Youfang Lin
DRFormer: A Dual-Regularized Bidirectional Transformer for Person Re-identification
Feb 01, 2026Abstract:Both fine-grained discriminative details and global semantic features can contribute to solving person re-identification challenges, such as occlusion and pose variations. Vision foundation models (\textit{e.g.}, DINO) excel at mining local textures, and vision-language models (\textit{e.g.}, CLIP) capture strong global semantic difference. Existing methods predominantly rely on a single paradigm, neglecting the potential benefits of their integration. In this paper, we analyze the complementary roles of these two architectures and propose a framework to synergize their strengths by a \textbf{D}ual-\textbf{R}egularized Bidirectional \textbf{Transformer} (\textbf{DRFormer}). The dual-regularization mechanism ensures diverse feature extraction and achieves a better balance in the contributions of the two models. Extensive experiments on five benchmarks show that our method effectively harmonizes local and global representations, achieving competitive performance against state-of-the-art methods.
RIPCN: A Road Impedance Principal Component Network for Probabilistic Traffic Flow Forecasting
Dec 25, 2025Abstract:Accurate traffic flow forecasting is crucial for intelligent transportation services such as navigation and ride-hailing. In such applications, uncertainty estimation in forecasting is important because it helps evaluate traffic risk levels, assess forecast reliability, and provide timely warnings. As a result, probabilistic traffic flow forecasting (PTFF) has gained significant attention, as it produces both point forecasts and uncertainty estimates. However, existing PTFF approaches still face two key challenges: (1) how to uncover and model the causes of traffic flow uncertainty for reliable forecasting, and (2) how to capture the spatiotemporal correlations of uncertainty for accurate prediction. To address these challenges, we propose RIPCN, a Road Impedance Principal Component Network that integrates domain-specific transportation theory with spatiotemporal principal component learning for PTFF. RIPCN introduces a dynamic impedance evolution network that captures directional traffic transfer patterns driven by road congestion level and flow variability, revealing the direct causes of uncertainty and enhancing both reliability and interpretability. In addition, a principal component network is designed to forecast the dominant eigenvectors of future flow covariance, enabling the model to capture spatiotemporal uncertainty correlations. This design allows for accurate and efficient uncertainty estimation while also improving point prediction performance. Experimental results on real-world datasets show that our approach outperforms existing probabilistic forecasting methods.
A Generative Adaptive Replay Continual Learning Model for Temporal Knowledge Graph Reasoning
Jun 04, 2025Abstract:Recent Continual Learning (CL)-based Temporal Knowledge Graph Reasoning (TKGR) methods focus on significantly reducing computational cost and mitigating catastrophic forgetting caused by fine-tuning models with new data. However, existing CL-based TKGR methods still face two key limitations: (1) They usually one-sidedly reorganize individual historical facts, while overlooking the historical context essential for accurately understanding the historical semantics of these facts; (2) They preserve historical knowledge by simply replaying historical facts, while ignoring the potential conflicts between historical and emerging facts. In this paper, we propose a Deep Generative Adaptive Replay (DGAR) method, which can generate and adaptively replay historical entity distribution representations from the whole historical context. To address the first challenge, historical context prompts as sampling units are built to preserve the whole historical context information. To overcome the second challenge, a pre-trained diffusion model is adopted to generate the historical distribution. During the generation process, the common features between the historical and current distributions are enhanced under the guidance of the TKGR model. In addition, a layer-by-layer adaptive replay mechanism is designed to effectively integrate historical and current distributions. Experimental results demonstrate that DGAR significantly outperforms baselines in reasoning and mitigating forgetting.
TransferTraj: A Vehicle Trajectory Learning Model for Region and Task Transferability
May 19, 2025Abstract:Vehicle GPS trajectories provide valuable movement information that supports various downstream tasks and applications. A desirable trajectory learning model should be able to transfer across regions and tasks without retraining, avoiding the need to maintain multiple specialized models and subpar performance with limited training data. However, each region has its unique spatial features and contexts, which are reflected in vehicle movement patterns and difficult to generalize. Additionally, transferring across different tasks faces technical challenges due to the varying input-output structures required for each task. Existing efforts towards transferability primarily involve learning embedding vectors for trajectories, which perform poorly in region transfer and require retraining of prediction modules for task transfer. To address these challenges, we propose TransferTraj, a vehicle GPS trajectory learning model that excels in both region and task transferability. For region transferability, we introduce RTTE as the main learnable module within TransferTraj. It integrates spatial, temporal, POI, and road network modalities of trajectories to effectively manage variations in spatial context distribution across regions. It also introduces a TRIE module for incorporating relative information of spatial features and a spatial context MoE module for handling movement patterns in diverse contexts. For task transferability, we propose a task-transferable input-output scheme that unifies the input-output structure of different tasks into the masking and recovery of modalities and trajectory points. This approach allows TransferTraj to be pre-trained once and transferred to different tasks without retraining. Extensive experiments on three real-world vehicle trajectory datasets under task transfer, zero-shot, and few-shot region transfer, validating TransferTraj's effectiveness.
Harmonizing Intra-coherence and Inter-divergence in Ensemble Attacks for Adversarial Transferability
May 02, 2025Abstract:The development of model ensemble attacks has significantly improved the transferability of adversarial examples, but this progress also poses severe threats to the security of deep neural networks. Existing methods, however, face two critical challenges: insufficient capture of shared gradient directions across models and a lack of adaptive weight allocation mechanisms. To address these issues, we propose a novel method Harmonized Ensemble for Adversarial Transferability (HEAT), which introduces domain generalization into adversarial example generation for the first time. HEAT consists of two key modules: Consensus Gradient Direction Synthesizer, which uses Singular Value Decomposition to synthesize shared gradient directions; and Dual-Harmony Weight Orchestrator which dynamically balances intra-domain coherence, stabilizing gradients within individual models, and inter-domain diversity, enhancing transferability across models. Experimental results demonstrate that HEAT significantly outperforms existing methods across various datasets and settings, offering a new perspective and direction for adversarial attack research.
Towards An Efficient and Effective En Route Travel Time Estimation Framework
Apr 05, 2025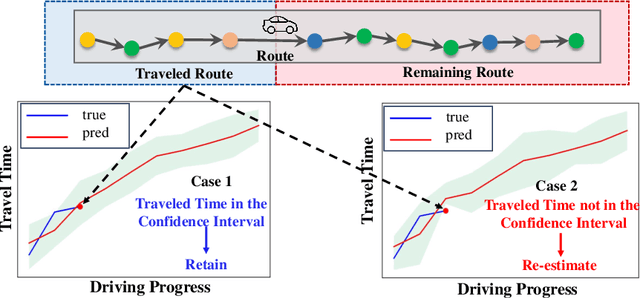

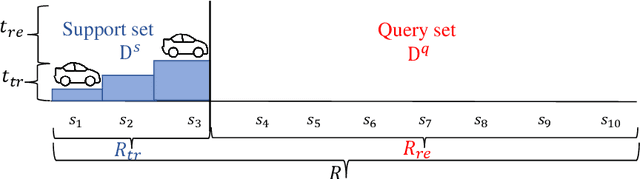

Abstract:En route travel time estimation (ER-TTE) focuses on predicting the travel time of the remaining route. Existing ER-TTE methods always make re-estimation which significantly hinders real-time performance, especially when faced with the computational demands of simultaneous user requests. This results in delays and reduced responsiveness in ER-TTE services. We propose a general efficient framework U-ERTTE combining an Uncertainty-Guided Decision mechanism (UGD) and Fine-Tuning with Meta-Learning (FTML) to address these challenges. UGD quantifies the uncertainty and provides confidence intervals for the entire route. It selectively re-estimates only when the actual travel time deviates from the predicted confidence intervals, thereby optimizing the efficiency of ER-TTE. To ensure the accuracy of confidence intervals and accurate predictions that need to re-estimate, FTML is employed to train the model, enabling it to learn general driving patterns and specific features to adapt to specific tasks. Extensive experiments on two large-scale real datasets demonstrate that the U-ERTTE framework significantly enhances inference speed and throughput while maintaining high effectiveness. Our code is available at https://github.com/shenzekai/U-ERTTE
CoDe: Communication Delay-Tolerant Multi-Agent Collaboration via Dual Alignment of Intent and Timeliness
Jan 09, 2025



Abstract:Communication has been widely employed to enhance multi-agent collaboration. Previous research has typically assumed delay-free communication, a strong assumption that is challenging to meet in practice. However, real-world agents suffer from channel delays, receiving messages sent at different time points, termed {\it{Asynchronous Communication}}, leading to cognitive biases and breakdowns in collaboration. This paper first defines two communication delay settings in MARL and emphasizes their harm to collaboration. To handle the above delays, this paper proposes a novel framework, Communication Delay-tolerant Multi-Agent Collaboration (CoDe). At first, CoDe learns an intent representation as messages through future action inference, reflecting the stable future behavioral trends of the agents. Then, CoDe devises a dual alignment mechanism of intent and timeliness to strengthen the fusion process of asynchronous messages. In this way, agents can extract the long-term intent of others, even from delayed messages, and selectively utilize the most recent messages that are relevant to their intent. Experimental results demonstrate that CoDe outperforms baseline algorithms in three MARL benchmarks without delay and exhibits robustness under fixed and time-varying delays.
CognTKE: A Cognitive Temporal Knowledge Extrapolation Framework
Dec 21, 2024



Abstract:Reasoning future unknowable facts on temporal knowledge graphs (TKGs) is a challenging task, holding significant academic and practical values for various fields. Existing studies exploring explainable reasoning concentrate on modeling comprehensible temporal paths relevant to the query. Yet, these path-based methods primarily focus on local temporal paths appearing in recent times, failing to capture the complex temporal paths in TKG and resulting in the loss of longer historical relations related to the query. Motivated by the Dual Process Theory in cognitive science, we propose a \textbf{Cogn}itive \textbf{T}emporal \textbf{K}nowledge \textbf{E}xtrapolation framework (CognTKE), which introduces a novel temporal cognitive relation directed graph (TCR-Digraph) and performs interpretable global shallow reasoning and local deep reasoning over the TCR-Digraph. Specifically, the proposed TCR-Digraph is constituted by retrieving significant local and global historical temporal relation paths associated with the query. In addition, CognTKE presents the global shallow reasoner and the local deep reasoner to perform global one-hop temporal relation reasoning (System 1) and local complex multi-hop path reasoning (System 2) over the TCR-Digraph, respectively. The experimental results on four benchmark datasets demonstrate that CognTKE achieves significant improvement in accuracy compared to the state-of-the-art baselines and delivers excellent zero-shot reasoning ability. \textit{The code is available at https://github.com/WeiChen3690/CognTKE}.
DRL4AOI: A DRL Framework for Semantic-aware AOI Segmentation in Location-Based Services
Dec 06, 2024



Abstract:In Location-Based Services (LBS), such as food delivery, a fundamental task is segmenting Areas of Interest (AOIs), aiming at partitioning the urban geographical spaces into non-overlapping regions. Traditional AOI segmentation algorithms primarily rely on road networks to partition urban areas. While promising in modeling the geo-semantics, road network-based models overlooked the service-semantic goals (e.g., workload equality) in LBS service. In this paper, we point out that the AOI segmentation problem can be naturally formulated as a Markov Decision Process (MDP), which gradually chooses a nearby AOI for each grid in the current AOI's border. Based on the MDP, we present the first attempt to generalize Deep Reinforcement Learning (DRL) for AOI segmentation, leading to a novel DRL-based framework called DRL4AOI. The DRL4AOI framework introduces different service-semantic goals in a flexible way by treating them as rewards that guide the AOI generation. To evaluate the effectiveness of DRL4AOI, we develop and release an AOI segmentation system. We also present a representative implementation of DRL4AOI - TrajRL4AOI - for AOI segmentation in the logistics service. It introduces a Double Deep Q-learning Network (DDQN) to gradually optimize the AOI generation for two specific semantic goals: i) trajectory modularity, i.e., maximize tightness of the trajectory connections within an AOI and the sparsity of connections between AOIs, ii) matchness with the road network, i.e., maximizing the matchness between AOIs and the road network. Quantitative and qualitative experiments conducted on synthetic and real-world data demonstrate the effectiveness and superiority of our method. The code and system is publicly available at https://github.com/Kogler7/AoiOpt.
An Experimental Evaluation of Imputation Models for Spatial-Temporal Traffic Data
Dec 06, 2024



Abstract:Traffic data imputation is a critical preprocessing step in intelligent transportation systems, enabling advanced transportation services. Despite significant advancements in this field, selecting the most suitable model for practical applications remains challenging due to three key issues: 1) incomprehensive consideration of missing patterns that describe how data loss along spatial and temporal dimensions, 2) the lack of test on standardized datasets, and 3) insufficient evaluations. To this end, we first propose practice-oriented taxonomies for missing patterns and imputation models, systematically identifying all possible forms of real-world traffic data loss and analyzing the characteristics of existing models. Furthermore, we introduce a unified benchmarking pipeline to comprehensively evaluate 10 representative models across various missing patterns and rates. This work aims to provide a holistic understanding of traffic data imputation research and serve as a practical guideline.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge