Mingwei Lin
MarineGym: A High-Performance Reinforcement Learning Platform for Underwater Robotics
Mar 12, 2025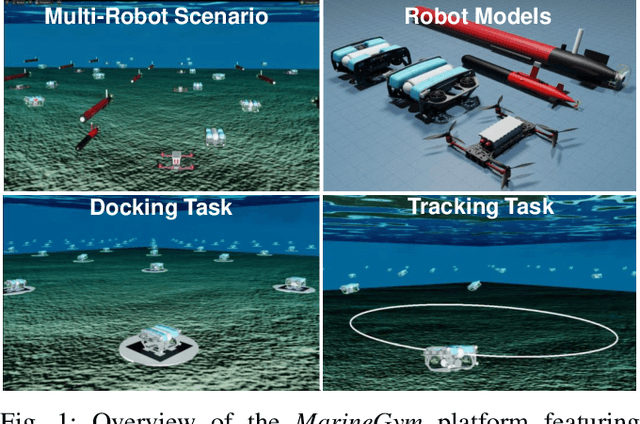
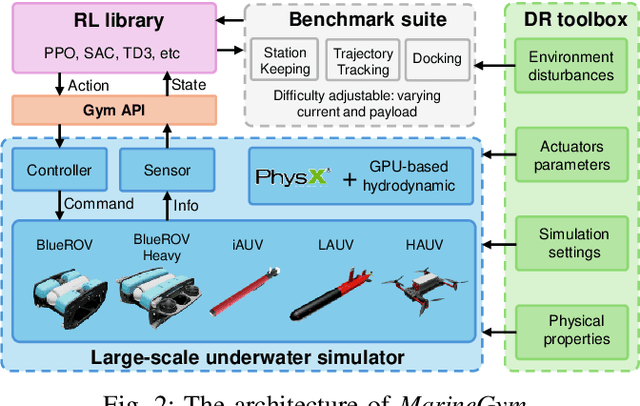
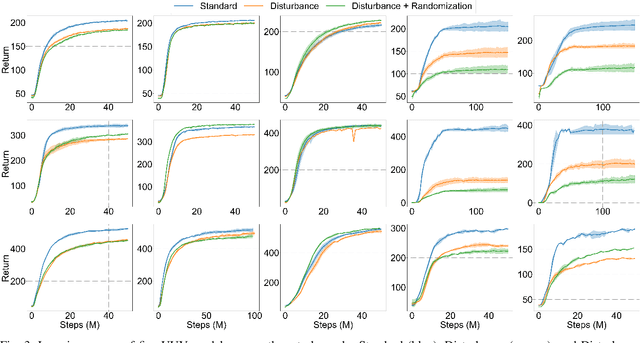
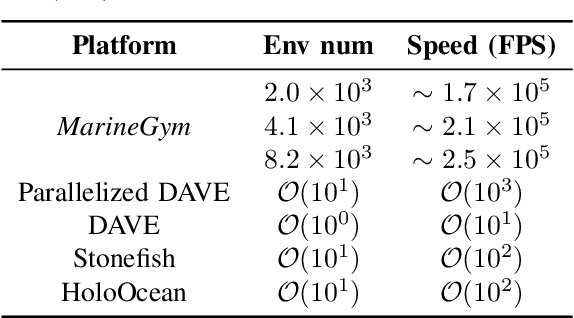
Abstract:This work presents the MarineGym, a high-performance reinforcement learning (RL) platform specifically designed for underwater robotics. It aims to address the limitations of existing underwater simulation environments in terms of RL compatibility, training efficiency, and standardized benchmarking. MarineGym integrates a proposed GPU-accelerated hydrodynamic plugin based on Isaac Sim, achieving a rollout speed of 250,000 frames per second on a single NVIDIA RTX 3060 GPU. It also provides five models of unmanned underwater vehicles (UUVs), multiple propulsion systems, and a set of predefined tasks covering core underwater control challenges. Additionally, the DR toolkit allows flexible adjustments of simulation and task parameters during training to improve Sim2Real transfer. Further benchmark experiments demonstrate that MarineGym improves training efficiency over existing platforms and supports robust policy adaptation under various perturbations. We expect this platform could drive further advancements in RL research for underwater robotics. For more details about MarineGym and its applications, please visit our project page: https://marine-gym.com/.
MarineGym: Accelerated Training for Underwater Vehicles with High-Fidelity RL Simulation
Oct 18, 2024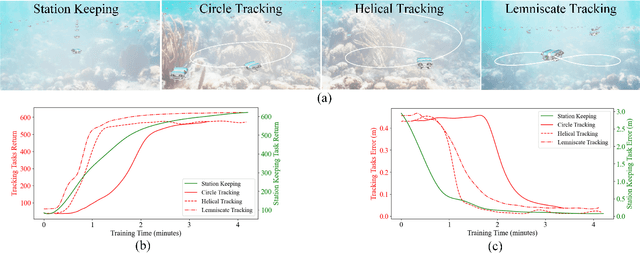
Abstract:Reinforcement Learning (RL) is a promising solution, allowing Unmanned Underwater Vehicles (UUVs) to learn optimal behaviors through trial and error. However, existing simulators lack efficient integration with RL methods, limiting training scalability and performance. This paper introduces MarineGym, a novel simulation framework designed to enhance RL training efficiency for UUVs by utilizing GPU acceleration. MarineGym offers a 10,000-fold performance improvement over real-time simulation on a single GPU, enabling rapid training of RL algorithms across multiple underwater tasks. Key features include realistic dynamic modeling of UUVs, parallel environment execution, and compatibility with popular RL frameworks like PyTorch and TorchRL. The framework is validated through four distinct tasks: station-keeping, circle tracking, helical tracking, and lemniscate tracking. This framework sets the stage for advancing RL in underwater robotics and facilitating efficient training in complex, dynamic environments.
Evidential Deep Partial Multi-View Classification With Discount Fusion
Aug 23, 2024Abstract:Incomplete multi-view data classification poses significant challenges due to the common issue of missing views in real-world scenarios. Despite advancements, existing methods often fail to provide reliable predictions, largely due to the uncertainty of missing views and the inconsistent quality of imputed data. To tackle these problems, we propose a novel framework called Evidential Deep Partial Multi-View Classification (EDP-MVC). Initially, we use K-means imputation to address missing views, creating a complete set of multi-view data. However, the potential conflicts and uncertainties within this imputed data can affect the reliability of downstream inferences. To manage this, we introduce a Conflict-Aware Evidential Fusion Network (CAEFN), which dynamically adjusts based on the reliability of the evidence, ensuring trustworthy discount fusion and producing reliable inference outcomes. Comprehensive experiments on various benchmark datasets reveal EDP-MVC not only matches but often surpasses the performance of state-of-the-art methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge