Youliang Zhang
Making Avatars Interact: Towards Text-Driven Human-Object Interaction for Controllable Talking Avatars
Feb 02, 2026Abstract:Generating talking avatars is a fundamental task in video generation. Although existing methods can generate full-body talking avatars with simple human motion, extending this task to grounded human-object interaction (GHOI) remains an open challenge, requiring the avatar to perform text-aligned interactions with surrounding objects. This challenge stems from the need for environmental perception and the control-quality dilemma in GHOI generation. To address this, we propose a novel dual-stream framework, InteractAvatar, which decouples perception and planning from video synthesis for grounded human-object interaction. Leveraging detection to enhance environmental perception, we introduce a Perception and Interaction Module (PIM) to generate text-aligned interaction motions. Additionally, an Audio-Interaction Aware Generation Module (AIM) is proposed to synthesize vivid talking avatars performing object interactions. With a specially designed motion-to-video aligner, PIM and AIM share a similar network structure and enable parallel co-generation of motions and plausible videos, effectively mitigating the control-quality dilemma. Finally, we establish a benchmark, GroundedInter, for evaluating GHOI video generation. Extensive experiments and comparisons demonstrate the effectiveness of our method in generating grounded human-object interactions for talking avatars. Project page: https://interactavatar.github.io
StreamAvatar: Streaming Diffusion Models for Real-Time Interactive Human Avatars
Dec 26, 2025Abstract:Real-time, streaming interactive avatars represent a critical yet challenging goal in digital human research. Although diffusion-based human avatar generation methods achieve remarkable success, their non-causal architecture and high computational costs make them unsuitable for streaming. Moreover, existing interactive approaches are typically limited to head-and-shoulder region, limiting their ability to produce gestures and body motions. To address these challenges, we propose a two-stage autoregressive adaptation and acceleration framework that applies autoregressive distillation and adversarial refinement to adapt a high-fidelity human video diffusion model for real-time, interactive streaming. To ensure long-term stability and consistency, we introduce three key components: a Reference Sink, a Reference-Anchored Positional Re-encoding (RAPR) strategy, and a Consistency-Aware Discriminator. Building on this framework, we develop a one-shot, interactive, human avatar model capable of generating both natural talking and listening behaviors with coherent gestures. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our method achieves state-of-the-art performance, surpassing existing approaches in generation quality, real-time efficiency, and interaction naturalness. Project page: https://streamavatar.github.io .
ActAvatar: Temporally-Aware Precise Action Control for Talking Avatars
Dec 22, 2025Abstract:Despite significant advances in talking avatar generation, existing methods face critical challenges: insufficient text-following capability for diverse actions, lack of temporal alignment between actions and audio content, and dependency on additional control signals such as pose skeletons. We present ActAvatar, a framework that achieves phase-level precision in action control through textual guidance by capturing both action semantics and temporal context. Our approach introduces three core innovations: (1) Phase-Aware Cross-Attention (PACA), which decomposes prompts into a global base block and temporally-anchored phase blocks, enabling the model to concentrate on phase-relevant tokens for precise temporal-semantic alignment; (2) Progressive Audio-Visual Alignment, which aligns modality influence with the hierarchical feature learning process-early layers prioritize text for establishing action structure while deeper layers emphasize audio for refining lip movements, preventing modality interference; (3) A two-stage training strategy that first establishes robust audio-visual correspondence on diverse data, then injects action control through fine-tuning on structured annotations, maintaining both audio-visual alignment and the model's text-following capabilities. Extensive experiments demonstrate that ActAvatar significantly outperforms state-of-the-art methods in both action control and visual quality.
A Plug-and-Play Physical Motion Restoration Approach for In-the-Wild High-Difficulty Motions
Dec 23, 2024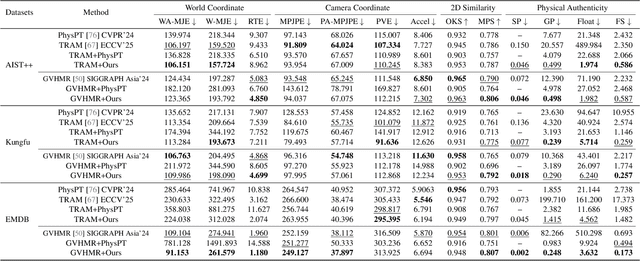
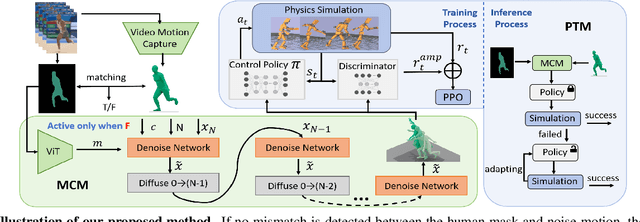
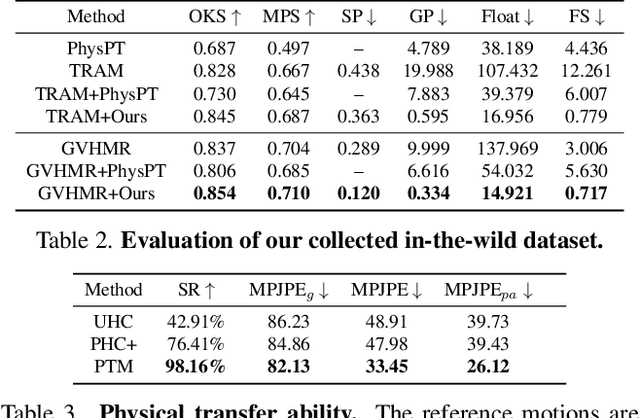

Abstract:Extracting physically plausible 3D human motion from videos is a critical task. Although existing simulation-based motion imitation methods can enhance the physical quality of daily motions estimated from monocular video capture, extending this capability to high-difficulty motions remains an open challenge. This can be attributed to some flawed motion clips in video-based motion capture results and the inherent complexity in modeling high-difficulty motions. Therefore, sensing the advantage of segmentation in localizing human body, we introduce a mask-based motion correction module (MCM) that leverages motion context and video mask to repair flawed motions, producing imitation-friendly motions; and propose a physics-based motion transfer module (PTM), which employs a pretrain and adapt approach for motion imitation, improving physical plausibility with the ability to handle in-the-wild and challenging motions. Our approach is designed as a plug-and-play module to physically refine the video motion capture results, including high-difficulty in-the-wild motions. Finally, to validate our approach, we collected a challenging in-the-wild test set to establish a benchmark, and our method has demonstrated effectiveness on both the new benchmark and existing public datasets.https://physicalmotionrestoration.github.io
InterDance:Reactive 3D Dance Generation with Realistic Duet Interactions
Dec 22, 2024



Abstract:Humans perform a variety of interactive motions, among which duet dance is one of the most challenging interactions. However, in terms of human motion generative models, existing works are still unable to generate high-quality interactive motions, especially in the field of duet dance. On the one hand, it is due to the lack of large-scale high-quality datasets. On the other hand, it arises from the incomplete representation of interactive motion and the lack of fine-grained optimization of interactions. To address these challenges, we propose, InterDance, a large-scale duet dance dataset that significantly enhances motion quality, data scale, and the variety of dance genres. Built upon this dataset, we propose a new motion representation that can accurately and comprehensively describe interactive motion. We further introduce a diffusion-based framework with an interaction refinement guidance strategy to optimize the realism of interactions progressively. Extensive experiments demonstrate the effectiveness of our dataset and algorithm.
Lodge++: High-quality and Long Dance Generation with Vivid Choreography Patterns
Oct 27, 2024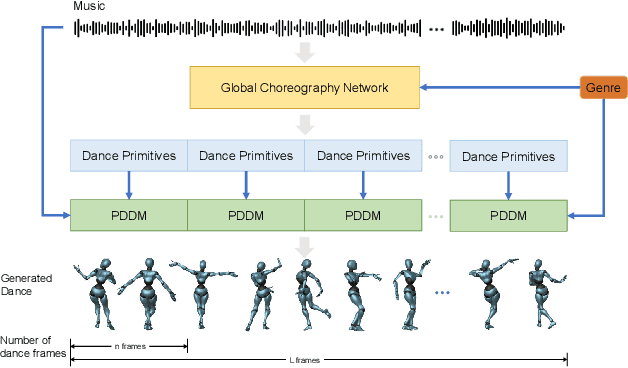
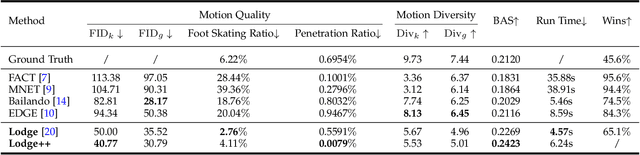
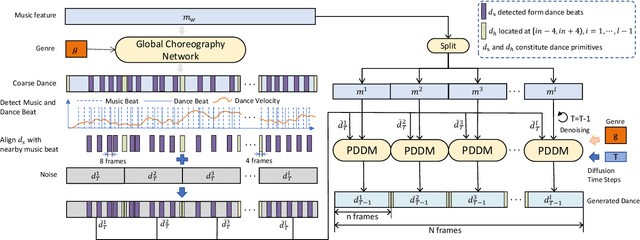
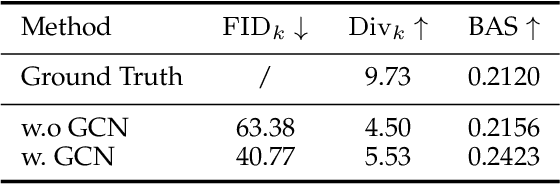
Abstract:We propose Lodge++, a choreography framework to generate high-quality, ultra-long, and vivid dances given the music and desired genre. To handle the challenges in computational efficiency, the learning of complex and vivid global choreography patterns, and the physical quality of local dance movements, Lodge++ adopts a two-stage strategy to produce dances from coarse to fine. In the first stage, a global choreography network is designed to generate coarse-grained dance primitives that capture complex global choreography patterns. In the second stage, guided by these dance primitives, a primitive-based dance diffusion model is proposed to further generate high-quality, long-sequence dances in parallel, faithfully adhering to the complex choreography patterns. Additionally, to improve the physical plausibility, Lodge++ employs a penetration guidance module to resolve character self-penetration, a foot refinement module to optimize foot-ground contact, and a multi-genre discriminator to maintain genre consistency throughout the dance. Lodge++ is validated by extensive experiments, which show that our method can rapidly generate ultra-long dances suitable for various dance genres, ensuring well-organized global choreography patterns and high-quality local motion.
Group Activity Recognition via Dynamic Composition and Interaction
May 09, 2023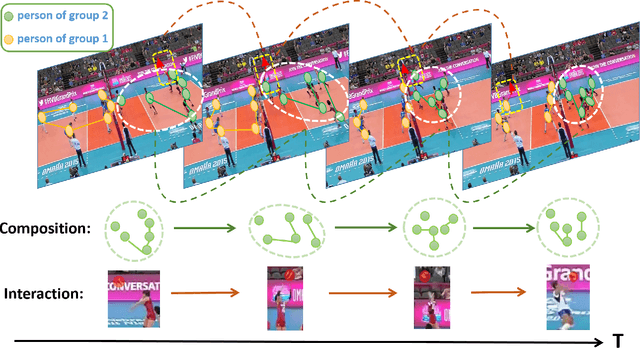
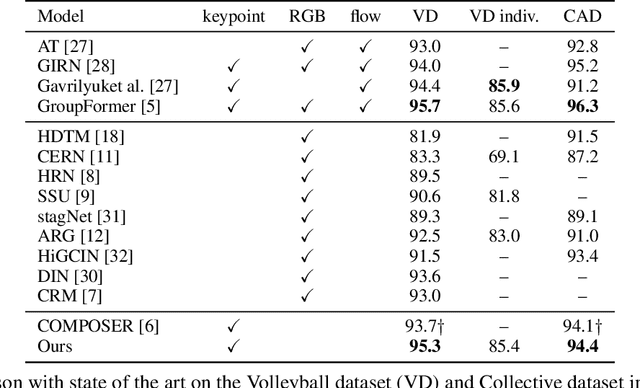
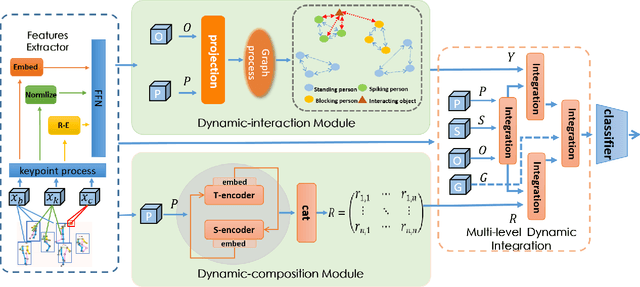
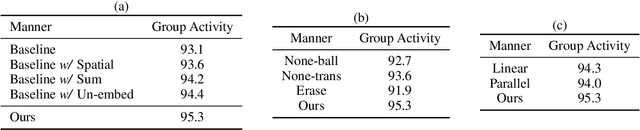
Abstract:Previous group activity recognition approaches were limited to reasoning using human relations or finding important subgroups and tended to ignore indispensable group composition and human-object interactions. This absence makes a partial interpretation of the scene and increases the interference of irrelevant actions on the results. Therefore, we propose our DynamicFormer with Dynamic composition Module (DcM) and Dynamic interaction Module (DiM) to model relations and locations of persons and discriminate the contribution of participants, respectively. Our findings on group composition and human-object interaction inspire our core idea. Group composition tells us the location of people and their relations inside the group, while interaction reflects the relation between humans and objects outside the group. We utilize spatial and temporal encoders in DcM to model our dynamic composition and build DiM to explore interaction with a novel GCN, which has a transformer inside to consider the temporal neighbors of human/object. Also, a Multi-level Dynamic Integration is employed to integrate features from different levels. We conduct extensive experiments on two public datasets and show that our method achieves state-of-the-art.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge