Jiuzhou Lei
4D Metric-Semantic Mapping for Persistent Orchard Monitoring: Method and Dataset
Sep 29, 2024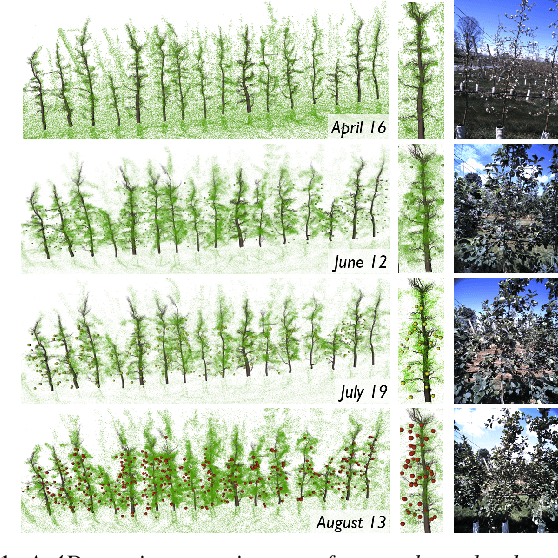
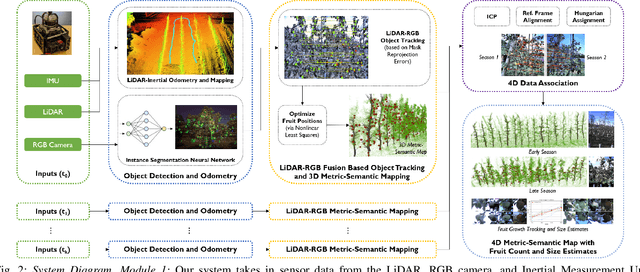

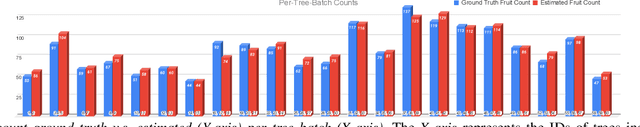
Abstract:Automated persistent and fine-grained monitoring of orchards at the individual tree or fruit level helps maximize crop yield and optimize resources such as water, fertilizers, and pesticides while preventing agricultural waste. Towards this goal, we present a 4D spatio-temporal metric-semantic mapping method that fuses data from multiple sensors, including LiDAR, RGB camera, and IMU, to monitor the fruits in an orchard across their growth season. A LiDAR-RGB fusion module is designed for 3D fruit tracking and localization, which first segments fruits using a deep neural network and then tracks them using the Hungarian Assignment algorithm. Additionally, the 4D data association module aligns data from different growth stages into a common reference frame and tracks fruits spatio-temporally, providing information such as fruit counts, sizes, and positions. We demonstrate our method's accuracy in 4D metric-semantic mapping using data collected from a real orchard under natural, uncontrolled conditions with seasonal variations. We achieve a 3.1 percent error in total fruit count estimation for over 1790 fruits across 60 apple trees, along with accurate size estimation results with a mean error of 1.1 cm. The datasets, consisting of LiDAR, RGB, and IMU data of five fruit species captured across their growth seasons, along with corresponding ground truth data, will be made publicly available at: https://4d-metric-semantic-mapping.org/
SlideSLAM: Sparse, Lightweight, Decentralized Metric-Semantic SLAM for Multi-Robot Navigation
Jun 25, 2024



Abstract:This paper develops a real-time decentralized metric-semantic Simultaneous Localization and Mapping (SLAM) approach that leverages a sparse and lightweight object-based representation to enable a heterogeneous robot team to autonomously explore 3D environments featuring indoor, urban, and forested areas without relying on GPS. We use a hierarchical metric-semantic representation of the environment, including high-level sparse semantic maps of object models and low-level voxel maps. We leverage the informativeness and viewpoint invariance of the high-level semantic map to obtain an effective semantics-driven place-recognition algorithm for inter-robot loop closure detection across aerial and ground robots with different sensing modalities. A communication module is designed to track each robot's observations and those of other robots within the communication range. Such observations are then used to construct a merged map. Our framework enables real-time decentralized operations onboard robots, allowing them to opportunistically leverage communication. We integrate and deploy our proposed framework on three types of aerial and ground robots. Extensive experimental results show an average localization error of 0.22 meters in position and -0.16 degrees in orientation, an object mapping F1 score of 0.92, and a communication packet size of merely 2-3 megabytes per kilometer trajectory with 1,000 landmarks. The project website can be found at https://xurobotics.github.io/slideslam/.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge