Pratik Chaudhari
Neurosim: A Fast Simulator for Neuromorphic Robot Perception
Feb 16, 2026Abstract:Neurosim is a fast, real-time, high-performance library for simulating sensors such as dynamic vision sensors, RGB cameras, depth sensors, and inertial sensors. It can also simulate agile dynamics of multi-rotor vehicles in complex and dynamic environments. Neurosim can achieve frame rates as high as ~2700 FPS on a desktop GPU. Neurosim integrates with a ZeroMQ-based communication library called Cortex to facilitate seamless integration with machine learning and robotics workflows. Cortex provides a high-throughput, low-latency message-passing system for Python and C++ applications, with native support for NumPy arrays and PyTorch tensors. This paper discusses the design philosophy behind Neurosim and Cortex. It demonstrates how they can be used to (i) train neuromorphic perception and control algorithms, e.g., using self-supervised learning on time-synchronized multi-modal data, and (ii) test real-time implementations of these algorithms in closed-loop. Neurosim and Cortex are available at https://github.com/grasp-lyrl/neurosim .
The LUMirage: An independent evaluation of zero-shot performance in the LUMIR challenge
Dec 17, 2025Abstract:The LUMIR challenge represents an important benchmark for evaluating deformable image registration methods on large-scale neuroimaging data. While the challenge demonstrates that modern deep learning methods achieve competitive accuracy on T1-weighted MRI, it also claims exceptional zero-shot generalization to unseen contrasts and resolutions, assertions that contradict established understanding of domain shift in deep learning. In this paper, we perform an independent re-evaluation of these zero-shot claims using rigorous evaluation protocols while addressing potential sources of instrumentation bias. Our findings reveal a more nuanced picture: (1) deep learning methods perform comparably to iterative optimization on in-distribution T1w images and even on human-adjacent species (macaque), demonstrating improved task understanding; (2) however, performance degrades significantly on out-of-distribution contrasts (T2, T2*, FLAIR), with Cohen's d scores ranging from 0.7-1.5, indicating substantial practical impact on downstream clinical workflows; (3) deep learning methods face scalability limitations on high-resolution data, failing to run on 0.6 mm isotropic images, while iterative methods benefit from increased resolution; and (4) deep methods exhibit high sensitivity to preprocessing choices. These results align with the well-established literature on domain shift and suggest that claims of universal zero-shot superiority require careful scrutiny. We advocate for evaluation protocols that reflect practical clinical and research workflows rather than conditions that may inadvertently favor particular method classes.
Concurrence: A dependence criterion for time series, applied to biological data
Dec 17, 2025Abstract:Measuring the statistical dependence between observed signals is a primary tool for scientific discovery. However, biological systems often exhibit complex non-linear interactions that currently cannot be captured without a priori knowledge or large datasets. We introduce a criterion for dependence, whereby two time series are deemed dependent if one can construct a classifier that distinguishes between temporally aligned vs. misaligned segments extracted from them. We show that this criterion, concurrence, is theoretically linked with dependence, and can become a standard approach for scientific analyses across disciplines, as it can expose relationships across a wide spectrum of signals (fMRI, physiological and behavioral data) without ad-hoc parameter tuning or large amounts of data.
Symskill: Symbol and Skill Co-Invention for Data-Efficient and Real-Time Long-Horizon Manipulation
Oct 02, 2025Abstract:Multi-step manipulation in dynamic environments remains challenging. Two major families of methods fail in distinct ways: (i) imitation learning (IL) is reactive but lacks compositional generalization, as monolithic policies do not decide which skill to reuse when scenes change; (ii) classical task-and-motion planning (TAMP) offers compositionality but has prohibitive planning latency, preventing real-time failure recovery. We introduce SymSkill, a unified learning framework that combines the benefits of IL and TAMP, allowing compositional generalization and failure recovery in real-time. Offline, SymSkill jointly learns predicates, operators, and skills directly from unlabeled and unsegmented demonstrations. At execution time, upon specifying a conjunction of one or more learned predicates, SymSkill uses a symbolic planner to compose and reorder learned skills to achieve the symbolic goals, while performing recovery at both the motion and symbolic levels in real time. Coupled with a compliant controller, SymSkill enables safe and uninterrupted execution under human and environmental disturbances. In RoboCasa simulation, SymSkill can execute 12 single-step tasks with 85% success rate. Without additional data, it composes these skills into multi-step plans requiring up to 6 skill recompositions, recovering robustly from execution failures. On a real Franka robot, we demonstrate SymSkill, learning from 5 minutes of unsegmented and unlabeled play data, is capable of performing multiple tasks simply by goal specifications. The source code and additional analysis can be found on https://sites.google.com/view/symskill.
Prospective Learning in Retrospect
Jul 10, 2025Abstract:In most real-world applications of artificial intelligence, the distributions of the data and the goals of the learners tend to change over time. The Probably Approximately Correct (PAC) learning framework, which underpins most machine learning algorithms, fails to account for dynamic data distributions and evolving objectives, often resulting in suboptimal performance. Prospective learning is a recently introduced mathematical framework that overcomes some of these limitations. We build on this framework to present preliminary results that improve the algorithm and numerical results, and extend prospective learning to sequential decision-making scenarios, specifically foraging. Code is available at: https://github.com/neurodata/prolearn2.
Gaussian Splatting as a Unified Representation for Autonomy in Unstructured Environments
May 17, 2025Abstract:In this work, we argue that Gaussian splatting is a suitable unified representation for autonomous robot navigation in large-scale unstructured outdoor environments. Such environments require representations that can capture complex structures while remaining computationally tractable for real-time navigation. We demonstrate that the dense geometric and photometric information provided by a Gaussian splatting representation is useful for navigation in unstructured environments. Additionally, semantic information can be embedded in the Gaussian map to enable large-scale task-driven navigation. From the lessons learned through our experiments, we highlight several challenges and opportunities arising from the use of such a representation for robot autonomy.
An Analytical Characterization of Sloppiness in Neural Networks: Insights from Linear Models
May 13, 2025Abstract:Recent experiments have shown that training trajectories of multiple deep neural networks with different architectures, optimization algorithms, hyper-parameter settings, and regularization methods evolve on a remarkably low-dimensional "hyper-ribbon-like" manifold in the space of probability distributions. Inspired by the similarities in the training trajectories of deep networks and linear networks, we analytically characterize this phenomenon for the latter. We show, using tools in dynamical systems theory, that the geometry of this low-dimensional manifold is controlled by (i) the decay rate of the eigenvalues of the input correlation matrix of the training data, (ii) the relative scale of the ground-truth output to the weights at the beginning of training, and (iii) the number of steps of gradient descent. By analytically computing and bounding the contributions of these quantities, we characterize phase boundaries of the region where hyper-ribbons are to be expected. We also extend our analysis to kernel machines and linear models that are trained with stochastic gradient descent.
Estimating the Diameter at Breast Height of Trees in a Forest With a Single 360 Camera
May 06, 2025Abstract:Forest inventories rely on accurate measurements of the diameter at breast height (DBH) for ecological monitoring, resource management, and carbon accounting. While LiDAR-based techniques can achieve centimeter-level precision, they are cost-prohibitive and operationally complex. We present a low-cost alternative that only needs a consumer-grade 360 video camera. Our semi-automated pipeline comprises of (i) a dense point cloud reconstruction using Structure from Motion (SfM) photogrammetry software called Agisoft Metashape, (ii) semantic trunk segmentation by projecting Grounded Segment Anything (SAM) masks onto the 3D cloud, and (iii) a robust RANSAC-based technique to estimate cross section shape and DBH. We introduce an interactive visualization tool for inspecting segmented trees and their estimated DBH. On 61 acquisitions of 43 trees under a variety of conditions, our method attains median absolute relative errors of 5-9% with respect to "ground-truth" manual measurements. This is only 2-4% higher than LiDAR-based estimates, while employing a single 360 camera that costs orders of magnitude less, requires minimal setup, and is widely available.
An Effective Gram Matrix Characterizes Generalization in Deep Networks
Apr 24, 2025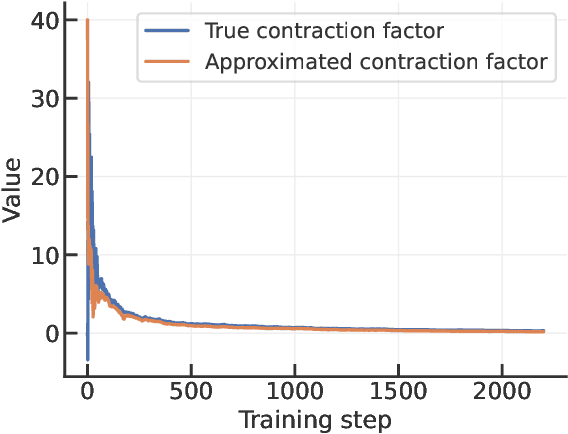

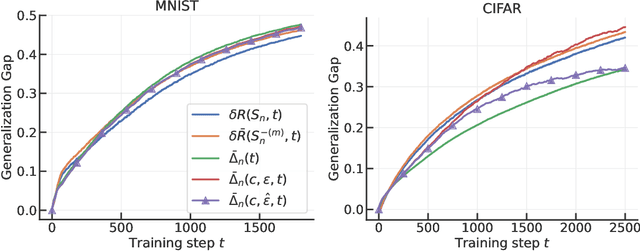
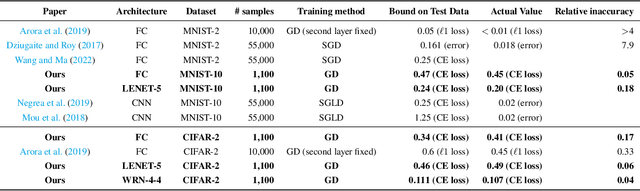
Abstract:We derive a differential equation that governs the evolution of the generalization gap when a deep network is trained by gradient descent. This differential equation is controlled by two quantities, a contraction factor that brings together trajectories corresponding to slightly different datasets, and a perturbation factor that accounts for them training on different datasets. We analyze this differential equation to compute an ``effective Gram matrix'' that characterizes the generalization gap after training in terms of the alignment between this Gram matrix and a certain initial ``residual''. Empirical evaluations on image classification datasets indicate that this analysis can predict the test loss accurately. Further, at any point during training, the residual predominantly lies in the subspace of the effective Gram matrix with the smallest eigenvalues. This indicates that the training process is benign, i.e., it does not lead to significant deterioration of the generalization gap (which is zero at initialization). The alignment between the effective Gram matrix and the residual is different for different datasets and architectures. The match/mismatch of the data and the architecture is primarily responsible for good/bad generalization.
ATLAS Navigator: Active Task-driven LAnguage-embedded Gaussian Splatting
Feb 27, 2025Abstract:We address the challenge of task-oriented navigation in unstructured and unknown environments, where robots must incrementally build and reason on rich, metric-semantic maps in real time. Since tasks may require clarification or re-specification, it is necessary for the information in the map to be rich enough to enable generalization across a wide range of tasks. To effectively execute tasks specified in natural language, we propose a hierarchical representation built on language-embedded Gaussian splatting that enables both sparse semantic planning that lends itself to online operation and dense geometric representation for collision-free navigation. We validate the effectiveness of our method through real-world robot experiments conducted in both cluttered indoor and kilometer-scale outdoor environments, with a competitive ratio of about 60% against privileged baselines. Experiment videos and more details can be found on our project page: https://atlasnav.github.io
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge