Wim van Houtum
Clustering of Acoustic Environments with Variational Autoencoders for Hearing Devices
Oct 02, 2025Abstract:Particularly in hearing devices, the environmental context is taken into account for audio processing, often through classification. Traditional acoustic environment classification relies on classical algorithms, which are unable to extract meaningful representations of high-dimensionality data, or on supervised learning, being limited by the availability of labels. Knowing that human-imposed labels do not always reflect the true structure of acoustic scenes, we explore the (unsupervised) clustering of acoustic environments using variational autoencoders (VAEs), presenting a structured latent space suitable for the task. We propose a VAE model for categorical latent clustering employing a Gumbel-Softmax reparameterization with a time-context windowing scheme, tailored for real-world hearing device scenarios. Additionally, general adaptations on VAE architectures for audio clustering are also proposed. The approaches are validated through the clustering of spoken digits, a simpler task where labels are meaningful, and urban soundscapes, which recordings present strong overlap in time and frequency. While all variational methods succeeded when clustering spoken digits, only the proposed model achieved effective clustering performance on urban acoustic scenes, given its categorical nature.
Physics-Aware Initialization Refinement in Code-Aided EM for Blind Channel Estimation
Apr 15, 2025Abstract:This paper addresses the well-known local maximum problem of the expectation-maximization (EM) algorithm in blind intersymbol interference (ISI) channel estimation. This problem primarily results from phase and shift ambiguity during initialization, which blind estimation is inherently unable to distinguish. We propose an effective initialization refinement algorithm that utilizes the decoder output as a model selection metric, incorporating a technique to detect phase and shift ambiguity. Our results show that the proposed algorithm significantly reduces the number of local maximum cases to nearly one-third for a 3-tap ISI channel under highly uncertain initial conditions. The improvement becomes more pronounced as initial errors increase and the channel memory grows. When used in a turbo equalizer, the proposed algorithm is required only in the first turbo iteration, which limits any complexity increase with subsequent iterations.
Hybrid Real- and Complex-valued Neural Network Architecture
Apr 04, 2025Abstract:We propose a \emph{hybrid} real- and complex-valued \emph{neural network} (HNN) architecture, designed to combine the computational efficiency of real-valued processing with the ability to effectively handle complex-valued data. We illustrate the limitations of using real-valued neural networks (RVNNs) for inherently complex-valued problems by showing how it learnt to perform complex-valued convolution, but with notable inefficiencies stemming from its real-valued constraints. To create the HNN, we propose to use building blocks containing both real- and complex-valued paths, where information between domains is exchanged through domain conversion functions. We also introduce novel complex-valued activation functions, with higher generalisation and parameterisation efficiency. HNN-specific architecture search techniques are described to navigate the larger solution space. Experiments with the AudioMNIST dataset demonstrate that the HNN reduces cross-entropy loss and consumes less parameters compared to an RVNN for all considered cases. Such results highlight the potential for the use of partially complex-valued processing in neural networks and applications for HNNs in many signal processing domains.
Target Speaker Selection for Neural Network Beamforming in Multi-Speaker Scenarios
Mar 24, 2025



Abstract:We propose a speaker selection mechanism (SSM) for the training of an end-to-end beamforming neural network, based on recent findings that a listener usually looks to the target speaker with a certain undershot angle. The mechanism allows the neural network model to learn toward which speaker to focus, during training, in a multi-speaker scenario, based on the position of listener and speakers. However, only audio information is necessary during inference. We perform acoustic simulations demonstrating the feasibility and performance when the SSM is employed in training. The results show significant increase in speech intelligibility, quality, and distortion metrics when compared to the minimum variance distortionless filter and the same neural network model trained without SSM. The success of the proposed method is a significant step forward toward the solution of the cocktail party problem.
Unsupervised Variational Acoustic Clustering
Mar 24, 2025



Abstract:We propose an unsupervised variational acoustic clustering model for clustering audio data in the time-frequency domain. The model leverages variational inference, extended to an autoencoder framework, with a Gaussian mixture model as a prior for the latent space. Specifically designed for audio applications, we introduce a convolutional-recurrent variational autoencoder optimized for efficient time-frequency processing. Our experimental results considering a spoken digits dataset demonstrate a significant improvement in accuracy and clustering performance compared to traditional methods, showcasing the model's enhanced ability to capture complex audio patterns.
Modified Baum-Welch Algorithm for Joint Blind Channel Estimation and Turbo Equalization
Dec 10, 2024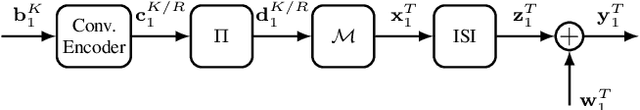
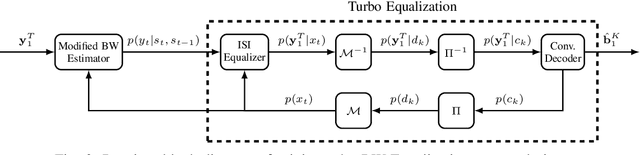
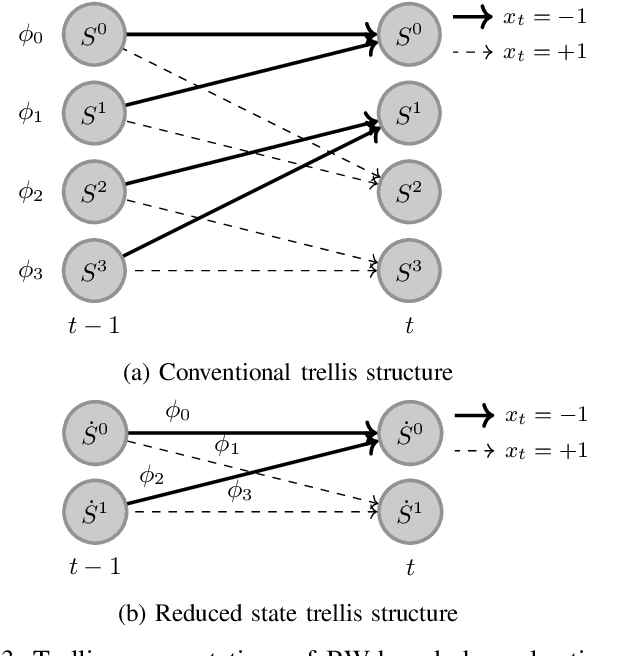
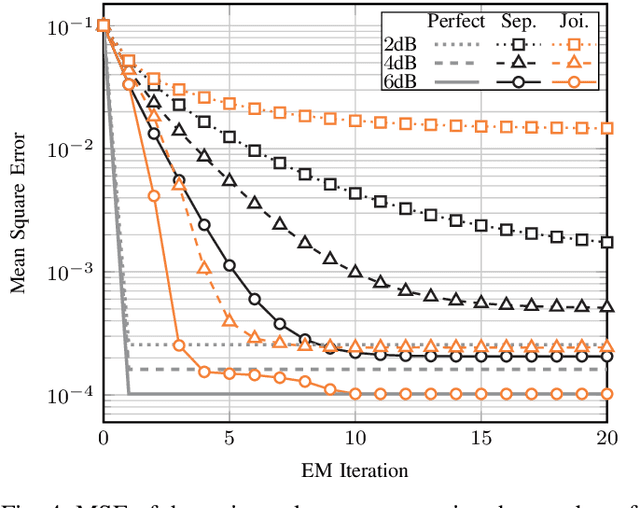
Abstract:Blind estimation of intersymbol interference channels based on the Baum-Welch (BW) algorithm, a specific implementation of the expectation-maximization (EM) algorithm for training hidden Markov models, is robust and does not require labeled data. However, it is known for its extensive computation cost, slow convergence, and frequently converges to a local maximum. In this paper, we modified the trellis structure of the BW algorithm by associating the channel parameters with two consecutive states. This modification enables us to reduce the number of required states by half while maintaining the same performance. Moreover, to improve the convergence rate and the estimation performance, we construct a joint turbo-BW-equalization system by exploiting the extrinsic information produced by the turbo decoder to refine the BW-based estimator at each EM iteration. Our experiments demonstrate that the joint system achieves convergence in just 4 EM iterations, which is 8 iterations less than a separate system design for a signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) of 6 dB. Additionally, the joint system provides improved estimation accuracy with a mean square error (MSE) of $10^{-4}$. We also identify scenarios where a joint design is not preferable, especially when the channel is noisy (e.g., SNR=2 dB) and the turbo decoder is unable to provide reliable extrinsic information for a BW-based estimator.
Spectral Masking with Explicit Time-Context Windowing for Neural Network-Based Monaural Speech Enhancement
Aug 28, 2024
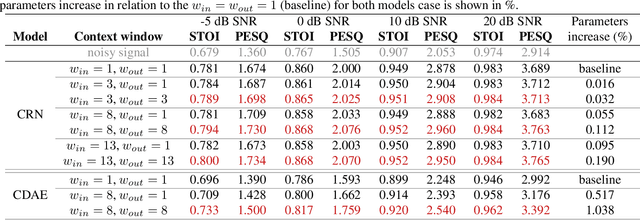

Abstract:We propose and analyze the use of an explicit time-context window for neural network-based spectral masking speech enhancement to leverage signal context dependencies between neighboring frames. In particular, we concentrate on soft masking and loss computed on the time-frequency representation of the reconstructed speech. We show that the application of a time-context windowing function at both input and output of the neural network model improves the soft mask estimation process by combining multiple estimates taken from different contexts. The proposed approach is only applied as post-optimization in inference mode, not requiring additional layers or special training for the neural network model. Our results show that the method consistently increases both intelligibility and signal quality of the denoised speech, as demonstrated for two classes of convolutional-based speech enhancement models. Importantly, the proposed method requires only a negligible ($\leq1\%$) increase in the number of model parameters, making it suitable for hardware-constrained applications.
Data-Driven Symbol Detection for Intersymbol Interference Channels with Bursty Impulsive Noise
May 17, 2024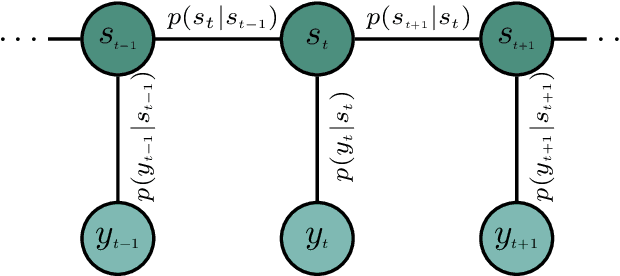
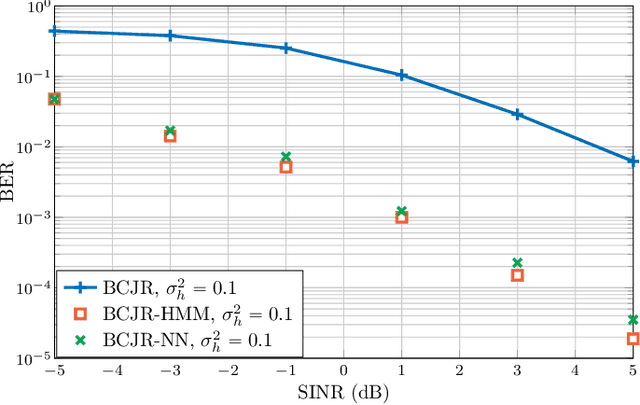
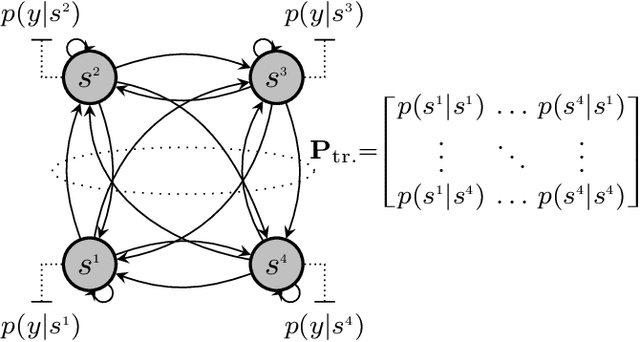
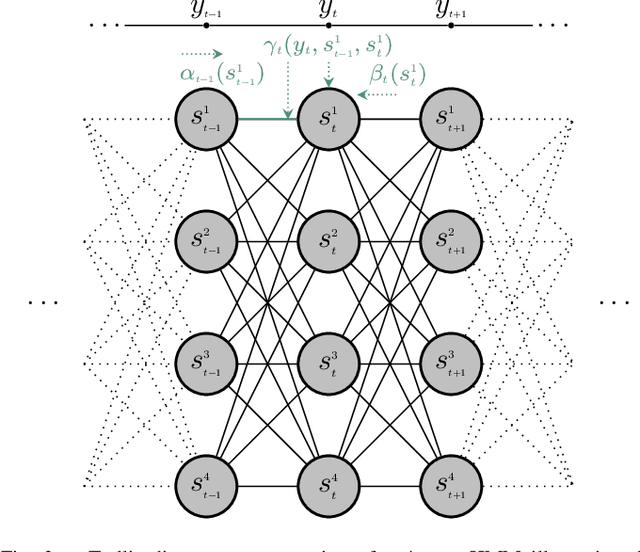
Abstract:We developed machine learning approaches for data-driven trellis-based soft symbol detection in coded transmission over intersymbol interference (ISI) channels in presence of bursty impulsive noise (IN), for example encountered in wireless digital broadcasting systems and vehicular communications. This enabled us to obtain optimized detectors based on the Bahl-Cocke-Jelinek-Raviv (BCJR) algorithm while circumventing the use of full channel state information (CSI) for computing likelihoods and trellis state transition probabilities. First, we extended the application of the neural network (NN)-aided BCJR, recently proposed for ISI channels with additive white Gaussian noise (AWGN). Although suitable for estimating likelihoods via labeling of transmission sequences, the BCJR-NN method does not provide a framework for learning the trellis state transitions. In addition to detection over the joint ISI and IN states we also focused on another scenario where trellis transitions are not trivial: detection for the ISI channel with AWGN with inaccurate knowledge of the channel memory at the receiver. Without access to the accurate state transition matrix, the BCJR- NN performance significantly degrades in both settings. To this end, we devised an alternative approach for data-driven BCJR detection based on the unsupervised learning of a hidden Markov model (HMM). The BCJR-HMM allowed us to optimize both the likelihood function and the state transition matrix without labeling. Moreover, we demonstrated the viability of a hybrid NN and HMM BCJR detection where NN is used for learning the likelihoods, while the state transitions are optimized via HMM. While reducing the required prior channel knowledge, the examined data-driven detectors with learned trellis state transitions achieve bit error rates close to the optimal full CSI-based BCJR, significantly outperforming detection with inaccurate CSI.
Analysis of Impulsive Interference in Digital Audio Broadcasting Systems in Electric Vehicles
May 17, 2024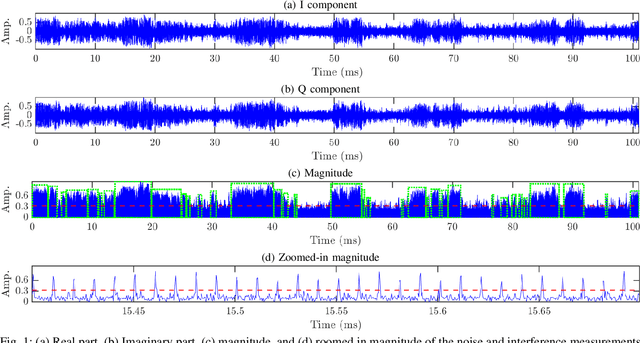
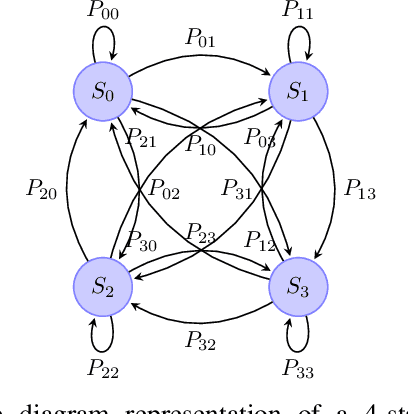
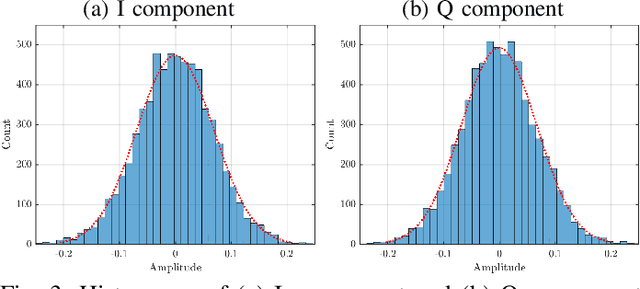
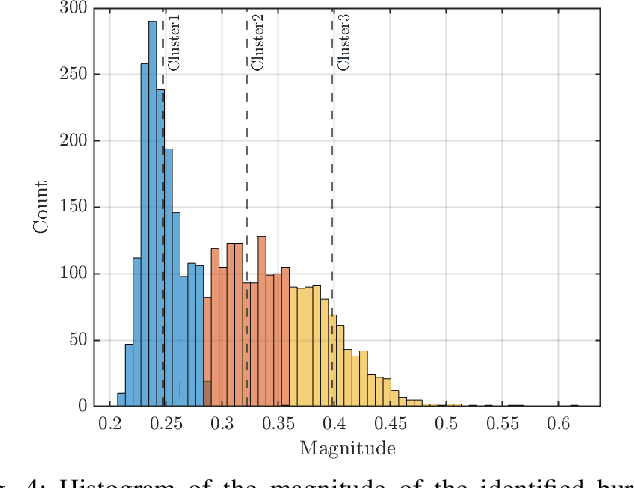
Abstract:Recently, new types of interference in electric vehicles (EVs), such as converters switching and/or battery chargers, have been found to degrade the performance of wireless digital transmission systems. Measurements show that such an interference is characterized by impulsive behavior and is widely varying in time. This paper uses recorded data from our EV testbed to analyze the impulsive interference in the digital audio broadcasting band. Moreover, we use our analysis to obtain a corresponding interference model. In particular, we studied the temporal characteristics of the interference and confirmed that its amplitude indeed exhibits an impulsive behavior. Our results show that impulsive events span successive received signal samples and thus indicate a bursty nature. To this end, we performed a data-driven modification of a well-established model for bursty impulsive interference, the Markov-Middleton model, to produce synthetic noise realization. We investigate the optimal symbol detector design based on the proposed model and show significant performance gains compared to the conventional detector based on the additive white Gaussian noise assumption.
On the Robustness of Deep Learning-aided Symbol Detectors to Varying Conditions and Imperfect Channel Knowledge
Jan 23, 2024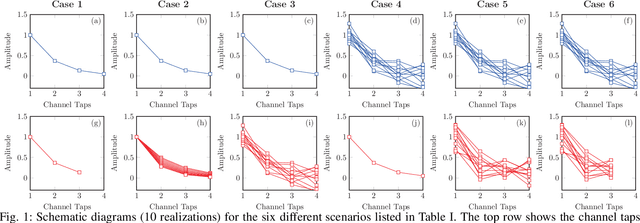
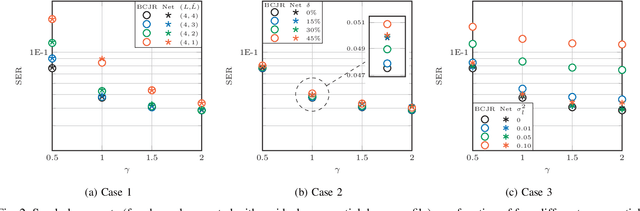
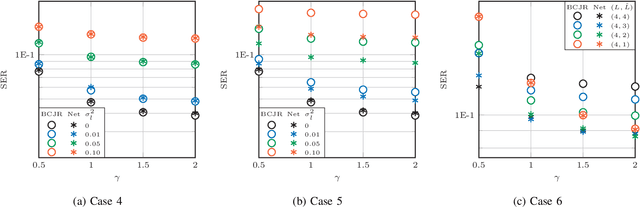
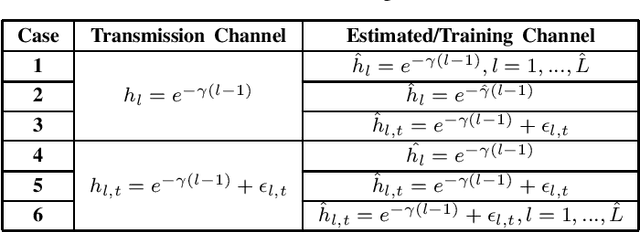
Abstract:Recently, a data-driven Bahl-Cocke-Jelinek-Raviv (BCJR) algorithm tailored to channels with intersymbol interference has been introduced. This so-called BCJRNet algorithm utilizes neural networks to calculate channel likelihoods. BCJRNet has demonstrated resilience against inaccurate channel tap estimations when applied to a time-invariant channel with ideal exponential decay profiles. However, its generalization capabilities for practically-relevant time-varying channels, where the receiver can only access incorrect channel parameters, remain largely unexplored. The primary contribution of this paper is to expand upon the results from existing literature to encompass a variety of imperfect channel knowledge cases that appear in real-world transmissions. Our findings demonstrate that BCJRNet significantly outperforms the conventional BCJR algorithm for stationary transmission scenarios when learning from noisy channel data and with imperfect channel decay profiles. However, this advantage is shown to diminish when the operating channel is also rapidly time-varying. Our results also show the importance of memory assumptions for conventional BCJR and BCJRNet. An underestimation of the memory largely degrades the performance of both BCJR and BCJRNet, especially in a slow-decaying channel. To mimic a situation closer to a practical scenario, we also combined channel tap uncertainty with imperfect channel memory knowledge. Somewhat surprisingly, our results revealed improved performance when employing the conventional BCJR with an underestimated memory assumption. BCJRNet, on the other hand, showed a consistent performance improvement as the level of accurate memory knowledge increased.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge