Yonglong Zhang
DCIRNet: Depth Completion with Iterative Refinement for Dexterous Grasping of Transparent and Reflective Objects
Jun 11, 2025Abstract:Transparent and reflective objects in everyday environments pose significant challenges for depth sensors due to their unique visual properties, such as specular reflections and light transmission. These characteristics often lead to incomplete or inaccurate depth estimation, which severely impacts downstream geometry-based vision tasks, including object recognition, scene reconstruction, and robotic manipulation. To address the issue of missing depth information in transparent and reflective objects, we propose DCIRNet, a novel multimodal depth completion network that effectively integrates RGB images and depth maps to enhance depth estimation quality. Our approach incorporates an innovative multimodal feature fusion module designed to extract complementary information between RGB images and incomplete depth maps. Furthermore, we introduce a multi-stage supervision and depth refinement strategy that progressively improves depth completion and effectively mitigates the issue of blurred object boundaries. We integrate our depth completion model into dexterous grasping frameworks and achieve a $44\%$ improvement in the grasp success rate for transparent and reflective objects. We conduct extensive experiments on public datasets, where DCIRNet demonstrates superior performance. The experimental results validate the effectiveness of our approach and confirm its strong generalization capability across various transparent and reflective objects.
HTMNet: A Hybrid Network with Transformer-Mamba Bottleneck Multimodal Fusion for Transparent and Reflective Objects Depth Completion
May 28, 2025Abstract:Transparent and reflective objects pose significant challenges for depth sensors, resulting in incomplete depth information that adversely affects downstream robotic perception and manipulation tasks. To address this issue, we propose HTMNet, a novel hybrid model integrating Transformer, CNN, and Mamba architectures. The encoder is based on a dual-branch CNN-Transformer framework, the bottleneck fusion module adopts a Transformer-Mamba architecture, and the decoder is built upon a multi-scale fusion module. We introduce a novel multimodal fusion module grounded in self-attention mechanisms and state space models, marking the first application of the Mamba architecture in the field of transparent object depth completion and revealing its promising potential. Additionally, we design an innovative multi-scale fusion module for the decoder that combines channel attention, spatial attention, and multi-scale feature extraction techniques to effectively integrate multi-scale features through a down-fusion strategy. Extensive evaluations on multiple public datasets demonstrate that our model achieves state-of-the-art(SOTA) performance, validating the effectiveness of our approach.
Commenting Higher-level Code Unit: Full Code, Reduced Code, or Hierarchical Code Summarization
Mar 13, 2025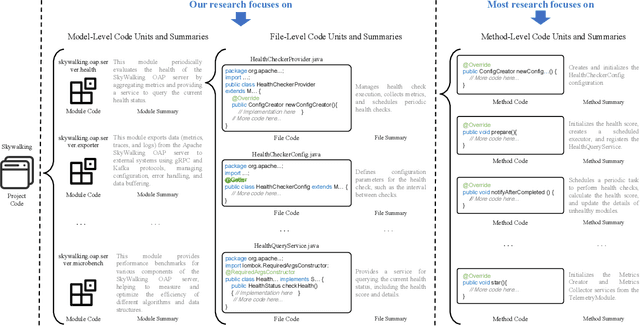
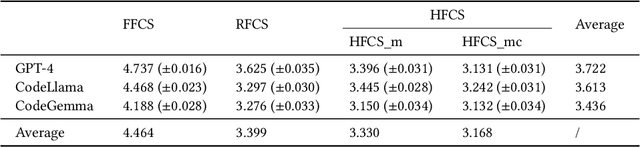
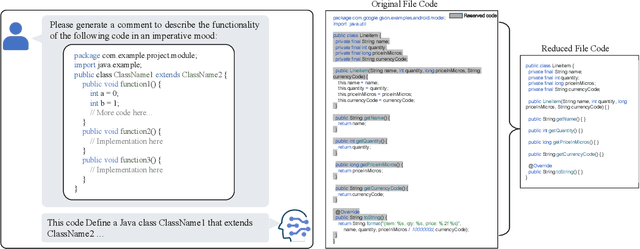
Abstract:Commenting code is a crucial activity in software development, as it aids in facilitating future maintenance and updates. To enhance the efficiency of writing comments and reduce developers' workload, researchers has proposed various automated code summarization (ACS) techniques to automatically generate comments/summaries for given code units. However, these ACS techniques primarily focus on generating summaries for code units at the method level. There is a significant lack of research on summarizing higher-level code units, such as file-level and module-level code units, despite the fact that summaries of these higher-level code units are highly useful for quickly gaining a macro-level understanding of software components and architecture. To fill this gap, in this paper, we conduct a systematic study on how to use LLMs for commenting higher-level code units, including file level and module level. These higher-level units are significantly larger than method-level ones, which poses challenges in handling long code inputs within LLM constraints and maintaining efficiency. To address these issues, we explore various summarization strategies for ACS of higher-level code units, which can be divided into three types: full code summarization, reduced code summarization, and hierarchical code summarization. The experimental results suggest that for summarizing file-level code units, using the full code is the most effective approach, with reduced code serving as a cost-efficient alternative. However, for summarizing module-level code units, hierarchical code summarization becomes the most promising strategy. In addition, inspired by the research on method-level ACS, we also investigate using the LLM as an evaluator to evaluate the quality of summaries of higher-level code units. The experimental results demonstrate that the LLM's evaluation results strongly correlate with human evaluations.
Continuous Concepts Removal in Text-to-image Diffusion Models
Nov 30, 2024
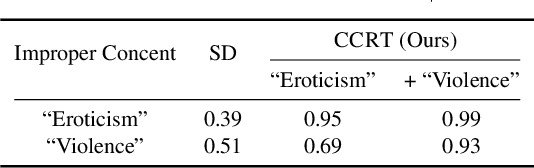

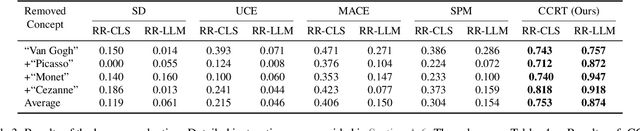
Abstract:Text-to-image diffusion models have shown an impressive ability to generate high-quality images from input textual descriptions. However, concerns have been raised about the potential for these models to create content that infringes on copyrights or depicts disturbing subject matter. Removing specific concepts from these models is a promising potential solution to this problem. However, existing methods for concept removal do not work well in practical but challenging scenarios where concepts need to be continuously removed. Specifically, these methods lead to poor alignment between the text prompts and the generated image after the continuous removal process. To address this issue, we propose a novel approach called CCRT that includes a designed knowledge distillation paradigm. It constrains the text-image alignment behavior during the continuous concept removal process by using a set of text prompts generated through our genetic algorithm, which employs a designed fuzzing strategy. We conduct extensive experiments involving the removal of various concepts. The results evaluated through both algorithmic metrics and human studies demonstrate that our CCRT can effectively remove the targeted concepts in a continuous manner while maintaining the high generation quality (e.g., text-image alignment) of the model.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge