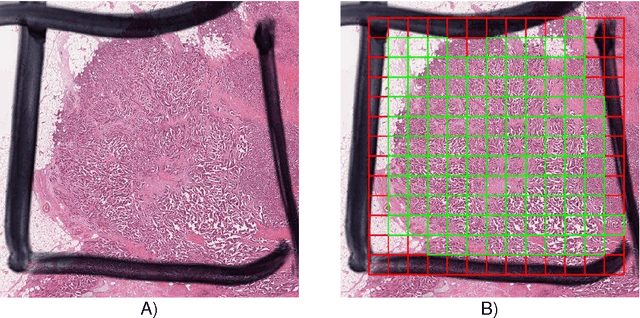
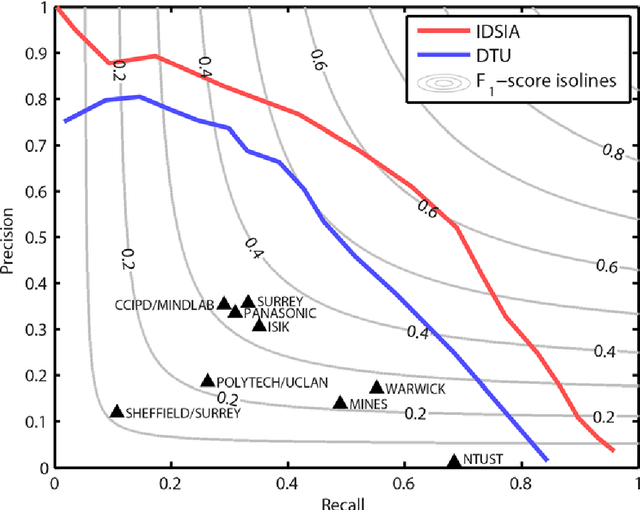
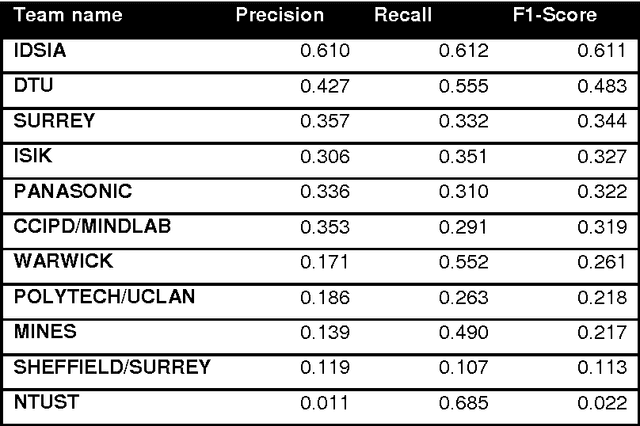
Abstract:The proliferative activity of breast tumors, which is routinely estimated by counting of mitotic figures in hematoxylin and eosin stained histology sections, is considered to be one of the most important prognostic markers. However, mitosis counting is laborious, subjective and may suffer from low inter-observer agreement. With the wider acceptance of whole slide images in pathology labs, automatic image analysis has been proposed as a potential solution for these issues. In this paper, the results from the Assessment of Mitosis Detection Algorithms 2013 (AMIDA13) challenge are described. The challenge was based on a data set consisting of 12 training and 11 testing subjects, with more than one thousand annotated mitotic figures by multiple observers. Short descriptions and results from the evaluation of eleven methods are presented. The top performing method has an error rate that is comparable to the inter-observer agreement among pathologists.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge